
Mega Food Park – Encouraging Food Projects in India
Setting up of Maga Food Parks in the country under Mega Food Park Scheme of Pradhan MantriKrisanSampadaYojna (PMSKY)
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), which is a private body incorporated under the Companies Act, is executing the mega food park project. For the implementation of the Mega Food Park Scheme, the state government, state government agencies, and cooperatives are not expected to establish a separate SPV. The funds are issued to the SPVs, according to the terms of the Scheme Requirements being met.
Related Projects:- Food Processing and Agriculture Based Projects, Snack Food, Frozen Food, Agro Processing Technology, Processed Food, Instant Food, Food Industry
Mega Food Park comprises of infrastructure developed for supply chain, also includes the cold chain, primary processing centers, central processing centers, and collection centers. The project also constitutes approximately 25-30 completely built plots to create food processing units for entrepreneurs.
The mega food park scheme aims at proffering a process to connect the agricultural production to the market. By bringing together producers, processors, and retailers in order to optimize the added value, reduce waste, increase the income of farmers and generate job opportunities, especially in the rural region. Centered on the ‘Cluster’ strategy, the Mega Food Park Scheme foresees the construction of state-of-the-art support infrastructure in a well-developed agri-horticultural area for the establishment of modern food processing units in industrial parcels supplied by a well-established supply chain in the park.
Related Books:- Food Additives, Food Colours, Colors, Flavours, Flavors, Gums And Stabilizers, Food Industry Ingredients
Concept of Mega Food Park Scheme in India
Since 2008, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries has been introducing the Mega Food Park Scheme (MFPS) to build new infrastructure for the food industry. This structure has now become a part of the Central Sector Umbrella Scheme i.e., Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY). The goal of the Mega Food Park Scheme (MFPS) is to provide modern food processing infrastructure facilities along the supply chain from farm to shop.
Related Projects:- Food Colours, Colors, Flavours, Flavors, Gums, Stabilizers, Food Industry Ingredients, Hydrocolloids and Additives Projects
As of date, 37 mega food parks in 23 States/UTs that are at separate stages of implementation have been given final approval by the Ministry. Out of this, 19 MFPs are operating. The government envisaged a total of 42 Mega Food Parks (MFPs).
According to the scheme guidelines, each fully operational Mega Food Park would provide over 5,000 people with direct/indirect jobs. The primary purpose of the Mega Food Park Scheme is to provide modern facilities for food processing infrastructure along the supply chain from the field to the market.
This will include the construction of near-farm facilities (i.e., storage centers and main processing centers), transport, logistics, and consolidated processing centers, infrastructures for logistics and primary processing centers.
Related Videos:- Agro-Food Processing Industries
Salient features of mega food park scheme
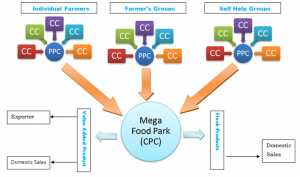
The key goal of the MFPS is the provision of modern food processing infrastructure facilities along the supply chain from the field to the consumer. It would require the development of near-farm.
The Scheme’s Salient Features are as follows:-
- The purpose of the Scheme is to encourage the development of a good food processing system. A productive supply chain sponsored by the sector, which will involve collection centers, key centers for manufacturing, and infrastructure for the cold chain.
The Food under the system, production units will be housed at the Central Processing Center (CPC) with common facilities focused on needs needed for manufacturing, packaging, systems for environmental safety, quality management laboratories, centers for trade facilitation, etc.
- On average, each project is projected to have about 25-30 foodstuffs. Processing units with approximately Rs. 250 crore aggregate investment that will ultimately, an annual turnover of approximately Rs. 450-500 crore and the development of absolute/indirect jobs of approximately 5000 people.
Every MFP on the completion of being completely around 25000 farmers would also benefit from organizational gains.
The project specification may vary according to the business plan for each Mega Food Park. That should be the net expenditure in CPC, PPCs, and CCs proportionate and commensurate with the scale of the overall scheme, taking into account the scale-based economies.
- The spirit of the Mega Food Parks Scheme’s guidance is to encourage the setting up of industries of only food processing. Consequently, only the food processing industry must be allowed to make food items suitable for human/animal use to be built in the Mega Food Parks. Food products packaging services as it would also be eligible for establishment in the food processing industries ancillary to the Mega Food Park.
Related Videos:- Food Processing and Agriculture Based Projects
Benefits of Mega Food Park Project in India
- The main purpose of the MFPS is to offer state-of-the-art food processing technology services along the value chain, from the field to the consumer. It would require the development of near-farm utilities, shipping, logistics, and consolidated processing centers.
- A cluster-based strategy is the core aspect of the Scheme. The scheme would be demand-driven, pre-marketed, and promote the meeting of environmental, safety, and social requirements by food processing units.
- MFPS is projected to promote the achievement of the Ministry of Food Processing Industries’ Vision 2015 to increase the country’s perishable processing from the current 6 percent to 20 percent, value-added from 20 percent to 35 percent, and the share of global food trade from 1.5 % to 3 % by 2015.
- The anticipated outcomes are increased farmers’ realization, the development of high-quality production facilities, the reduction of waste, the capacity building of producers and processors, and the creation of a productive supply chain, along with the generation of substantial direct and indirect jobs.
Related Videos:- Business Ideas for Startups
What will be the Pattern of Assistance?
- The scheme awards a capital grant at a rate of 50% of the eligible project cost* for general areas and 75% of the eligible project cost for complicated and hilly areas, i.e. Including Sikkim, J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and ITDP, the North East Region has notified areas of the States subject to a limit of per project, Rs. 50 crore.
- The qualifying cost of the project is specified as the overall cost of the project but excludes property costs, pre-operational expenditures, and working capital margin money. That being said, up to 2 percent of the accepted grant will be interested while construction (IDC) as part of preoperative expenditures and charge to Project Management Contractor (PMC) up to 2% of the approved grant would be considered under eligible project cost.
Start a Business in Food Processing and Agriculture Based Industry, Click Here
- The Ministry will, for the sake of expeditious execution of the programs, involve a Program Management Organization (PMA) in order to provide leadership, capability, construction, coordination, and assistance for tracking. To meet the above expense of office spending & transport, as well as other promotional events by the Ministry, Scheme-related costs, up to 5% of the total grant available, will be earmarked.
For the purpose of eligibility under this Program, the expense of the project must consist of components of the following:
Projects:- Project Reports & Profiles
- Core Processing Facilities:-
Central Distribution Center– Cost of civil work & services such as laboratory testing, washing, marking, sorting and packaging facilities, dry warehouses, advanced storage facilities cold storage comprising regulated atmosphere chambers, pressure ventilators, dynamic humidity stocks, pre-cooling chambers, ripening chambers, etc.
- Primary Processing Centres and Farm Proximate Collection Centers- This may include components such as washing, grading, sorting, and packaging facilities (including equipment), dry warehouses, specialist cold stores, including pre-cooling chambers, ripening chambers (including equipment), reefer vans, mobile pre-coolers, mobile vans, etc.
Buildings for factories
The Mega Food Park has standard features, depending on the demand in the region. Medium and Small Businesses (MSEs) factory sheds that are to be designed on a limit of 10% of the CPC area as part of the plug and plug for MSEs, playrooms.
Books:- BOOKS & DATABASES
Enabling Elementary Facilities
- It would include the construction of the site, including the development of industrial parcels, boundary walls, roads, drains, water supplies, energy supply, including captive power plants, effluent treatment plants, telephone lines, parking bays, including traffic control systems, PPC and CPC weighbridges, etc.
- However, costs not exceeding Rs.10 crore of the overall proposed expense of the captive power plant shall be considered as qualifying project costs for grant evaluation. Any extra expense of setting up a captive power plant.
- Any extra expense of setting up a captive power plant only through the commitment of SPV by equity and debt will be expected to be fulfilled. The SPV must show a firm strategy to ensure the supply of power to prospective units in the Park is high quality and guaranteed.
Start a Business in Potential Countries for Doing Business, Click Here
Best Industry for Doing Business, Click Here
Business Ideas with Low, Medium & High Investment, Click Here
Looking for Most Demandable Business Ideas for Startups, Click Here
Start a Business in Africa, Click Here
Start a Business in India, Click Here
Start a Business in Middle East, Click Here
Start a Business in Asia, Click Here
- Non-Core Infrastructure
- Help structures such as administration buildings, recruitment center including laboratories, trade and show center, nursery, canteen, staff hostel, service company offices, worker rest and leisure facilities, publicity support system, etc. will be included.
- However, it will be available for grant purposes to offset the expenses of non-core infrastructure facilities not increasing 10% of the qualified project expense.
- Expenses for Project Execution
This will require the expense of employing domain consulting services from the SPVs for DPR planning, supply chain management, engineering/designing and management of the building, etc.
- Land
- The SPV shall arrange at least 50 acres of land for the project either by purchase or on a loan of at least 75 years. As part of the project expense and contribution/share of the SPV, the registered valuation of such property will be taken away.
- For the procurement/purchase of properties, the GoI grant is not used. The land and/or infrastructure has taken on lease for PPCs/CCs should have a lease term of at least 25 years
Market Research :- Market Research Report
Service mode
The Scheme has a solution focused on a cluster based on the concept of hub and spokes. It requires the construction of primary processing and storage infrastructure near the farm in the form of primary processing centers (PPCs) and collection centers (CCs) and common facilities and the facilitation of the central processing center infrastructure (CPC).
Who can participate in this project?
- As a member of SPV, every corporate investor, infrastructure group, foreign direct investor.
- Industrialists & pioneers who wish to join the food manufacturing industry.
- An emerging food & agro-business that is able to extend its existing activities or intend to start up a new enterprise.
First Mega Food Park In India
Greentech Mega Food Park Limited is the first mega food park in Rajasthan to be built under the flagship initiative of the central government, Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana and ‘Make in India.’

Related Project:- Mega Food Park
Union Minister for Food Production, inaugurated the Avantee Mega Food Park in Dewas, Madhya Pradesh. This first mega food park of central India is spread over 51 acres and was designed at a cost of approximately 150 crore rupees.

The Mega Food Parks Scheme, initiated by the government in 2008, offers up to 50 crores of financial assistance for the development of modern food production infrastructure called Mega Food Parks.
Functional Mega Food Parks in India
Initiatives for obtaining assistance underneath the framework are welcomed from time to time by expression of interest.
22 Mega Food Parks have been functional so far:
- Srini Mega Food Park, Chittoor, Andhra Pradesh.
- Godavari Mega Aqua Park, West Godavari, Andhra Pradesh.
- North East Mega Food Park, Nalbari, Assam.
- Indus Best Mega Food Park, Raipur, Chhattisgarh.
- Gujarat Agro Mega Food Park, Surat, Gujarat.
- Cremica mega Food park, Una, Himachal Pradesh.
- Integrated Mega Food Park, Tumkur, Karnataka.
- Kerala Industrial Infrastructure Development Corporation (KINFRA) Mega Food Park, Palakkad, Kerala.
- Indus Mega Food Park, Khargoan, Madhya Pradesh.
- Avantee Mega Food Park, Dewas, Madhya Pradesh.
- Paithan Mega Food Park, Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- Satara Mega Food Park, Satara, Maharashtra
- Zoram Mega Food Park, Kolasib, Mizoram.
- MITS Mega Food Park, Rayagada, Odisha
- International Mega Food Park, Fazilka, Punjab.
- Sukhjit Mega Food Park, Kapurthala, Punjab.
- Greentech Mega Food Park, Ajmer, Rajasthan
- Smart Agro Mega Food Park, Nizamabad, Telangana.
- Tripura Mega Food Park, West Tripura, Tripura.
- Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, Haridwar, Uttarakhand.
- Himalayan Mega Food Park, Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand.
- Jangipur Bengal Mega Food Park, Murshidabad, West Bengal.
Startups pursuing fully established industrial parcels to set up food processing units and to profit from other related services can contact Mega Food Parks promoters.


Comments are closed.