The Indian government launched the Make in India initiative in September 2014 to redefine the country’s industrial development policy. It aimed to boost domestic manufacturing, import reliance, create millions of jobs, improve ease of doing business, and transform India into a global manufacturing hub.
Since its launch, the initiative has earned significant recognition as a foreign and domestic investment magnet and is reshaping industrial India. The initiative is also a boon to entrepreneurs and startups as it provides government support, infrastructure, and access to emerging high-growth markets.
This article details the impacts of Make in India on the manufacturing industry, the opportunities it presents to upcoming businesses, growth prospects by sector, and how to approach manufacturing in a way that meets the program’s objectives.
Check out the Potential Business Opportunities in India
Achieving the Goals of Make in India
With the introduction of the Make in India program, there were three key objectives: increasing the share of manufacturing in India‘s GDP to 25%, creating 100 million new manufacturing jobs, and making India one of the most sought-after industrial investment havens. The government has allocated 25 focus sectors such as manufacturing and assembling automobiles, electronics, defense, and textiles, food processing, and chemicals, in which India could gain a competitive global advantage.
In order to reach these goals, the government sought a mix of policy changes, tax breaks, upgrades to foreign investment controls, infrastructural investment, and foreign investment relaxation. The ease of starting and operating a manufacturing company in India improved alongside India’s standing in the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business ranking. The focus is not only on large multinationals, but also on helping new businesses and small to medium enterprises integrate into the supply chain.
Related: How the Make in India Initiative is Shaping Government Policies for Manufacturing
Foreign Investment and World Partnerships
The most important change as a result of Make in India is the increase in foreign direct investment (FDI) related to manufacturing. There are now more liberalized FDI policies where foreign investment allows for 100% ownership in a handful of sectors. This has incentivized a number of foreign multinationals to establish factories and assembly lines in India. A good example is Apple, which has increased its iPhone assembly in India through contract manufacturers like Foxconn and Wistron. Samsung has opened one of the largest mobile manufacturing plants in the world, located in Noida.
In the automotive industry, these include Kia Motors, Hyundai, and MG Motor, which have set up advanced manufacturing plants for the local and export markets. New offset policies have also benefited the defense industry, which incentivizes global defense contractors to form joint ventures with Indian companies.
These partnerships have advanced India’s integration into global supply chains by acquiring advanced technologies, manufacturing experience, and high-value jobs.
Advent of MSMEs and Startups in Manufacturing
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India are crucial to the manufacturing economy and contribute significantly towards exports and employment opportunities. The Make in India initiative now enables MSMEs to secure government procurement contracts, receive credit line provisions for specific sectors, and obtain aid for technology. Startups are increasingly finding ways to integrate into the bigger manufacturing value chain as component suppliers, service providers, or technology partners.
As a case in point, the electronics industry has witnessed the rise of small companies that specialize in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs), batteries, and precision plastic molding for consumer electronics. Furthermore, in the automotive industry, startups are now supplying key components for electric vehicles, including lithium-ion battery packs, control systems, and charging infrastructures.
Business incubation centers sponsored by the government and industrial clusters have aided these firms by providing them with technical assistance, infrastructure, and streamlined access to skilled labor.
Skill development and job creation
The Make in India initiative has been particularly aimed at workforce development. There has been a rapid increase in industrial growth, which requires a large pool of skilled workforce. In order to meet this need, skill enhancement programs have also been started, such as Skill India and Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
The specific training provided to skilled workers has not only increased employment opportunities for the younger generation but has also enhanced the competitiveness of India in the global manufacturing landscape. In the future, as more industries such as defense manufacturing, heavy engineering, and renewable energy expand, the need for skilled personnel trained in these technologies will be even more essential.
Related: Start a Profitable Retail Franchise Business in India
Market Suggestions by Sector
To fully grasp the effects of Make in India, a look at the performance of key manufacturing sectors provides the most value.
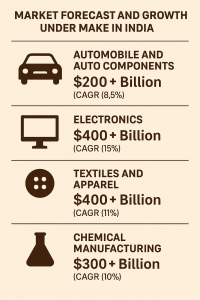
Automobile and Auto Components
India ranks as one of the largest automobile producers in the world. With the “Make in India” initiative, the industry is now undergoing a drive towards modernization and electrification. Under the FAME-II scheme, the government has provided incentives for the manufacturing of electric vehicles. At the same time, other OEMs are scaling up their production facilities to meet the expected domestic as well as international demand.
Industry estimates suggest that the automobile and auto component industry, valued at USD 118 billion in 2023, will likely cross USD 200 billion by 2030, achieving an average annual growth rate of approximately 8.5%. Electric vehicles, production for exports, and the growth of premium segments will drive this growth.
Electronics Manufacturing
Under the “Make in India” scheme, the Electronics sector has shown one of the fastest turnarounds. India has transformed from being an importer of mobile phones and other consumer electronic goods to one of the leading assembly belts for the world.
The electronics industry, which reached a value of USD 155 billion in 2023, will likely exceed USD 400 billion by 2030, growing at an annual rate of 14-15%.
Manufacturing of mobile devices, consumer packaged semiconductors, and consumer electronics appliances will complement this growth.
Textiles and Apparel
With the introduction of new export incentives and integrated textile parks, the textile sector has become a major employer, along with a global demand for sustainable fabrics. Additionally, the sector has a projected growth of USD 223 billion in 2023 to over USD 400 billion by 2030.
Chemical Manufacturing
The Make in India initiative has positively impacted India’s chemical industries, especially with specialty chemicals, which have seen increasing investments along with production-linked incentives and relaxed environmental norms for certain projects.
For more information check our Handbooks
How Manufacturing Typically Works Under Make in India
While products may differ, the guidelines fostered by Make in India emphasize efficiency, sustainability, and high standards. The journey typically starts from carrying out detailed market research to validate demand and competition. Once the product idea is approved, raw materials are ideally sourced from domestic suppliers to curb the need for imports.
The next step involves setting up the plant, installing the equipment, and automating processes where possible to optimize production costs. The manufacturing stage follows stringent quality control checks as per ISO, BIS, or relevant industry standards. Packaging as well as logistics are just as critical, as they make sure that products are delivered to the markets promptly and in the best possible condition.
Reasons for Growth in Manufacturing
The development in manufacturing under Make in India is impacted by multiple interconnected factors. Policy incentives and manufacturing-linked incentive schemes, tax perks, and GST regulations have made operations easier for manufacturers. Also, the modernization of ports along with the construction of industrial corridors and logistics hubs has improved the overall connectivity and decreased the transport costs.
The adoption of new technologies is a major factor as well. All levels of manufacturing are adopting higher level automation, robotics, and IoT monitoring Industry 4.0 practices, which improve efficiency and product quality. Strengthened new trade agreements also enable greater access to the global market. Indian manufacturers can now compete with countries in Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
Obstacles That Need to be Addressed
There is still noticeable improvement to be made in the areas that entrepreneurs are still keenly interested in. The gap in advanced skill sets of highly specialized labor in skilled fields with niche expertise remains an issue. Even with lessened regulatory delays, higher compliance sectors like pharmaceuticals and chemicals still face restrictive regulatory delays. Underdeveloped areas still have poor digitally connected infrastructure that lacks the roads to industrial expansion.
The latter mentioned challenges, lack skilled labor, regulatory delays, and underdeveloped infrastructure create a large welcoming space for startups that can work towards solving such issues. There is great scope for regulatory logistics, workforce training, regulatory consultants, and logistics innovation.
Opportunities for Entrepreneurs and Startups:
The present situation for manufacturing under Make in India is highly beneficial for entrepreneurs. There is rising potential in industries such as electric vehicles, battery technology, biodegradable packaging, medical devices, and specialty chemicals. Startups that prioritize innovation and cost-effective, sustainable methods are bound to come out on top.
One critical factor to consider for new entrepreneurs is to assimilate themselves into larger supply chains. Startups can earn trust and scale their operations by becoming specialized suppliers to established manufacturers before full independent production.
For more information, check out this related video
The Role of Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS):
NPCS is integral in aiding new entrepreneurs who are keen to start manufacturing businesses. The firm prepares detailed reports that cover every aspect of a proposed project such as a market survey and techno-economic feasibility analysis. These reports go as far as outlining the whole manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to plant layout design to financial analysis. By offering data-informed recommendations, NPCS helps assess the real possibility of either setting up new industries or expanding the existing ones.
Find Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
Conclusion
The Make in India initiative has changed India’s position in global manufacturing, attracting foreign investments while providing entrepreneurs with a favorable ecosystem to launch new ventures. Increased foreign investment, the strengthening of the MSME network, improved infrastructure, and skill development programs have advanced the sector. Even though challenges still exist, one thing is certain: the manufacturing sector’s contribution to the economy is bound to increase substantially in the next ten years.
For entrepreneurs who are willing to adapt and respond to global buyer demands, invest in quality manufacturing, embrace innovation, and adopt sustainability practices, Make in India not only provides a policy frame but also a realistic and actionable strategy to create world-class competitive manufacturing enterprises.







