India’s floriculture industry is quietly undergoing transformation. Rose Farming Business is one of the most lucrative sectors within it. Rose cultivation has evolved from horticulture to a commercial agribusiness with high returns.
This guide explains how to build a profitable and sustainable rose farming business. It covers everything from understanding market trends, selecting the right varieties and outlining the cultivation and manufacturing process.
Why Rose Farming is a Smart Business Decision Today
Rose farming has a unique benefit: it is a single crop that can generate multiple streams of income. Roses are a great way to reach both niche and mass markets. They can be used to supply fresh cut flowers for local markets, to make rose water or gulkand, or to extract essential oils to sell to global aromatherapy brands.
India’s climate naturally suits several rose varieties, and many states, including Maharashtra and Karnataka, as well as West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan, have become major centers of cultivation. The Damask variety of roses is in demand across a wide range of industries, from wedding décor and perfumery to herbal teas and Ayurveda digestion aids. This means that there is a consistent and growing market for both B2B as well as B2C.
Related: Why Polyhouse Farming is Changing Indian Agriculture in 2025
Understanding Market Demand and Sector Growth
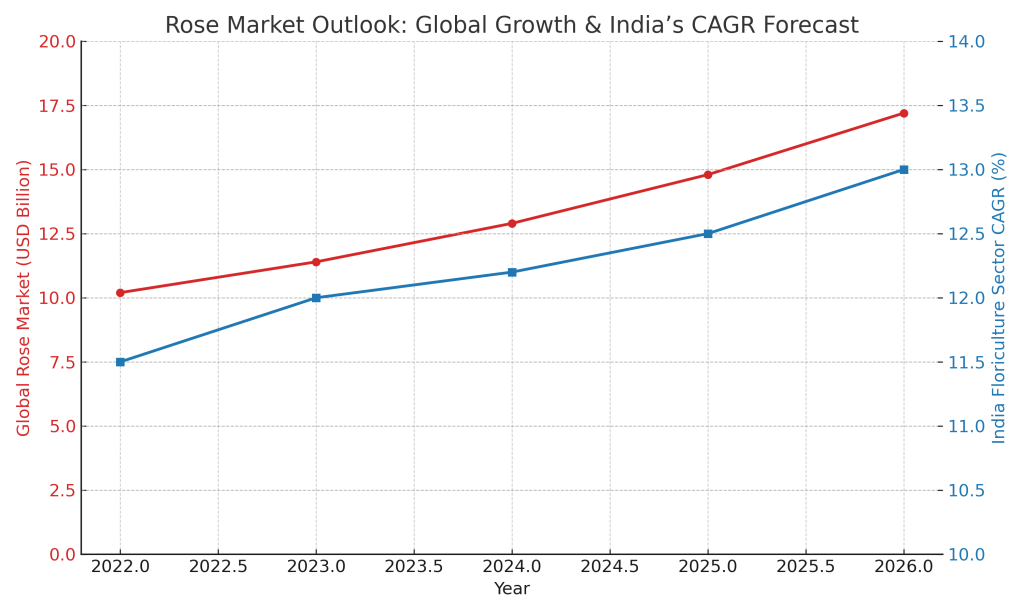
Global floriculture is growing rapidly. The cut flower market will reach USD 56,4 billion by 2029 at a CAGR over 6%. Roses make up the majority of the global trade in cut flowers, accounting for nearly 60%. Exports are dominated by countries like the Netherlands and Kenya. Demand is driven primarily by the U.S.A., Germany and the UK.
In India, this shift is even more compelling. The Indian rose market continues to grow at a rapid pace, driven by urbanization, rising disposable incomes and the wellness boom. The market is expected to grow from Rs6,700 crores in 2025 to Rs11,000 crores by 2030. The government’s support for floriculture clusters and export incentives as well as cold-chain infrastructure through APEDA, is also a major factor in this growth.
Even the domestic market is changing. The rose market has been reshaped by events, weddings and cosmetic brands. Ayurvedic brands, Ayurveda, e-commerce, and other channels have also emerged. The demand for rose-based products is not limited to the peak season, but rather it’s growing year-round across all segments.
Selecting the Right Varieties for Commercial Success
Your business model will determine the type of rose you choose. Due to their vibrant colors and long stems, hybrid teas such as Grand Gala or Taj Mahal will be ideal if you are targeting the wedding or export market. Damask Roses (Rosa Damascena), which produce high-quality oils, are best for industrial purposes such as rosewater, attar, and gulkand.
Climbing roses and miniature roses are popular for urban gardening and potted plants. To maximize profit, entrepreneurs must match their selection of cultivars with the end-use market.
Check our Handbooks on Herbal Products, Aromatic Plant Cultivation, Processing, Herb, Medicinal Plants, Herbs Cultivation, Processing, Herb, Herbs Extracts, Aloe Vera Cultivation, Cultivation, Research Findings, Products, Formulations, Extraction & Processing, Processing, Herbs
The Rose Cultivation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
To grow roses successfully, choose a fertile soil that is well-drained and has a pH level between 6.0 and 6.5. The ideal climate is between 15 °C and 28 °C. Most rose varieties thrive best in areas with moderate humidity and ample sunlight. The soil should be prepared by plowing the ground deeply, and adding organic compost or farmyard waste.
Planting usually takes place in the early winter or monsoon, depending on where you live. Most commonly, stem cuttings and budding are used for propagation. It is recommended to use drip irrigation as it maintains moisture levels efficiently without overwatering. Organic growers use Jeevamrut or neem cakes to enrich the soil.
Integrating pest and disease management into your farming operations is essential. Natural or biological agents can control common threats such as aphids and spider mites. For better airflow and flowering, pruning must be performed periodically. Harvesting flowers should take place in the morning, when the moisture content and fragrance is at its peak.
Many rose varieties produce multiple harvests each year with good practices. They can be harvested in 6-8 week cycles.
Related: Start a Profitable Agricultural Tools Business
After-Harvest Storage and Handling Practices
It is important to maintain flower quality after harvest and maximize shelf life. Cut flowers must be trimmed and hydrated before they are shipped to the market or exported. To maintain their freshness, roses that will be used to make oils, gulkand or petals need to be sorted and cleaned.
Investors in processing units should ensure that raw petals are as fresh as possible, since this will directly impact the product’s quality. Professional rose farming operations require cold storage, hygienic areas for handling, and packaging.
Rose Processing: Value-Added Products
Additionally, here are some common product lines that entrepreneurs should consider.
Rose Water is produced by steam distillation from fresh petals. Furthermore, it is widely used for cosmetics, Ayurveda, and culinary purposes. Specifically, rose water is made by setting up a distillation system, using stainless steel or copper vessels, and adhering to hygiene and packaging standards.
Rose Oil (Attar), a high-value, low-volume product, is used primarily in aromatherapy and perfumery. Moreover, one kilogram of rose oil is made from over 1,000 kg of petals, making it one of the most expensive essential oils in the world. Hydro-distillation is used to produce the oil, which is then sold in small, airtight containers.
Gulkand is a sweet preserve made from rose petals, sugar, or mishri. Moreover, it has Ayurvedic benefits for digestion. The product is made by exposing sugar and rose petals in jars to sunlight for three to four weeks. Gulkand, with the right branding, can be sold both locally and online.
Dried Rose Petals, as well as Rose Powder, are becoming increasingly popular in the herbal teas, skincare and wellness industries. The petals are dried either by sun or mechanically, and then packed in moisture-proof containers. These products are easy to store, transport and have a long shelf life.
With a moderate investment in equipment and access to high-quality roses of high quality, entrepreneurs can build a rose processing unit that serves multiple markets.
Distribution Channels & Selling Strategies
Your chosen business model will determine how you market rose-based products. You can build a recurring market if you grow roses to sell as cut flowers. Partnerships with florists and decorators will help. It is common to sell flowers through mandis and flower auctions, but margins are volatile.
You can partner with Ayurveda shops, natural skincare brands, or health-focused retailers to sell processed products like rosewater or gulkand. Amazon and Flipkart, e-commerce platforms with a niche organic positioning are great for launching D2C brands.
Exporting roses or rose oil can open up global markets of premium quality, but requires certifications like APEDA registration as well as compliance with phytosanitary standards. Entrepreneurs can either work with export houses or directly look for international buyers to secure long-term contracts.
Branding, traceability and quality assurance are important in establishing trust, especially in the wellness and organic sector. A brand that is based on a story and backed up by products of high quality, free from chemicals, can have a significant impact on customer loyalty.
Opportunities and Competitive Advantages
India’s rose-growing sector is poised to diversify and grow at high margins. Innovation is the key to success in traditional flower markets. Startups can launch D2C brand for rose-based skin care, herbal teas and aromatherapy.
Farmers can create cooperatives and aggregate the production of roses, investing in processing units that are shared. This will increase income and reduce risk. Rose farming can be integrated with agritourism, where visitors are able to experience rose gardens and distillation demonstrations. They can also buy directly from the farm.
Entrepreneurs who have a vision of scaling up can look into organic certifications and international trade shows, as well as digital storytelling, to position rose-based products in the premium lifestyle market.
For more information, check out this related video
NPCS can support your rose farming venture
Niir Project Consultancy Services provides comprehensive support for entrepreneurs who are interested in entering the rose processing or rose farming business. Their Market Survey and Detailed Techno-Economic Feasibility Reports provide valuable insight for making decisions.
Each NPCS Report includes a detailed manufacturing procedure, a list of raw materials required, and an optimized plant layout. NPCS assists new and existing companies in assessing the feasibility of setting up agro-based manufacturing units. It also provides recommendations on technical and commercial aspects.
Find the Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
Conclusion
Rose farming is more than just an ornamental or seasonal activity. It’s the gateway to a year-round, diversified business with many product lines. Strategic planning can help entrepreneurs tap into the domestic, digital, and export markets by growing high-quality flowers or creating branded rose oil or water.
It is important to choose the right variety, maintain post-harvest standards, match consumer preferences, and invest in value addition. The rose farming industry is a great opportunity to grow sustainably and with high margins. Government support, easy access to e-commerce, and a growing interest in natural products are all factors that contribute.
You can make rose farming a profitable and scalable business by building a solid foundation with feasibility studies and product innovations.









