The Government of India’s consistent and concerted endeavours to usher in reforms for boosting agricultural exports have been highly fruitful. Despite the pandemic, India met rising global demand and emerged as a major supplier of food and essential agricultural products.
Despite COVID-19 logistical challenges, India’s agricultural and processed-food exports rose over 23% in USD. This increase covers April 2020–January 2021 compared to the same period the previous year.
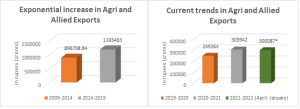
Agriculture and allied exports grew from ₹896,708.84 crore (2009–14) to ₹1,193,463 crore during 2014–19. Exports hit ₹855,293 crore during 2019–22, with April 2021–January 2022 alone exceeding ₹3 lakh crore.
Start a Business in Food Processing and Agriculture-Based Industry:-
The source of data for 2009 to 2015 is the Annual Reports. For data beyond 2015,
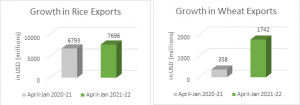
APEDA exports rose from USD 15,974 million (Apr 2020–Jan 2021) to USD 19,709 million in the same period. APEDA exports make up about 50% of India’s total agricultural exports. The Commerce Ministry set the 2021–22 APEDA export target at USD 23,713 million. Rice topped forex earnings at USD 7,696 million (Apr–Jan 2021–22), up 13% from USD 6,793 million last year.
The export of wheat recorded a huge surge at USD 1742 million during April-January 2021-22, growing 387 per cent over the corresponding period in 2020-21 when it touched USD 358 million, while other cereals registered a growth of 66 per cent by fetching USD 869 million during April-January 2021-22 over the corresponding period in 2020-21 when it touched USD 527 million.
Meat, dairy, and poultry products exports grew over 13 per cent, standing at USD 3408 million in April-January 2021-22 compared to USD 3005 million in the corresponding ten-month period of 2020-21. Fruits and vegetables exports were up by 16 per cent to touch USD 1207 million during April-January 2021-22 against USD 1037 million in April-January 2020-21, while processed fruits and vegetables exports were up by 11 per cent to reach USD 1269 million during first ten months of 2021-22 against USD 1143 million in the corresponding period of the previous year.
Exports of cereal preparations and other processed food items grew by 14 per cent during April-January 2021-22 to touch USD 2956 million against USD 2599 million in April-January 2020-
21. The cashew exports also grew by 11 per cent to USD 383 million in the first ten months of the current fiscal year compared to the same period the previous year.
Related Feasibility Study Reports: Food Processing and Agriculture Based Projects, Snack Food, Frozen Food, Agro Processing Technology, Processed Food, Instant Food, Food Industry, Food Preservation, Canned Food, Packed Food, Ready to Eat Food, Cereal Food, Pickle, Spices, Grain Milling
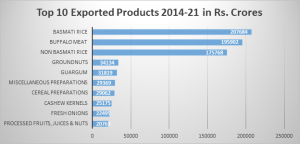
The top ten agriculture and allied products exported under APEDA during 2014-2021, along with their values, are as follows:
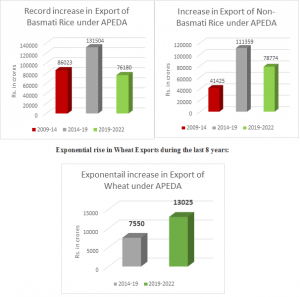
Below are the graphs showing increasing trends of exported Rice: The export of Basmati Rice saw a major increase from Rs. 86023 crores in 2009-14 to Rs. 131504 crores in 2014-19. The export has already reached Rs. 76180 crores in 2019-22 amid Covid pandemic.
The export of non-Basmati rice almost tripled from Rs. 41425 crores in 2009-14 to Rs. 111359 crores in 2014-19. It has already touched the Rs. 78774 crore mark during 2019-22.
PROMOTION OF AGRICULTURAL EXPORTS:
It has been the constant endeavour of the Government to formulate policies and also provide the requisite support to export promotion bodies and the farmers so as to enable them to increase exports of agricultural products from the country. The government has taken a slew of measures in the last seven years, significantly boosting exports.
Read our Books Here: Agriculture, Agro-Based, Cereal Food, Milk, Cocoa, Chocolate, Ice Cream, Plantation, Farming, Food & Beverages
Agriculture Export Policy
To promote agricultural exports, the Government has introduced a comprehensive Agriculture Export Policy (AEP) with the following vision
“Harness the export potential of Indian agriculture, through suitable policy instruments, to make India a global power in agriculture, and raise farmers’ income.”
The objectives of the Agriculture Export policy are as follows:
To diversify our export basket, destinations, and boost high-value and value-added agricultural exports, including a focus on perishables.
- To promote novel, indigenous, organic, ethnic, traditional, and non-traditional Agri products exports.
- To provide an institutional mechanism for pursuing market access, tackling barriers, and dealing with sanitary and phytosanitary issues.
- To strive to double India’s share in world agri exports by integrating with global value chains.
- Enable farmers to benefit from export opportunities in the overseas market.
Under the AEP, twenty-one States, viz. Maharashtra, U.P., Kerala, Nagaland, Tamil Nadu, Assam, Punjab, Karnataka, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Manipur, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, M.P., Mizoram, Meghalaya, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, and Himachal Pradesh, and the 2 UTs viz Ladakh and Andaman & Nicobar Islands have finalized the State-specific Action Plans.
Officials have identified 46 unique product-district clusters for export promotion. They have formed 29 Cluster Level Committees in these districts and formulated country- and product-specific action plans to promote exports.
Specific Export Promotion Forums
Products Specific Export Promotion Forums give impetus to the export of potential products as well as to remove the bottlenecks in the supply chain, Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) has formed Export Promotion Forums (EPFs) under the Chairmanship of Chairman, APEDA and having representatives of Department of Commerce, Department of Agriculture, State Governments, National Referral Laboratories and top 10 leading exporters of each product for the products, viz., Grapes, Onions, Mango, Banana, Pomegranate, Floriculture, Rice, Dairy Products and Nutri cereals.
Ministry of Commerce & Industry
Moreover, the Department of Commerce under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry has also initiated several schemes to promote exports, including exports of agricultural products, such as the Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES), Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme, Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS), and others.
In addition, assistance to the exporters of agricultural products is also available under the Export Promotion Schemes of APEDA, Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA), Tobacco Board, Tea Board, Coffee Board, Rubber Board, and Spices Board. Further, in order to boost honey exports, India has made NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) testing mandatory for honey exported to the USA.
Watch other Informative Videos on Food Processing and Agriculture-Based Projects
Central Sector Scheme for providing Transport and Marketing Assistance
The Government has recently introduced a Central Sector Scheme — “Transport and Marketing Assistance for Specified Agriculture Products” — to provide assistance for the international component of freight. Additionally, it aims to mitigate freight disadvantages for agricultural exports and further support the marketing of agricultural products.
Farmer Connect Portal
A Farmer Connect Portal has been set up to provide a platform for farmers, Farmer-Producer Organizations (FPOs), and cooperatives to interact with exporters. Buyer-Seller Meets (BSMs) have been organized in clusters to provide export-market linkages. Regular interactions, through video conferences, have been held with Indian Missions abroad to assess and exploit export opportunities. Country-specific BSMs, through Indian Missions, have also been organized.
Common Digital Platform
A Common Digital Platform for Certificate of Origin has been launched to facilitate trade and increase FTA utilization by exporters.
Agri-Cells in Indian embassies abroad
Thirteen Agri-Cells in Vietnam, USA, Bangladesh, Nepal, UAE, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, China, Japan, and Argentina were created in Indian embassies to provide real-time inputs to improve Indian exports. The role of Indian missions abroad in promoting trade, tourism, technology, and investment goals has been enhanced.
For more information on reforms to promote agri-exports, refer to official government and APEDA releases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 — How big were India’s agricultural exports during Apr 2021–Jan 2022?
India’s agricultural exports exceeded ₹3,00,000 crore during April 2021–January 2022 (APEDA-covered exports ≈ USD 19,709 million).
Q2 — Which items earned the most foreign exchange in that period?
Rice was the top forex earner (≈ USD 7,696 million), followed by meat/dairy/poultry, cereal preparations, wheat, and processed fruits & vegetables.
Q3 — Why did wheat exports surge by nearly four times?
Wheat exports jumped mainly due to sharply higher global demand, India’s exportable surplus, and supportive government export-promotion measures.
Q4 — What government measures helped boost agri-exports?
Key measures include the Agriculture Export Policy (AEP), APEDA export forums, state action plans, transport and marketing assistance, and digital platforms like the Farmer Connect Portal.
Q5 — How can a farmer or exporter tap these opportunities?
Register with APEDA (if applicable), join local FPOs/clusters, use the Farmer Connect Portal, comply with destination rules (e.g., testing), and apply for available export support schemes.







