This is indeed the Indian economy, where bio-fertilizers have become an integral part of Indian farmers. Indeed, monsoon rains cater to the majority of agricultural activities in India, yet a good bio-fertilizer helps the farmer to improve his field output and affords much soil fertility. Next, let’s define types, roles, advantages, and disadvantages of biofertilizer.
What are Biofertilizers?
Biofertilizers are the products that, in addition to the soil, contain those microorganisms that are important to the fertility of the soil and plant growth. According to that definition, a biofertilizer is a chemical containing living microorganisms, with those microorganisms that colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant directly or indirectly when applied to seeds, plant surfaces, or soil, and encourages growth by decreasing the availability or use of primary nutrients to the plant host.
Related Article on: Organic Farming and Biofertilizer Production
Biofertilizers provide the nutritional supply, which includes nitrogen fixation, solubilization of phosphorus, and promotion of growth hormones with other natural processes. Importantly, they restore the natural nutrient cycles in the soil and help to build up organic matter in the soil.
Healthy plants can thrive under biofertilizers, helping to improve the health and sustainability of soils. Under their utilization, bio-fertilizers are expected to reduce dependence on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, but cannot replace them involved.
Types of Biofertilisers
Some important types of biofertilizers are as follows:
1. Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
These symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium, get all their food and shelter from the plants, and provide them with fixed nitrogen in return. The most significant symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria are Rhizobium. Here, the bacteria seek shelter and food from plants. In exchange, they assist the plants by delivering free nitrogen.
2. A Loose Association of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
Some bacteria may not establish a direct relationship with the plant but live near the plant. For instance, A bacterium such as Azospirillum is nitrogen-fixing and lives in the vicinity of the roots of higher plants and does not necessarily bond with these. It is also called the rhizosphere association because these bacteria collect plant exudate and eat it. This phenomenon is called associative mutualism.
3. Symbiotic Nitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria
There are a number of species of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, such as those occurring in the liverworts, cycad roots, as well as producing bacteria produced by fern plant decay. Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae form symbiotic associations with several plants: the fern Anabaena, in leaf cavities, in charge of nitrogen fixation, decomposes fern plants for the uptake of rice plants. Azolla pinnata is a fern that grows in rice fields, but does not affect the growth of the plant.
View Book on: The Complete Technology Book on Biofertilizer and Organic Farming
4. Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
Free-living bacteria are present in soil; they also reduce nitrogen. These include Clostridium, Azotobacter, and Bacillus polymyxin. They are bacteria found in soil as free-living nitrogen fixers. They include Clostridium beijerinckii, Azotobacter, and other saprotrophic anaerobes. The terms Rhizobium and Azo-spirillum are used extensively as biofertilizers.
Biofertilizer Market Demand
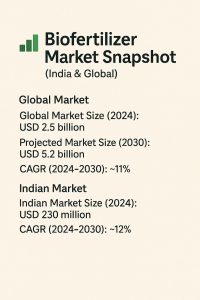
Biofertilizer Market Snapshot (India & Global)
Global Market Size (2024): USD 2.5 billion
Projected Market Size (2030): USD 5.2 billion
CAGR (2024–2030): ~11%
Indian Market Size (2024): USD 230 million
Projected Market Size (2030): USD 510 million
CAGR (2024–2030): ~12%
Growth Drivers
Rising demand for organic farming
High use of sustainable agri-inputs
Govt. subsidies & National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
Reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers
Components of Biofertilisers
Components of biofertilizers include:
- Bio Compost: Eco-friendly, it is produced from waste products coming from the sugar industry. It also contains some bacteria, fungi, and some plants.
- Tricho-Card: This product is eco-friendly and non-pathogenic and is beneficial for many crops and plants, as it acts as a productive destroyer against things harmful to the crop.
- Azotobacter: States nitrogen fixation from the atmosphere and serves as a barrier between the plant roots and pathogens in the soil.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus fertilizers are essential in determining the nitrogen needs of a plant and its nitrogen level in the soil.
- Vermicompost: Possibly one of the most bio-friendly fertilizers for hasty soil fertility improvement, vitamins, sulphur, hormones, organic carbon, and antibiotic content are greatly needed in the growth of a plant.
Project Report on: Biofertilizer
Importance of Biofertilisers
They realize many uses of biofertilizers, making them very important: improve soil quality, protect plants from pathogens, prevent their pollution by the environment, destroy harmful substances present in the soil, and so forth. All these things make biofertilizers very useful.
Role of Biofertilizers
- Biofertilizers play an important role in improving the fertility of the soil, are non-polluting, improve soil texture, and some biofertilizers protect the crops from various soil-borne diseases.
- Some biofertilizers, such as Azolla and BGA, mitigate the toxic effect arising from the use of fertilizers and pesticides, while others are environmentally friendly as biofertilizers and provide environmental protection.
- Biofertilizer applications cause increases in mineral and water uptake, root development, vegetative growth, and nitrogen fixation.
- Some Biofertilizers (e.g., Rhizobium, BGA, Azotobacter sp.) stimulate the production of several growth-promoting substances like the B-complex vitamins, Indole acetic acid (IAA), Gibberellic acids, etc.
- BGA contributes significantly to the nitrogen economy of rice fields in tropical regions. Azotobacter inoculants applied to many non-leguminous crop plants promote seed germination and initial vigor of plants through their growth-promoting substances.
- These bio-fertilizers contain the nitrogen-fixing, phosphorus-mobilizing, and cellulolytic microorganisms and thereby enhance the uptake of P, Zn, S, and water that results in uniform growth and increased yield, and also strengthen the disease resistance from root pathogens to improve hardiness in transplant stock. They liberate growth-promoting substances and vitamins and help in maintaining soil fertility.
Watch Video:- What is Biofertilizer? Benefits, Uses & Business Opportunity
Applications of Biofertilisers
These are some applications of biofertilizers:
- Seedlings Root Dipping: In this method, the seedlings are submerged in a water bed for another 8 to 10 hrs before transplanting.
- Seed Treatment: In this type of treatment, the seeds will be dipped in nitrogen-phosphorus mixed fertilizer supernatant and dried for early planting.
- Soil treatment: The biofertilizers and compost mixture is kept overnight and spread over the soil the next day. This is done before seeds are sown.
Disadvantages of Fertilisers
If there is an advantage of biofertilizers, they also have some disadvantages, and here it is:
- Biofertilizers are supplements to chemical fertilizers. Biofertilizers improve productivity and enrich the soil.
- They are not alternatives to chemical fertilizers. Biofertilizers increase crop productivity by 20 to 30 percent; they do not increase productivity significantly differently from chemical fertilizers.
- Specific fertilizers are essential for specific crops. This is equally applicable for microorganisms living in symbiosis. Application of non-specific Rhizobium as fertilizer will neither increase root nodulation nor crop productivity.
- Good aseptic precautions are necessary while formulating microbial fertilizer. Contamination is a common hazard caused by an environmental factor during the time of microbial mass production.
- Because microorganisms are sensitive to light, they perish if exposed to sunlight for a prolonged period.
- Microbial fertilizers have to be utilized within 6 months when preserved at Room Temperature and within 2 years when kept under Chilling temperatures.
Conclusion
This is the great role of bio-fertilizers for increasing crop production. Likewise, they do not leave behind an inevitable residual effect like that of chemical fertilizers. Biofertilizers are cost-effective, organic, and environmentally sustainable. In fact, the relation of biofertilizers with crop improvement, besides long-term soil fertility maintenance, which is essential to meet the demand for food globally through the interaction of microbes with crop plants to improve their immunity, growth, and development, can be elaborated.
How NPCS Can Help You Start and Grow a Successful Business
Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS) is a trusted partner for entrepreneurs, startups, and small business owners across India. With decades of experience, NPCS provides in-depth support to turn innovative ideas into scalable businesses — especially in emerging sectors like agro-waste-based manufacturing, specialty chemicals, home-based businesses, and more.
Market Research & Techno-Economic Feasibility Reports
NPCS delivers comprehensive market research reports that include:
- Industry trends and demand analysis
- Legal and regulatory requirements
- Raw material sourcing and local supply chain insights
- Cost structure and value chain assessment
These reports help you validate your business idea and understand its viability in the real market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are biofertilizers, and why are they important for Indian agriculture?
Biofertilizers are natural fertilizers containing living microorganisms that improve soil fertility and plant growth. They play a crucial role in Indian agriculture by fixing nitrogen, solubilizing phosphorus, and enhancing organic matter in the soil. This reduces dependency on chemical fertilizers, improves crop yields, and supports sustainable farming practices.
Q2. What are the main types of biofertilizers used by farmers?
The major types of biofertilizers include symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium), free-living nitrogen fixers (e.g., Azotobacter), associative nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Azospirillum), cyanobacteria/blue-green algae (e.g., Anabaena and Azolla), and phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Each type supports different crops and soil conditions.
Q3. How do biofertilizers improve soil fertility and crop productivity?
Biofertilizers enhance soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen, mobilizing essential nutrients like phosphorus, zinc, and sulfur, and promoting the production of natural growth hormones. They improve root development, water uptake, and overall crop health, leading to a 20–30% increase in productivity when used alongside organic and chemical fertilizers.
Q4. Can biofertilizers replace chemical fertilizers completely?
No, biofertilizers cannot fully replace chemical fertilizers. They are best used as supplements to reduce chemical usage while maintaining soil health. Biofertilizers improve soil sustainability and crop quality but are most effective when integrated with organic manures and balanced chemical fertilizer use.
Q5. What are the main advantages of using biofertilizers over chemical fertilizers?
The key advantages include eco-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, improved soil health, reduced pollution, and long-term sustainability. Unlike chemical fertilizers, biofertilizers do not leave harmful residues, improve soil biodiversity, and enhance the natural nutrient cycle.








Biofertilizers play a crucial role in boosting crop production while maintaining soil health and sustainability. Unlike chemical fertilizers, they leave no harmful residues, making them a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution for long-term agricultural growth.
Biofertilizers seem like a game-changer for sustainable farming! It’s great to see a natural solution that boosts crop production while maintaining soil health long-term.