Rice production generates around 20 million tonnes of husk in India. While often overlooked in the past, rice husk is rich in lignin, cellulose, and silica, which can be used to manufacture a variety of products. Entrepreneurs in rice-growing regions, such as Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh, easily have access to rice husk at a low cost.
Rice husk can be processed into many different products, serving a variety of different industries. The degree of technological advancement and capital investment can be adjusted to fit the firm’s needs and capabilities.
Understanding the True Value of Rice Husk
Rice husk, which makes up 20% of the paddy weight, consists mainly of lignin, cellulose, and silica. This composition makes it thermally stable, fire-resistant, biodegradable, and suitable for conversion into a wide range of industrial raw materials and finished products.
While India produces enormous amounts of rice husk, only a small fraction is currently used in high-value industries. Most is either combusted in inefficient furnaces or ends up as low-grade ash. But with increasing government pressure to control emissions, reduce plastic use, and promote sustainability, rice husk is gaining renewed attention, especially among new-age industrial entrepreneurs.
Related: Starting a Profitable Silica Gel Business from Rice Husk
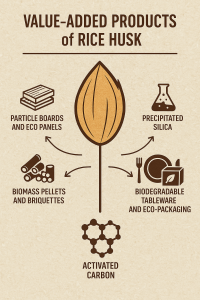
Top Value-Added Products You Can Manufacture from Rice Husk
Each product below has distinct technical requirements, markets, and scalability potential. Let’s explore them in detail.
1. Rice Husk Particle Boards and Eco Panels
These boards are manufactured by pressing rice husk powder mixed with resin adhesives into molds using hydraulic or pneumatic presses under controlled heat. The resulting board can mimic plywood and MDF, but is:
Termite-resistant
Moisture-tolerant
Cost-effective
Formaldehyde-free (if bio-based resins are used)
Use Cases: Office furniture, interior partitions, modular kitchens, prefab homes, low-cost housing
Market Insight: With real estate moving towards modular construction and furniture retailers looking for eco-boards, demand is increasing rapidly. India’s particle board and MDF market is projected to grow at over 7.5% CAGR, reaching USD 3.5 billion by 2030.
2. Precipitated Silica from Rice Husk Ash (RHA)
Rice husk, when burned under controlled conditions, yields ash rich in amorphous silica, over 85% purity. This can be extracted chemically using acid leaching, filtered, and dried to produce precipitated silica, which is used in:
Rubber & tire manufacturing
Paints and coatings
Toothpaste and personal care
Food anti-caking agents
Advanced materials like lithium batteries
Technology Note: The process requires a calcination furnace, acid reactors, and precipitation tanks, making it more capital-intensive, but highly profitable due to rising global silica prices.
Market Insight: The global market for precipitated silica is valued at USD 2.5 billion (2024) and is expected to grow at 6.7% CAGR, driven by its use in green tires and industrial rubber.
3. Biodegradable Tableware and Eco-Packaging
Rice husk, when ground and blended with natural binders like corn starch, PLA (polylactic acid), or bio-based polymers, can be molded into:
Disposable plates, trays, and bowls
Compostable food containers and boxes
Eco-friendly cups and cutlery
Use Cases: Food delivery, QSR chains, wedding/event catering, export to countries with single-use plastic bans
Compliance Needs: BIS or ISO certifications for food-grade use, compostability labeling for export
Market Insight: The global biodegradable tableware market is projected to cross USD 10 billion by 2030. With India’s ban on single-use plastics, local demand is also exploding.
4. Biomass Pellets and Briquettes
Rice husk can be compressed into cylindrical pellets or briquettes that serve as clean-burning fuel in:
Industrial boilers (textile, dairy, chemicals)
Decentralized power plants
Biomass-based gasifiers
Community kitchens and rural stoves
Technology Note: Pellet mills are widely available and can be operated in semi-automated mode. A small unit can produce 1–3 tons/day, depending on size.
Policy Push: The Indian government is offering capital subsidies under the National Bioenergy Mission to promote biomass fuel, especially in industrial clusters and Tier 2/3 towns.
5. Activated Carbon
This high-purity, porous form of carbon is used in:
Water and air filtration
Pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
Gold recovery in mining
Gas purification
Manufacturing Steps:
Carbonization: Husk is heated in absence of oxygen to form char
Activation: Steam or chemical agents (phosphoric acid, KOH) are used to enhance porosity
Market Insight: India’s activated carbon market is growing due to demand from RO water purifier manufacturers, pharma industries, and regulatory pressure on pollution control.
6. Silicon Carbide and Nano Silica (Advanced Materials)
Advanced R&D now enables the extraction of nano-silica and the production of silicon carbide from rice husk, used in:
Semiconductor components
Solar cells
Industrial abrasives
Specialty coatings
While not yet mainstream due to high capital and R&D needs, these products represent the future of rice husk valorization in deep-tech sectors.
View our books on Rice Husk
Rice Husk’s Adaptability
Rice husk boards are an efficient and budget-friendly material for modular construction and interior furnishing when compared to plywood and MDF. These boards are manufactured by mixing rice husk powder with resin to create a unique blend.
They are then put through a process of heat and pressure, which compresses them to create durable, termite-resistant panels. These panels are gaining a lot of popularity within the affordable housing and prefabricated construction markets. They are also suitable to humid and fire-prone regions due to their moisture resistance and fire-retardant properties.
Another valuable use is the extraction of precipitated silica from rice husk ash. This process begins by burning rice husks in controlled environments, which produces a silica-rich ash.
After going through a series of chemical extractions and purifications, the resulting silica can be used to manufacture tires, paint, and even certain cosmetics and electronics. While this specific business model may require more technology and funding, it can be highly profitable considering the global demand for industrial silica.
Related: How to Start a Profitable Rice Husk Pellet Plant
Understanding the Market Dynamics
Moreover, the market for products derived from rice husks is developing steadily in India and worldwide. Consequently, there is growing construction and furniture industry demand for sustainable alternatives to wood, driving growth in the particleboard segment.
Increased environmental awareness and export potential are some of the factors driving the biodegradable tableware segment, which is growing at over 9% CAGR. Government policies aimed at reducing single-use plastics are fostering the use of rice husk-based products, especially in urban areas and tier-1 hospitality markets.
In the industrial segment, the rubber and tire sectors are driving demand for precipitated silica due to a shift towards silica-based fillers for better strength and durability. India’s market for silica is close to ₹900 crore, and will receive a boost with growth in the automotive and electronics markets.
Making Rice Husk Products
In general, the process for rice husk production starts with the same steps for all product silos, spanning the collection and sorting of raw material through refining and final packaging.
Initially, the first stage is to source rice husk, with local mills being the primary port of collection. Agreements or partnerships with millers grant uninterrupted consistency for the raw material. Before processing, the rice husk is cleaned and dried to remove unwanted matter such as sand and stones, as well as dust.
Subsequently, in the second stage, the husk is ground or pulverized into a fine powder, which is then set aside for different purposes based on the end product. For board production, once pulverized, the husk powder is mixed with adhesives and then hydraulically pressed into sheets at high temperatures. Meanwhile, to extract silica, the husk is burned under controlled conditions to produce ash, which is then chemically treated to isolate the silica.
In packaging, the husk is blended with biodegradable polymers, shaped by compression or injection molding, and then heat-treated to improve durability. Pellitized husk is also used to produce fuel in the form of briquettes or pellets, where the husk is compacted using specialized pellet machines and then dried.
In the third stage, quality assurance is done for attributes such as product strength, thermal stability, purity, and biodegradability to ensure the product meets industrial or export standards.
Challenges and Considerations
Some challenges need to be addressed by a starting rice husk manufacturing business. Proactively managing supply chains is a necessity during seasonal availability of rice husk to avoid disruptions in production. It is recommended to locate the unit within rice-producing regions to avoid high transportation costs and storage complications.
Furthermore, one of the most difficult challenges to address is the intricate technology management of some products. Staff with proper training and the right equipment is needed to produce high-purity silica or activated carbon. In these scenarios, working with research institutions or employing consultants to aid in overcoming initial-stage technical obstacles is helpful.
Government Support and Policy Environment
There is proactive encouragement from the Indian government for the conversion of agricultural waste to industrial products. Schemes of the Ministry of MSME, MNRE, and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) have sponsored and continue to seek such initiatives by providing funding, training, and technical help.
Startup India, PM-FME, and Waste to Wealth Mission offer benefits to entrepreneurs developing products from agri-waste materials. Furthermore, other initiatives such as biomass energy generation subsidies, tax-free status on packaged compostable products, and easier credit access via MUDRA and CGTMSE schemes have made doing business in this industry more accessible.
Incubators and local governments are also proffering additional support in the form of infrastructure, common facility centers, and research and development linkages for new manufacturing initiatives.
For more information, check out this video on Rice Husk
How NPCS Supports Your Industrial Journey
To start a rice husk-based manufacturing business, many entrepreneurs require more than just an idea. They require planning, data, and hands-on help. This is the gap NPCS (Niir Project Consultancy Services) fills.
To aid such entrepreneurs, NPCS creates Market Survey cum Detailed Techno Economic Feasibility Reports for rice husk and other industrial projects. These reports have comprehensive details of raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, plant layout, and financial estimations.
With decades of experience, NPCS also helps in regulatory compliance, technology selection, and operational optimization, aiding in seamless concept-to-execution transitioning.
Find the Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
Conclusion: Transforming Rice Husk into Industrial Gold
In the context of sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and innovative technology, rice husks stand out prominently. With India’s aims to curb pollution, reduce plastic consumption, and foster self-reliance, rice husk-based enterprises have the opportunity to flourish.
The goal is not just the development of sustainable products. The focus also lies on the renewable resource that can support several sectors, create jobs, and establish a business that caters to global needs.
NPCS serves as a reliable consultant resource for entrepreneurs. With a solid plan, industry expertise, and effective guidance, NPCS turns byproducts into sustainable foundations for advanced green manufacturing that India can lead.







