In recent years, the spinning yarn market has grown globally due to increased textile consumption in both the apparel and non-apparel sectors. The fashion sector drives demand, while increased style changes and performance fabrics ensure year-round yarn demand. The market for technical textiles in industries like automotive, healthcare, geotextiles, and filtration is growing faster, creating niches for specialized spinning operations.
Asia dominates production due to abundant cotton cultivation, competitive labor costs, and established textile clusters. The global market growth rate is around 4-6% CAGR, with India, China, and Vietnam leading production and exporting globally.
By the end of the decade, production is forecast to reach around 140 million metric tons annually, driven by an expanding middle class and the adoption of sustainable and eco-friendly fibers.
Global Market Size Prediction for Yarn Spinning (2025-2030)
| Year | Projected Market Size (Million Metric Tons) | CAGR % | Key Market Drivers |
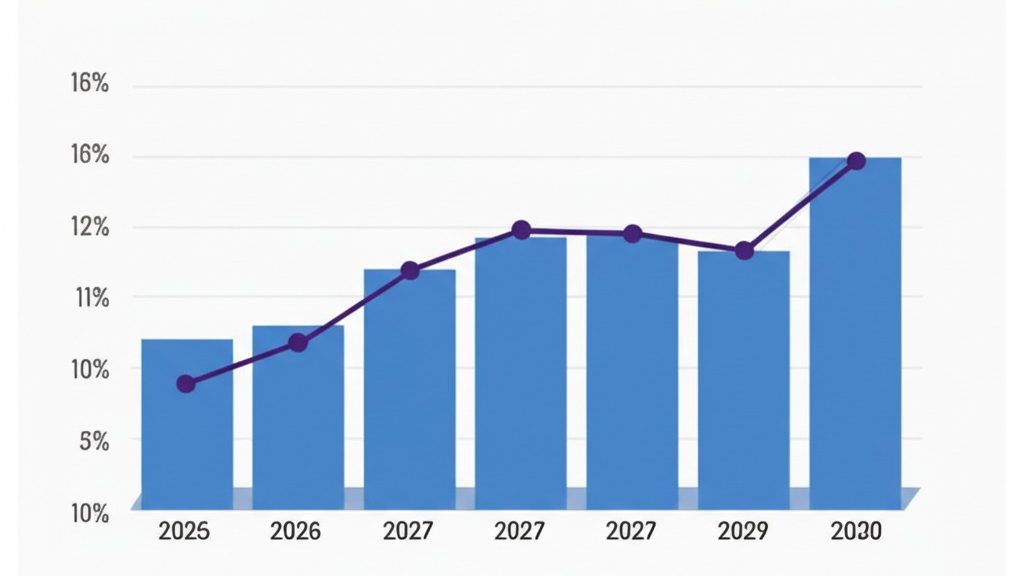
| 2025 | 116 | – | Increased apparel demand and expansion of technical textiles |
| 2026 | 121 | 4.3% | Use of sustainable yarns and production regional hubs |
| 2027 | 126 | 4.1% | E-commerce and fashion brand sales |
| 2028 | 132 | 4.7% | Home furnishings and industrial textiles |
| 2029 | 137 | 3.8% | Automated spinning mills and improved efficiency |
| 2030 | 143 | 4.1% | Demand in developing economies and nearshoring |
For more information, check out this Handbook on Textile Spinning, Processing, Natural Fibers
Regional Growth Forecast
The Asia-Pacific region leads as an industry center due to cotton production in India, textile manufacturing in China, and the apparel export industry in Vietnam. Government and textile park incentives in India are further driving the region’s growth. The Africa region, particularly Ethiopia, Kenya, and Egypt, is emerging as a production hub due to low labor and cotton costs, along with trade agreements like AGOA.
Mexico and Brazil are leaders in Latin America for producing and exporting cotton-based yarns to North America. In Europe, manufacturing focuses on high-value yarns and technical textiles, importing raw fibers for processing with advanced spinning and finishing methods.
Countries like Turkey and Egypt are investing in modern spinning facilities for regional apparel and home textile markets. While Asia dominates, strategically located smaller mills can operate in other regions.
Demand Drivers and Growth Trends
Sustainability and traceability of yarns are significant trends. European and North American buyers prefer certified yarns like GOTS and OEKO-TEX®. This drives increased production of organic cotton yarns and recycled polyester blends.
Adoption of automation, IoT-based quality monitoring, and predictive maintenance technologies streamlines production processes and reduces defects. Digital systems monitor yarn evenness, twist, and production speed in real-time to reduce waste and maintain consistency.
Demand for high-performance yarns is rising. Specialized sectors use yarns with flame-retardant, antimicrobial, or conductive properties. These advanced yarns, though expensive, come with long-term contracts, stabilizing income outside the fashion industry.
Related: Spinning Mill: Turning Cotton Into Thread For The World
Strategic Positioning for New Businesses
Achieving success for a spinning mill startup depends on location, product mix, and technology. A good location lowers logistics expenses and preserves fiber quality, needing proximity to cotton-growing areas, polyester chip suppliers, or ports. Consistent electricity, transportation routes, and a reliable water supply are essential.
Product mix decisions are important. Many new mills start with commodity yarns like carded cotton and polyester blends for the mass market, which have low margins and stiff competition. Others specialize in compact combed yarns, eco-friendly blends, or specialty yarns for technical applications, offering higher margins but requiring precise marketing and manufacturing.
The spinning method must match the market strategy. Ring spinning is effective for fine yarns, while open-end or rotor spinning is cost-effective for coarse yarns. Specialized methods like compact and air-jet spinning are gaining popularity. Automation with advanced monitoring tools increases consistency while optimizing cost.
Manufacturing Process
The process of transforming raw fiber into yarn is methodical and divided into steps. It starts with the receipt and preparation of raw materials, which is done in the blowroom. During this process, incoming bales of raw cotton or synthetic fibers are opened, cleaned, and blended to produce a fiber mix. This stage optimally smooths out variance in the yarn by ensuring consistency.
The carding process follows and is the next stage of production. It involves aligning and separating fibers, forming them into a continuous web. A carding engine helps with this. This stage is critical in the removal of impurities and also in determining the basic quality of the yarn. For the production of the best quality yarns, the combing stage is added, which helps in the removal of short fibers and only allows the longer and uniform fibers to go through the further stages of production.
The last steps include the winding stage, in which yarn is transferred to cones or packages. The packages are then checked for any faults, which are automatically cleared. Quality control is very important in this stage, as any small defects will impact the performance of the yarn in the downstream processes like weaving or knitting.
Related: Smart Textiles: The Intersection of Fashion and Technology
Future Opportunities and Sector Trends
The milling and spinning industry is advancing towards sustainable practices along with increased efficiency and production. Mills that use recycled fibers, implement clean energy, and pursue green certifications will greatly benefit from lucrative export opportunities. There is also a shift towards “nearshoring” in textile supply chains as brands look to source from regions closer to consumer markets. This shift is a great opportunity for smaller, more flexible spinning mills with quick response times and customized and tailored services.
Another important shift will be the digital transformation. The way spinning mills operate and compete will change with the introduction of AI in production scheduling and blockchain for supply chain verification. For startups, adopting such innovations from the outset can set them apart in the market.
For more information, check out this video
The Role of Expert Advisory
Establishing a spinning mill requires as much technical knowledge and market insight as it does thoughtful feasibility planning. For entrepreneurs, Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS) has established itself as a reliable advisor. The company prepares a Market Survey cum Detailed Techno Economic Feasibility Report containing a Manufacturing Process, a Bill of Materials, Plant Layout, and a Financial Projection.
NPCS protects new companies from ill-advised industrial initiatives, allowing them to enter the market with a clear and detailed strategy.
Which business to start? How to choose a business idea?
Final Thoughts
Spinning mills represent a long-lasting opportunity for investors who know how to marry a market opportunity with technical know-how. Startups in this critical part of the textile industry can establish a competitive presence by understanding global and regional demand drivers, selecting the right combination of products, and adopting lean manufacturing strategies.
Steady growth of the industry, along with new emerging niches for sustainable and technical yarns, would provide ground for new ventures. New spinning mills will need to meet market demand with production capability and the need for maintaining consistent quality fuels innovation. Operational discipline, strategic planning, and reliable industry insights can turn a spinning mill’s entrepreneurial vision into a successful industrial reality.







Hi, thank you for this imformative article. It was a very helpful blog. I got to know about a lot of unknown information. I would also like to add some points. As we are talking about spinning mills and their production facilities, Spinning Cans are one of the key tools to manufacture best quality yarn. So, to produce quality yarn it is important to use spinning cans.
Thank you, Jumac. We will take this information into consideration and if it fits our needs, we will also put it in our other articles.