India is a land rich in food, flavors, and traditions. The nation is in need of efficient food systems now more than ever. Food Parks are key players in India’s food industry. These centralized zones gather farmers, processors and vendors in order to create a vibrant supply chain. This article explores what India Food Parks, why they are important, how they operate, and their impact on the food industry.
What Exactly is a Food Park
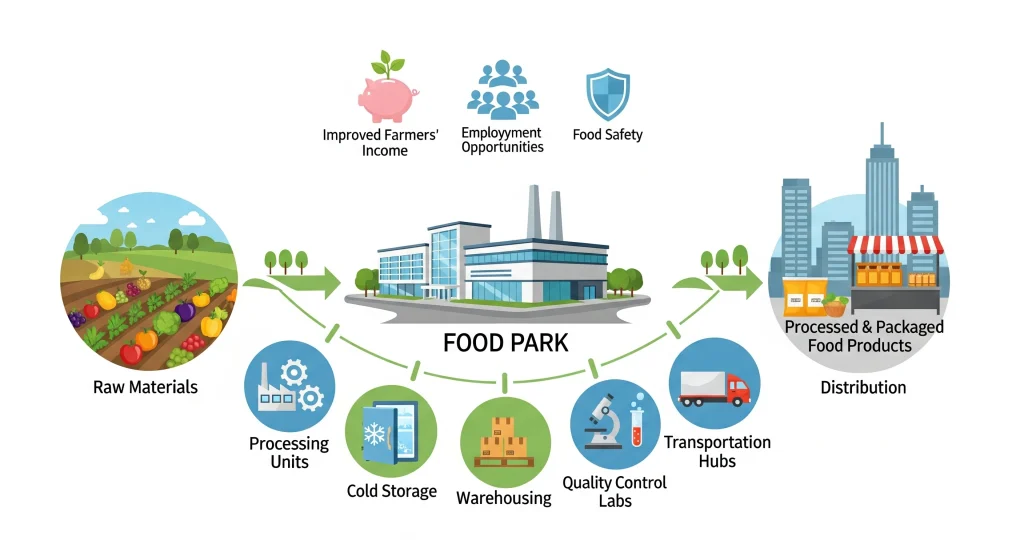
Imagine a space with a modern infrastructure that allows food businesses to operate smoothly. It’s an India Food Park, a specialized industry park for the food-processing sector. This is a food-specific factory zone, which offers:
- Units of Processing to convert fresh produce into packaged and ready-to-eat products
- Cold Storage Facilities To protect perishables such as fruits, vegetables and dairy products from spoilage
- Warehouses to store raw materials as well as finished products
- Quality Testing Labs Ensure that food meets safety and hygiene standards
- Transport hubs for seamless shipping and receiving
- Shared Utilities including water treatment, electricity, and waste management systems
- Administrative support for easier licensing and permits
Food parks reduce costs and improve efficiency by combining these services.
Why India needs food parks
Food parks are a crucial part of India’s transformation in agri-food for several reasons:
- Reducing Post Harvest Losses
India is losing a large portion of its harvest after harvest because of poor handling and storage. Food parks can help reduce waste and preserve quality by integrating cold chains and storage. - Accelerating the Food Processing Growth
India produces a lot of raw food but only a small amount is processed. Food parks offer the infrastructure to increase food processing, and encourage farmers. - Boosting rural employment
Create jobs in the food parks in Tier-2 and 3 towns. - Empowering Farmer
Food parks totally shake up the game for farmers. They sell their products nearby, so they skip those long, expensive trips just to make a sale. As a result, they actually keep more of their hard-earned cash. Even better, when there’s a processing center right next door, farmers can turn simple crops into things like sauces or jams. Suddenly, they’re not just selling tomatoes—they’re selling something worth a lot more. That’s extra money in their pockets, for real. So, when you cut those travel costs and add more ways to make products, farmers win big. Why wouldn’t they jump on that? - Improving food safety
Centralized laboratories help ensure that packaged foods and processed foods meet the standards of safety, so consumers are able to trust what they purchase. - Attracting investment An organized, plug-and play model attracts both domestic and international firms to food processing. This helps scale the sector.
- Supporting small businesses
The food parks provide shared facilities that are viable for SMEs, allowing them to compete without large investments.
Government Support and Mega Food Park Scheme
Food parks are supported by the Indian government through policies and subsidies.
Mega Food Park Scheme
The Ministry of Food Processing Industries is supporting mega food parks in all states under this flagship initiative. A typical mega food park includes:
- Central processing centers
- In farming areas, there are collection and primary processing centres.
- Cold chains and value-added units
Goals include:
- From farm to market: Strengthening infrastructure
- Fruits and vegetables: How to reduce waste
- Raising the income of farmers
- Create jobs in rural areas, especially
Each park is at least 50 acres in size and follows a cluster-based model. Private players set up the actual food processing units, with government funding only the core infrastructure.
Read Our Book: Click here
State-Level Support
To attract investors, state governments offer incentives such as tax rebates, land, utilities and easier approvals.
You can find detailed planning models and ideas in Niir’s Project Reports for Food Parks.
India Food Parks: A Win-Win Situation
For various stakeholders, food parks deliver clear advantages:
Farmers
- Enjoy higher margins and access to value-added services
- Reduce losses by storing in advance
- Transport and intermediary costs reduced
Food Processing Units
- Plug-and play infrastructure reduces capital requirements
- Easy access to inputs, utilities and services
- Easy compliance with quality standards
Consumers
- Access to safe and high-quality packaged foods
- Potential savings through streamlined supply chains
- Enjoy more variety and convenience
Economy
- Attracts investments into rural areas
- Creates jobs and improves lives
- Food waste reduction boosts GDP
Challenges & Solutions
Food parks are not without challenges, despite their high potential.
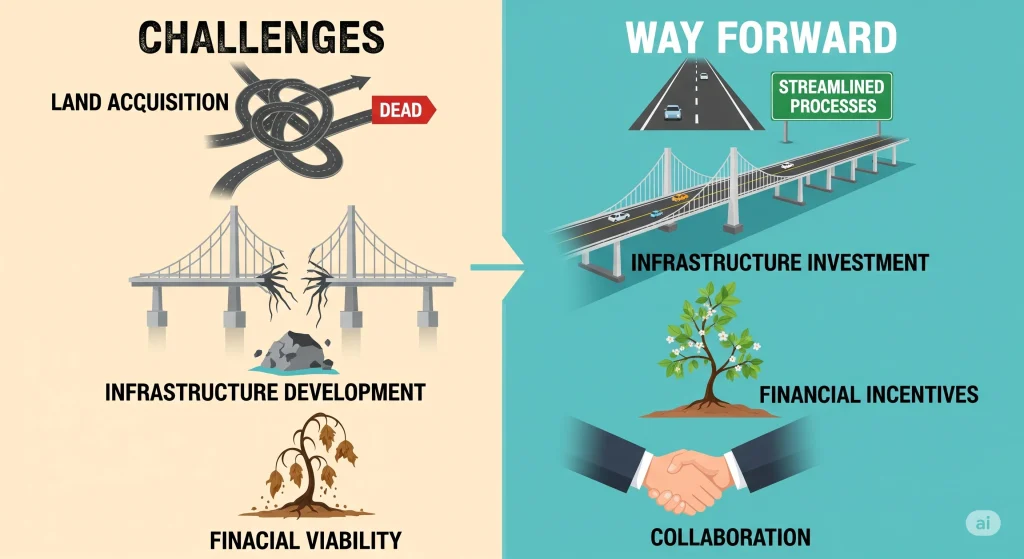
- Land acquisition – Getting large tracts of land together can be difficult and cause delays.
- Infrastructure Gaps– Power, roads and water infrastructure, as well as cold infrastructure, are all essential to smooth operations.
- Financial viability– Ensure that food parks are able to attract enough business to support operations.
- Coordinating– It is difficult to align roles among government agencies, private operators and stakeholders.
- Awareness– Small processors and farmers may not be aware of the benefits that food parks offer.
MSME Business Ideas by Government: Unlocking India’s Startup Revolution
Overcoming these barriers
- Clear state guidelines simplify land acquisition procedures.
- Public-private investments can be used to improve infrastructure.
- Give financial incentives such as soft loans, subsides, or capital grants.
- Create stakeholder forums for aligning goals and streamlining communication.
- Workshops on training and awareness for farmers and processors.
Check out this NPCS blog for practical guidance on how to start a food processing unit in a Food Park
The Future of Food Parks In India
Food parks will be a key part of India’s food scene as food demand increases. Key trends:
- Specialized parks in organic, frozen or health food processing
- Adoption of technology such as IoT, automation and to improve efficiency
- Integration of E-commerce for parks to directly connect with online customers
- Cold Chain Expansion for Deep Cold Storage of Perishables
- Design with eco-friendly and use of renewable energy within parks
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Conclusion
India’s Food Parks are shaking things up in the food game, no doubt. First off, farmers, food processors, and markets actually work together now, instead of everyone running around like headless chickens. Plus, the government’s jumping in with support, which—let’s be real—doesn’t happen every day. Next, these parks roll out smart infrastructure, so food doesn’t just sit there and rot. Farmers see more money (finally), and less produce ends up in the trash.
On top of that, shoppers score safer, better food. So yeah, everyone wins: farmers, businesses, and anyone who likes eating stuff that won’t wreck their stomach. Pretty sweet deal, if you ask me.
India Food Parks have proven that despite challenges such as land issues and coordination problems, they can be the cornerstone for a modern, resilient food system.
India Food Park: Frequently Answered Questions (FAQs)
Q1 What is the primary goal of a Food Park?
Answer: To provide an ecosystem with infrastructure to efficiently process food, reduce waste and improve food quality.
Q2 Who benefits from food park?
Answer: Farmers (better price), food processors, (infrastructure savings and cost reduction), consumers (quality foods), and the economy.
Q3 What are the facilities that food parks provide?
Answer: Cold storage, laboratories, processing units, logistic infrastructure, common utilities and support services.
Q4 What is Mega Food Park Scheme (MFP)?
Answer: A government initiative aimed at developing large-scale food park clusters, with essential infrastructure supporting processing units.
Q5 Can small businesses run in food parks?
Answer: Yes, they can, and it will reduce their costs of setup, as well as improve market access.
Q6 – What are the major challenges of developing food parks?
Answer: Land acquisition, infrastructure gaps and financial sustainability. Lack of awareness, lack coordination among stakeholders, lack in coordination with other stakeholders, and lack in coordination.







