How did the words you read in a book get there? Or the design of your favorite tee-shirt? How about the nutrition information on the cereal box, or the beautiful photograph on your wall. is the answer to these questions. It is a powerful, and often invisible, force that shapes the world we live in every day.
Printing is more than just ink on a piece of paper. It’s an art and science that has developed dramatically over the centuries. This is the engine of communications, the foundation of packaging and the future for manufacturing. This guide will take you on a journey through the fascinating world of printing. From its historic roots to the cutting-edge technologies of today and tomorrow, this guide will show you the best of the industry. We will explore the history of printing, its importance, and the future of this industry.
A Journey Through Time: Where It All Began

We must first look back at history to understand modern printing. In ancient China around 220 AD, woodblock printing was used to print.
It was around 1440 that the real revolution occurred. Gutenberg, a German inventor, created movable type, which allowed individual metal letters to be arranged into words and sentences.
Read More: Printing Technology Offset, Flexo, Gravure, Screen
Why did Gutenberg’s press have such importance?
- Speed It is much faster than handwriting or woodblock carving.
- Cost: Made books and documents cheaper to produce.
- Accessibility: Regular people finally got access to new ideas, not just the wealthy elite. This invention kicked off the Renaissance, sparked the Reformation, and set the Age of Enlightenment in motion. It changed society for good.
The Two Titans of Offset and Digital Printing
The world of printing today is dominated primarily by two methods: digital printing and offset printing. Both methods use ink to print on a surface but they do so in different ways.
Offset Lithography – The Industrial Workhorse
You’ve probably held an offset printed magazine, book or newspaper. This is the method of choice for commercial printing jobs that require high quality and high volume.
Offset printing works on a simple principle: Oil and Water don’t Mix.
- Plate: Firstly, the design is etched on a thin metal sheet. The image area has been treated to attract oily-based ink while the nonimage area has been treated to repel water.
- Inking A plate is placed on a rotating cylinder, which is then dampened with water before ink is rolled over it. Water sticks to non-image parts of the plate, repelling ink. Ink only adheres to image areas.
- Offset: After the image has been inked, it is “offset”, or transferred from the plate to a rubber blanket.
- To Paper: The paper is then pressed against a rubber sheet, which transfers the image to the page.
Best used for: Book, magazine, brochures and newspapers.
Read More: The Ultimate Guide to Offset, Flexo, Gravure, Screen, Digital, 3D Printing, Book Binding, and CTP
Digital Printing: Flexibility and Speed for the Modern Age
Most of us print digitally at home and in the office. Inkjet printing is a method of printing a digital document (such as a Word or PDF) without using any plates.
- Inkjet printing: Imagine an inkjet as a highly-accurate artist. It sprays thousands of tiny droplets of liquid on the paper in order to create a digital picture. Inkjets are great for printing photos because they can blend colors seamlessly.
- Laser printing: The laser printer creates a static charge by using fine powder called Toner. The static-charged areas attract toner powder. The toner powder is then transferred onto the paper as it rolls over the drum. Laser printers produce crisp, sharp text and are extremely fast. They’re perfect for office documents.
Best used for: Small print run, personalized items, office documents and home photo printing.
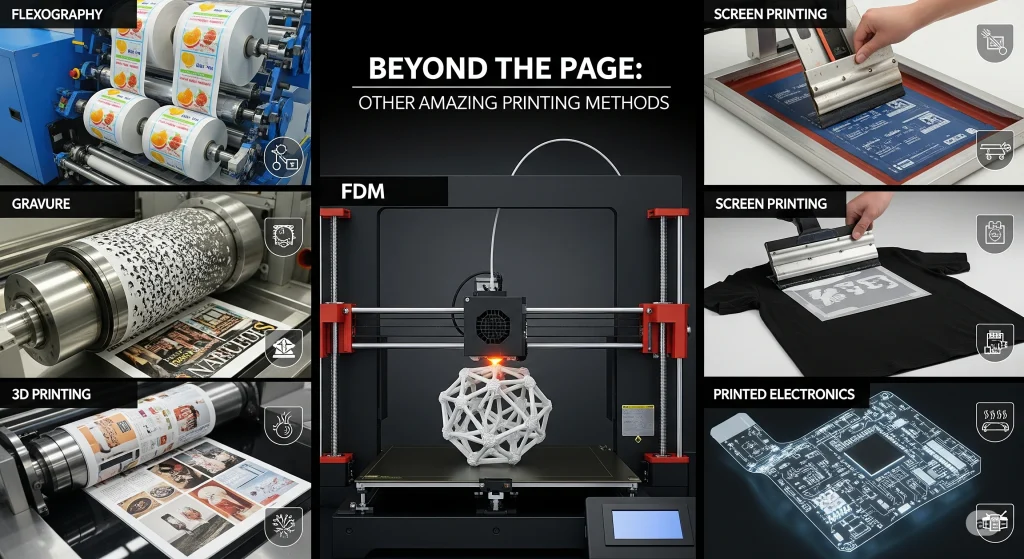
The Printing Process: More Amazing Methods
Although offset and digital printing are the most popular, there are several other speciality methods used for specific applications.
- Flexography It’s a high-speed, modern version of the rubber stamp. The process uses flexible plates that are wrapped around rotating cylinders. It is fast and can be used to print on a variety of materials.
- Use for: Food packaging and labels, plastic bags and cardboard boxes.
- Rotogravure: For high-volume printing, people go with rotogravure. They put ink on a metal cylinder, scrape off the extra, then press the paper hard against the cylinder. The paper grabs ink from the tiny grooves, and you get a sharp, detailed image.
- Serigraphy (Screen Printing): A very tactile technique, perfect for bold designs. The stencil is placed on a fine mesh screen and stretched over the frame. Ink then is pushed through to the material beneath the stencil.
- Use for: T shirts, posters and tote bags.
Read Our Book: Modern Technology of Printing & Writing Inks (with Formulae & Processes) 2nd Edition
The Next Chapter: New Printing Technologies
The printing technology is constantly evolving. New innovations are pushing boundaries.
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
This is the biggest change in printing since the invention of the printing press. 3D Printing builds physical objects from digital designs, layer by layer, instead of ink. The 3D printer can produce almost anything using materials such as plastic, resins, metals, and even concrete.
The technology is being used for everything from medical implants and prosthetic limbs to entire houses and custom phone cases. The technology is changing manufacturing because it allows for highly complex designs and on-demand production, which were previously impossible.
Start a Digital Printing Business: Read Our Project Report
Printed Electronics
Imagine a shirt that monitors your heart rate, or a label on food that indicates when it is close to expiration. printed electronic is a reality. Scientists cooked up these crazy conductive inks that let you literally draw working electronic circuits onto stuff like plastic, paper, or fabric. And I mean, the circuits actually work—this isn’t just artsy nonsense. Seriously, it’s like bridging the gap between doodling and engineering.
This technology is opening the door to flexible screens, smart packaging and wearable sensors.
Read More: From Space to Earth: Business Ideas Inspired by NASA Technology
Focus on sustainability
Printing industry also becomes more eco-conscious
- Eco Friendly Inks: Today, many printers use vegetable or soy-based inks as opposed to petroleum-based.
- Recycled Material: It is now common practice to use recycled paper, and other substrates.
- Reduced waste: Digital print allows “print-on demand,” meaning companies can only print the books or materials they need. This reduces waste by a great deal.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
The Conclusion: More than Ink on Paper
Printing technology has made an amazing journey. From the wooden blocks used in ancient China, to the 3D printers that create medical implants today. Printing technology is an important pillar in our society. It enables communication, drives commerce and has now revolutionized manufacturing.
Printing combines old-world craftsmanship with cutting-edge innovation. It allows us to tell stories, build brands and create art. Next time you pick up an object printed, appreciate the technology that created it. This technology continues to surprise and evolve.
Printing Technology – Quick Answers to Common Questions
Q1 What is the biggest difference between digital and offset printing?
The use of plates. Offset Printing is cost-effective when printing large quantities of material. Digital Printing prints from a computer without using plates.
Q2 Why is Johannes Gutenberg famous?
A2: Gutenberg invented a printing press in 1440 that used movable type. It allowed books to be produced quickly and inexpensively. This innovation transformed society and made knowledge available to everyone for the first.
Q3 What is CMYK?
A3: CMYK stands Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Key (black). These are the primary colors used for most color printing. Printers can create an entire spectrum of colors by combining dots of the four colors.
Q4 Is printing harmful to the environment?
A4: While historically printing had a negative impact on the environment, modern practices like the use of recycled paper, inks made from soy, and energy efficient digital printing have greatly reduced the industry’s footprint. Print-on demand technology helps reduce massive amounts of waste.
Q5 What is 3D Printing?
A5: 3D printing is a process that creates a three-dimensional product from a digital design. This is different than traditional manufacturing which involves cutting away material.
Q6 What is a good printing method for T-shirts?
A6: The most popular and common method of printing on tee-shirts and other clothing is Screen printing. The method is very durable and creates vibrant colors.









