Jaggery has been around for ages. People make it from sugarcane or palm sap. In India, they call it “gur” and use it in sweets, chai, and even in Ayurvedic medicine. Folks in Africa and Southeast Asia use it a lot, too. Since hundreds of years, the jaggery industry has played a major role in rural life.
People want healthier, more natural products now. Because of this, jaggery is becoming more popular than white sugar. This article explains how jaggery is made, the tools used, why it matters, and the challenges involved.
Jaggery: Understanding The Rural Economic Backbone
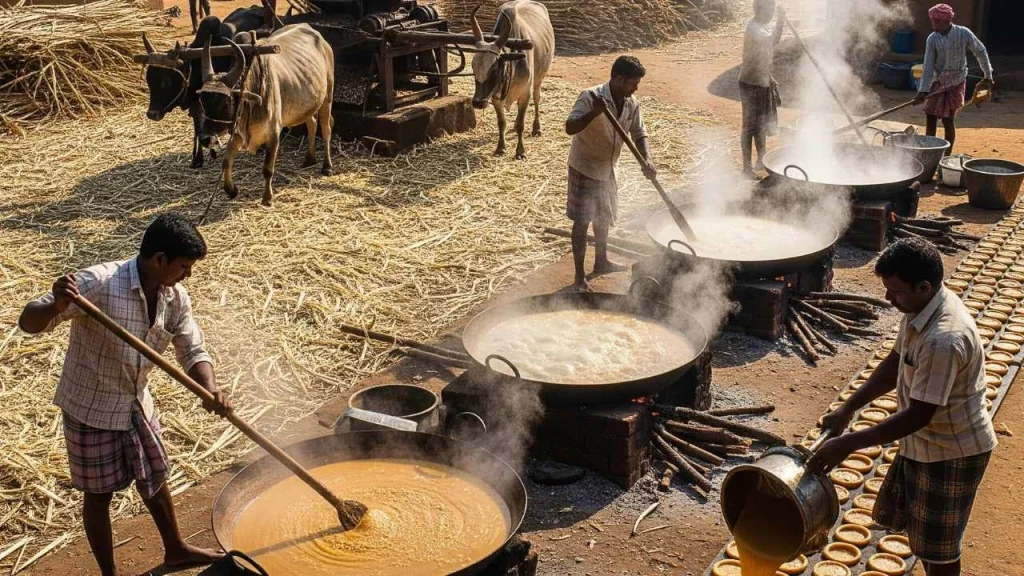

Most jaggery comes from small rural units. Local families and workers usually run these operations. As a result, jaggery production brings seasonal jobs. Also, it gives sugarcane farmers extra income.
People usually use small units called “Kolhus” or “Gud Bhattis” right near the sugarcane fields in villages.
Jaggery Making Industry: Raw Materials
- Sugarcane: Sugarcane is the primary raw material. Sugarcane is grown in tropical or subtropical areas. It is then brought to the jaggery unit after cutting.
- Clarifiers and Lime: Clarifiers derived from plants or lime are used to clean the juice. Most traditional units do not use chemicals.
- Water and Fuel: Cleaning and boiling water is done with water. Bagasse, or dry sugarcane waste, is used in the furnace.
Related Article: Top 10 Government Schemes for Food Processing Startups in India
Equipment used in Jaggery Making Units
Included are:
- Crusher: Used for extracting juice from sugarcane
- Pans: Juice boils in large iron pots
- Furnace (or Bhatti): Used for heating the pan with bagasse as fuel
- Wooden plates and moulds: Here, jaggery is poured into the moulds and shaped
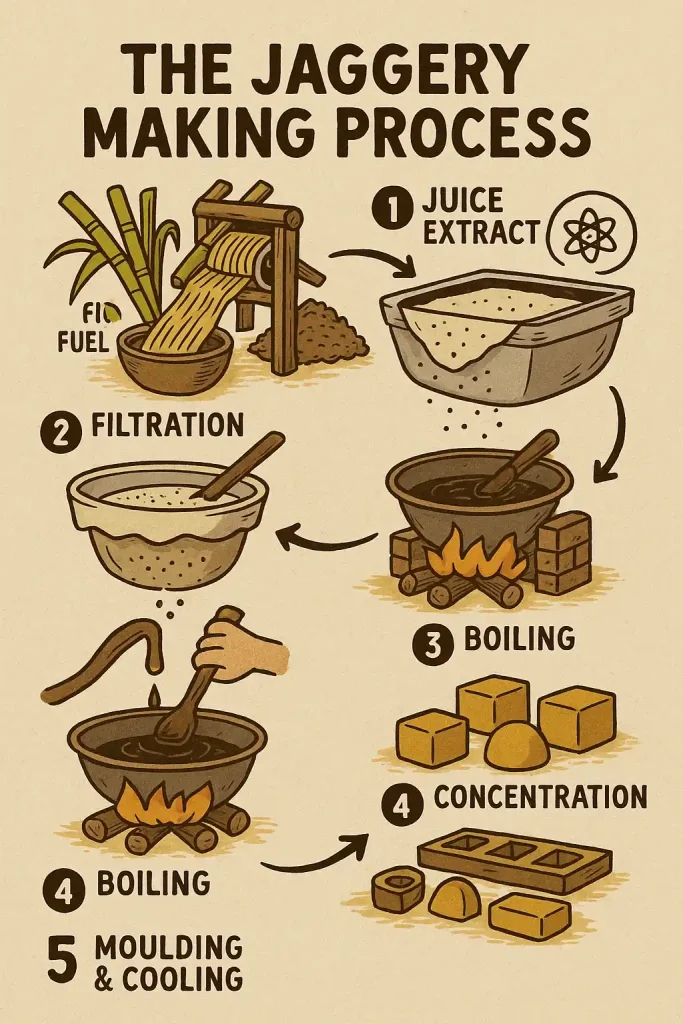
The Jaggery Making Process
- Juice Extraction: The sugarcane must first be crushed. The juice is collected into a container. Bagasse is set aside for use as fuel.
- Filtration: Filtering the juice removes dust, insects or leaves. To help remove impurities, lime or natural clarifiers must.
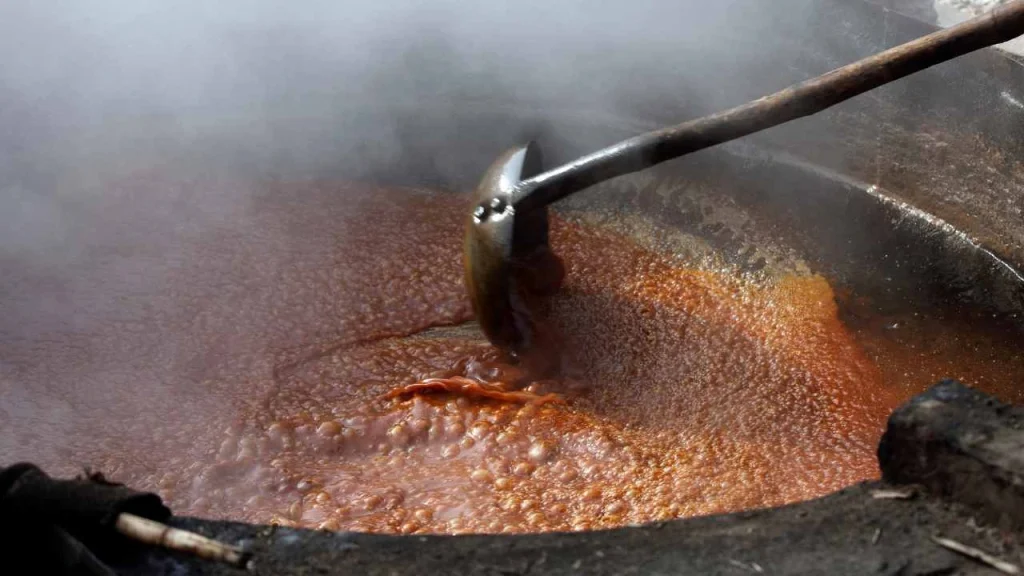
- Boiling: The filtered juice is then poured into a big iron pan, and boiled in a furnace. Bagasse is used as fuel. The juice is constantly stirred.
- Concentration: Continue boiling until the juice is thick and sticky. Check the consistency with a stick or by hand.
- Moulding & Cooling: The thick liquid is poured in wooden or iron molds. It becomes jaggery after cooling.
Types Of Jaggery
The method of production and the ingredients used will determine which types of jaggery you get.
- Solid Jaggery in Block Form
- Liquid Kakvi
- Granular Jaggery in Powder Form
You can add Cardamom or ginger to enhance flavor and provide health benefits.
Related Article: Starting a Profitable Cold Storage Business
Jaggery Making Industry: Environmental Impact
Jaggery is an eco-friendly product: This food industry is eco-friendly. They use the leftover bagasse as fuel. They filter and reuse the water, too. Smoke from bagasse burning increases air pollution. This is still lower than large sugar factories.
Employment and Economic Importance: In rural areas, jaggery production units have provided jobs. Farmers sell sugarcane straight to the jaggery units close by, so they save on transport and make more money. Local traders and laborers pick up extra work for the season. Women usually handle the sorting and packing.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Jaggery Making Industry: Health Benefits
Jaggery has antioxidants, iron, and magnesium. In Ayurveda, people use it to help with digestion and immunity. Unlike white sugar, jaggery does not have chemicals. People often say it is a healthier option. For many years, people have mixed jaggery with spices to treat coughs and colds.
Jaggery Industry: Challenges and Opportunities
The industry faces some challenges despite its many benefits:
- Lack modern equipment: The majority of units still use traditional techniques.
- Seasonal Production: During the sugarcane harvest season.
- Low awareness: Many people are unaware of the health benefits that jaggery can provide.
- Poor packaging: The packaging of jaggery is often dirty or open.
- No quality standards: Some units do not adhere to any fixed rules.
Read Our Project Report: Click Here
Future of the Jaggery Industry
Jaggery might grow in the future due to demand for natural products. Modern machines there, packaging is seeing improvements. Exports and online sales are on the rise. If farmers receive proper training, more of them could start making jaggery. The government is also bringing in schemes to help small jaggery makers.

Conclusion
Jaggery making is an old part of Indian culture. It creates jobs in rural areas and supports health and the environment. The industry can grow if farmers get more help and if packaging and marketing improve. Jaggery is a better choice than sugar and helps the local economy.
Jaggery Making Industry: FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Is sugar better than jaggery?
A: Jaggery contains minerals and is less processed. It’s a healthier alternative to white sugar.
Q2: For how long can you store jaggery?
A: If stored in a cool, dry place for six to twelve months, jaggery will last.
Q3: Is it possible to make jaggery at home?
A: You can make small batches at home with sugarcane juice, if you have the right tools.
Q4: What states produce the most jaggery in India?
A: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Karnataka are the major producers.
Q5: Does jaggery make money?
A: It is possible to make money if you maintain a high standard and reach the right markets.







