Acrylonitrile, a colorless, volatile liquid, is not a household name, but its products are everywhere. They can be found in everything from the clothes we wear to the automotive parts that we depend on. The colorless liquid, which is volatile, may not be a household word, but its products are all around us, from our clothes to automotive parts.
The unique chemical structure of acrylonitrile allows it to easily bond with other compounds and create strong, durable and heat-resistant materials. It is important that industries handle acrylonitrile with caution, as it can be hazardous to the environment and human health.
Understanding Acrylonitrile As The Essential Chemical Driving Modern Industries
This article will examine in detail the properties, production, uses, safety precautions, and global importance of acrylonitrile.
Chemical Structure
The chemical formula of Acrylonitrile is C3H3N. It consists three carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms with one nitrogen atom. Its simple, yet reactive composition makes it a good raw material for synthesized materials. It is a colorless, pungent liquid with an onion-like smell. volatility is one of its most notable characteristics. It evaporates rapidly at room temperature. It has a low boiling point, around 77degC (171degF). This makes it easy to distill.
The triple carbon-nitrogen bond gives it a strong reactivity. This allows it to copolymerize with other monomers such as styrene or butadiene. The flammability of acrylonitrile and its ability to ignite quickly is another reason why industries must store it in a controlled environment. These chemical properties are what make acrylonitrile both a valuable industrial material and a hazardous substance requiring careful management.
Read More: Production of Carbon Black. Profitable Opportunities in Carbon Black Business.
Production Process for Acrylonitrile
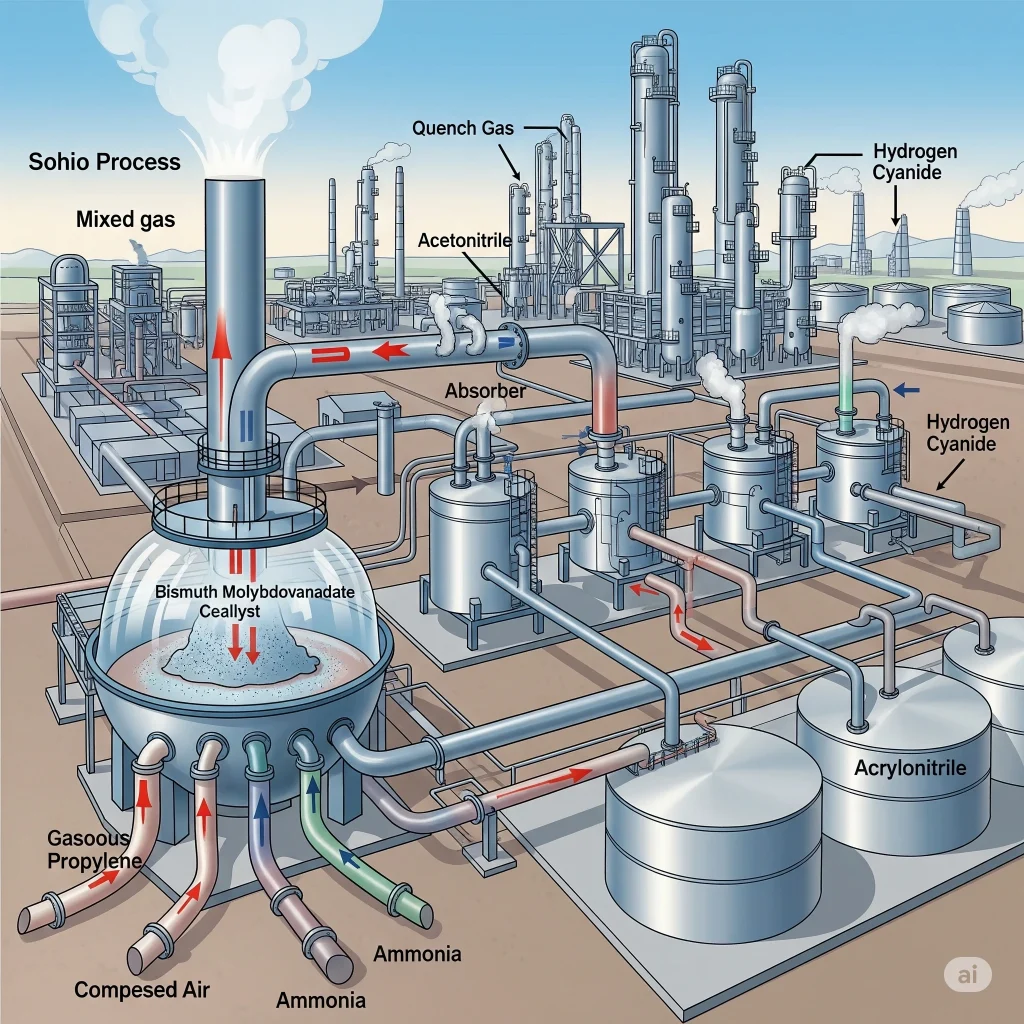
Standard Oil Company in Ohio developed the process for modern acrylonitrile manufacturing. This method involves the ammoxidation propylene. This is how it works:
- Preparation of Feedstock– Propylene, air, and ammonia are the primary raw materials. Propylene can be obtained from the refining of petroleum or gas.
- Reaction stage– At high temperatures (around 400 to 510degC), a mixture of ammonia and propylene is passed over a bismuth-phosphomolybdate catalyst.
- Ammoxidation reaction– The propylene is oxidized in the reactor while ammonia provides the nitrogen atom. The reaction yields acrylonitrile as well as water and other by-products such as acetonitrile or hydrogen cyanide.
- Cooling & Absorption The hot gases are quickly cooled to stop further reactions. The acrylonitrile then absorbs in water or another solvent.
- Purification– By using distillation, crude acrylonitrile can be separated from its by-products. The chemical is then stored in tanks, ready for industrial application.
The method is popular worldwide due to its high yields, efficient use of catalysts and low production costs.
Read Our Book: Click Here
Acrylonitrile: Major Applications
Its ability to create durable and lightweight materials is driving demand for acrylonitrile. The main applications of acrylonitrile include:
1. Acrylic Fibers
These fibers are popular for clothing, blankets and carpets because they are warm, soft and lightweight. These fibers have the same texture as wool, but are resistant to moths and mildew. The polymerization of acrylonitrile is used by textile manufacturers to make these fibers at a large-scale.
2. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Plastic
ABS plastic is a durable and impact-resistant material that’s used for everything from car dashboards, helmets, and toys such as LEGO bricks. Acrylonitrile gives the material strength and chemical resistance. Butadiene provides toughness and styrene adds a smooth surface.
Read More: Ductile Iron Pipe: A Strong, Reliable, And Long-Lasting Solution For Water Supply
3. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
The resistance of nitrile rubber to chemicals, oils and fuels is what makes it so valuable. It is used widely in automotive seals and fuel hoses as well as disposable gloves in healthcare settings.
4. Barrier Plastics
Plastics based on Acrylonitrile are excellent oxygen barriers and therefore ideal for packaging food and beverages. By preventing oxygen from spoiling contents, they help to extend shelf-life.
5. Specialty Resins
Specialty resins are also made from Acrylonitrile for use in electronics, construction materials, and water treatment.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Global Production and Market trends
The production of Acrylonitrile is concentrated in countries that have strong petrochemical industries, such as China and the United States. Global demand for ABS and nitrile glove products continues to grow. The demand for nitrile glove skyrocketed during the COVID-19 epidemic, which caused a temporary shortage in certain regions.
Environmental regulations have also pushed manufacturers towards cleaner production methods, and a reduction in emissions from acrylonitrile factories. This has led manufacturers to innovate in waste recycling and catalyst technology.
Environmental and Health Issues
Although acrylonitrile is a chemical with many industrial uses, it’s also a dangerous one. Long-term exposure to acrylonitrile can be harmful to human health and can also harm the environment.
Health Risks
The vapors of Acrylonitrile can cause irritation to the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Long-term exposure to acryliconitrile has been linked with nervous system damage as well as cancer risk. Occupational safety agencies have therefore set strict limits for workplace exposure.
Environmental Impact
If released in the environment, acrylonitrile may contaminate soil and water. In air, it degrades fairly quickly due to photochemical reaction, but can remain in water for a longer time, which is harmful to aquatic life. To prevent contamination, manufacturers must use pollution control equipment and follow proper waste disposal techniques.
Read Our Project: Click here
Safety measures in handling Acrylonitrile
Multiple safety strategies are used by industries handling acrylonitrile:
- Closed Systems– Production and Transfer are carried out in sealed pipelines, to minimize leakage.
- Ventilation systems – Work areas with strong ventilation to disperse vapors.
- Protective Equipment– Workers use gloves, goggles and respirators to handle the substance.
- Continuous monitoring – Sensors measure acrylonitrile levels in the air to ensure they remain below the safety limit.
- Emergency Procedures– Facilities prepare spill response and fire suppression plans because acrylonitrile can be flammable.

Future Outlook of Acrylonitrile
Future acrylonitrile manufacturing will likely focus on sustainability, and efficiency. Researchers are looking at bio-based sources of propylene to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels. The development of catalyst technology could also reduce energy consumption and harmful by-products. As industries seek lightweight and durable materials, acrylonitrile based products will might be in demand, especially from the automotive, electronic, and renewable energy sectors.
Read More: Build a Profitable EV Station Franchise: A Strategic Guide for New-Age Entrepreneurs
Conclusion
Acrylonitrile is a chemical that many people don’t know, but plays an important role in the creation of products we use on a daily basis. This versatile chemical is used in a wide range of products, from acrylic sweaters that keep you warm to ABS plastics that are durable and protective gloves made of nitrile. Its benefits are not without challenges. With ongoing research and technological improvements, the industry aims to make acrylonitrile production cleaner, safer, and more sustainable-ensuring it remains a vital part of global industry for decades to come.
FAQs About Acrylonitrile
Q1. What is acrylonitrile used for?
People mainly use acrylonitrile to make acrylic fibers, ABS plastics, and nitrile rubber. These end up in things like clothes, car parts, electronics, and safety gear. It’s kind of everywhere.
Q2. Is acrylonitrile dangerous?
Yes, it is. If you breathe it in, eat it, or get it on your skin, it can hurt you. Also, it catches fire easily. So, workers need to follow safety rules when they use it.
Q3. How do people make acrylonitrile?
Factories make it using the Sohio process. They mix propylene, ammonia, and air, then heat it up with a catalyst. That’s how acrylonitrile comes out.
Q4. Can acrylonitrile hurt the environment?
Yes, it can. If it gets into water or soil, it can harm animals and plants, especially fish. Because of this, factories must be careful not to let it leak out.
Q5. Which countries make the most acrylonitrile?
China, the United States, Japan, and South Korea make the most. They have big factories for it.