Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) play a vital role in India’s foreign trade setup. These non-profit groups are registered either under the Companies Act or the Societies Registration Act and are backed by the government to support Indian exporters.
EPCs focus on raising the visibility, competitiveness, and reputation of Indian goods and services in foreign markets. Acting as a bridge between the Government of India and the business community, they offer tailored advice and services that influence foreign trade policy and help firms navigate complex international regulations.
1. The Foundation of India’s Export Strategy
1.1 Definition and Principal Function in India’s Export Mechanism
Each EPC concentrates on a specific sector—such as engineering, textiles, pharmaceuticals, or agribusiness—allowing it to deliver practical, industry-tailored advice.
EPCs help exporters penetrate new markets through policy support and capacity-building initiatives. They help small businesses and large companies alike access government incentives, secure international quality certifications, and build lasting buyer networks abroad. Their strategic guidance positions India as a dependable global supplier.
1.2 Evolution and Historical Context of EPCs
EPCs started taking shape in the middle of the 20th century, with pioneering bodies like EPC India (earlier EEPC) and PLEXCONCIL set up in 1955. Over the last seventy years, these councils have moved from being rigid, paper-heavy offices to dynamic networks that effectively address the changing needs of global trade.
A clear illustration came during the COVID-19 pandemic. Faced with travel bans, EPCs quickly rolled out virtual trade fairs, launched helplines, and created mobile apps. These tools kept Indian exporters connected with overseas buyers while borders were closed. Such agility shows the councils’ capacity for innovation and cements their role as vital allies in India’s export ecosystem.
2. Core Functions: The Cumulative Roles of EPCs
Alongside their role in policy advocacy, EPCs provide many services designed to boost export performance and global competitiveness.
2.1 Market Opportunities Identification and Intelligence
EPCs conduct thorough studies of international markets, analyse trade statistics, and publish precise, actionable reports. These publications highlight shifting market trends, changing consumer preferences, and newly emerging segments of demand, helping exporters fine-tune their product ranges. Regular webinars and targeted buyer-seller meetings also supply up-to-the-minute details, directly connecting exporters with promising foreign partners.
2.2 Access to Government Schemes and Grants
Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are popular for helping businesses tap into government incentives. They walk exporters through key programs like the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP), the Interest Equalization Scheme for pre- and post-shipment loans, and the Raw Material Supply Scheme (RMSS). By breaking down the application process and clarifying eligibility, EPCs help exporters get the most savings, like lower yarn prices and cheaper export credit rates.
2.3 Simplified Export Documentation and Certification
First-time exporters often feel lost with paperwork. EPCs take away the confusion by issuing Registration-cum-Membership Certificates (RCMCs) and guiding businesses to the right quality certifications. Many EPCs even offer to cover 75% of the RCMC fee for new micro and small firms, lowering costs and helping them get ready for new markets.
2.4 Expanding Global Reach through Trade Events
For any country looking to build a strong brand, participating in international trade fairs and buyer-seller meet-ups is essential. Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) set up India zones at these global events, negotiate subsidized booth space, and coordinate reverse buyer missions. These carefully selected venues help exporters showcase their products, secure contracts, and gain wider market access.
2.5 Building Capacity and Enhancing Skills
EPCs recognize that expertise drives export success. They host workshops on quality control, packaging, compliance, and navigating market regulations. Some councils also launch incubation centers and mentorship schemes that provide product testing, personalized coaching, and detailed market feasibility studies.
2.6 Advocating for Policy and Government Support
As the official voice of exporters, EPCs gather and present sector-specific recommendations to the Ministries of Commerce, Finance, and MSME. Their lobbying efforts have streamlined customs, offered dedicated support to MSME exporters, and expanded export financing options, keeping policies aligned with the needs of the sector.
2.7 Strategic Planning and Export Data Analysis
EPCs use data analytics to watch monthly export numbers, check whether our goods are competitive, and predict future demand. With this information, they build strategic plans that encourage exporters to widen their reach to fast-growing markets, hone their product lines, and meet worldwide quality benchmarks.
2.8 Developing India’s Global Brand Image
Keeping product quality high is crucial for a strong international reputation. EPCs partner closely with the Bureau of Indian Standards and other agencies to align local regulations with global norms. By promoting quality and eco-responsible practices, EPCs help position India as a trusted source of superior goods.
3. Structure and Membership: Navigating the EPC Landscape
India’s EPC framework is supported by leading institutions and a network of complementary agencies.
3.1 Organizational Structure and Sectoral Specialization
At the top sits the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO), representing over 20,000 exporters and advocating for policy change across every sector. Under FIEO, 38 sector-specific councils focus on areas like apparel (AEPC), chemicals (CAPEXIL, CHEMEXCIL), and gems and jewellery (GJEPC). The Export Promotion Council for EOUs & SEZ Units (EPCES) zeroes in on Special Economic Zones, providing tailored support for 100% export-oriented units, no matter the industry.
3.2 Membership Models and Eligibility
Nearly all councils divide members into “Member Exporters”—companies with a proven history of exports—and “Registered Exporters”—which can include startups and first-time exporters. Fees differ among councils, often tied to company size and the volume of exports. For enterprises operating in SEZs or under the EOU scheme, EPCES membership is mandatory to unlock benefits tied to those zones.
3.3 The Importance of RCMC Registration
The RCMC, or Registration-cum-Membership Certificate, is the gateway to government incentives. This document, granted by the relevant EPC, confirms that the exporter qualifies for various support schemes. To encourage more small and medium enterprises to join, EPCs often subsidize the RCMC fee.
Find best business ideas for yourself using our startup selector tools
4. The Broader Export Promotion Ecosystem
EPCs mainly cover goods made in factories, but the export promotion system in India also includes Commodity Boards and Autonomous Bodies that specialize in agricultural and primary products.
4.1 Commodity Boards
Boards like the Coffee Board, Tea Board, Spices Board, and Rubber Board oversee both the export and the domestic production of their respective crops. They work to protect long-standing markets, train farmers in best practices, and issue quality certifications to maintain international standards.
4.2 Autonomous Bodies
Agencies like APEDA and MPEDA support niche industries by offering grants, promoting exports, and running focused marketing campaigns abroad.
Find Out Project Report on different business Ideas by Clicking Here
5. The Return on Investment: Specific Benefits for Exporters
Joining an Export Promotion Council (EPC) helps exporters:
- Financial Gains: Access MAI grants for trade fairs and secure RoDTEP refunds.
- Administrative Support: Receive priority clearances for customs and DGFT, plus assistance with ECGC claims and issues related to being flagged as a “risky exporter.”
- Networking Opportunities: Participate in buyer-seller meetings, reverse trade missions, and focused industry forums.
- Enhanced Credibility: Exhibit products in the official “India Pavilion” at global events and get assistance with quality certifications.
- Timely Information: Stay updated on DGFT notifications, GST changes, and international regulations.
6. The Proof in Numbers: EPCs Driving India’s Export Growth
EPCs have been instrumental in boosting India’s exports from $18.19 billion in 2001–02 to $447.46 billion in 2020–21. In the 2023–24 period, Special Economic Zones alone contributed over $157.3 billion, accounting for more than 20% of total exports. These figures underscore the success of targeted export promotion and the vital role EPCs play in uplifting the economy.
Exporters face an array of challenges that can stop their shipments in their tracks. From infrastructure bottlenecks and regulatory hurdles to currency risks and rising protectionism, the path to international markets is fraught with obstacles. Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) and similar bodies must step in with smart and timely solutions.
7. Overcoming Hurdles: Challenges and Solutions in Export Promotion
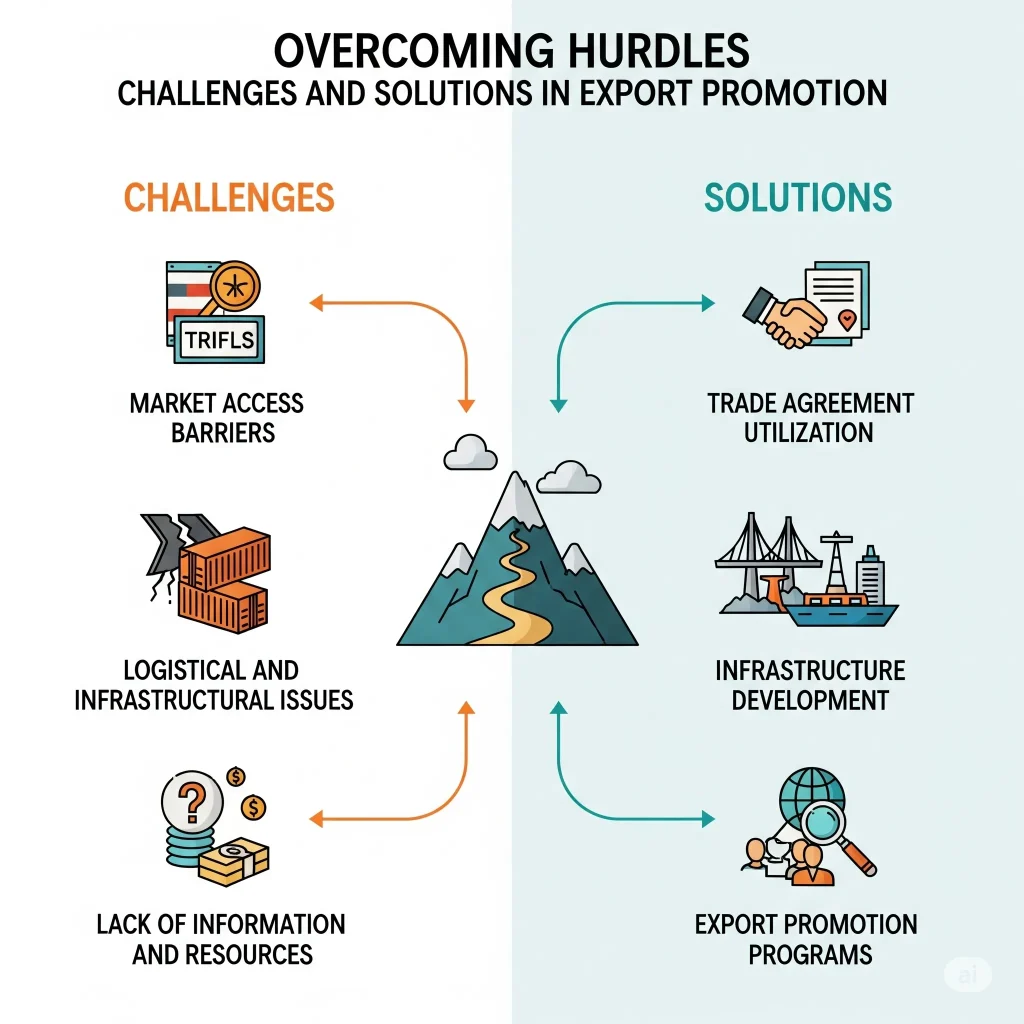
7.1 Bridging Infrastructure Gaps
Poor transport links and congested ports can delay shipments and add costs. A solution lies in partnerships between ECAs, multilateral banks, and regional development funds to finance critical infrastructure upgrades. Funding can be tied to measurable improvements, such as increased load-handling capacity, ensuring that investments translate to shorter wait times for exporters.
7.2 Cutting Through Regulatory Overload
Varying and often conflicting international rules for financing, licensing, and customs create a web of red tape. EPCs and ECAs can act as one-stop shops, providing exporters with clear guidance on critical paperwork. The use of template contracts that meet the requirements of multiple jurisdictions can significantly reduce repetitive administrative work.
7.3 Managing Currency Fluctuations
Export contracts often span long periods, making them vulnerable to currency volatility. ECAs can cushion companies by providing multi-currency borrowing options that align with revenue streams. They can also underwrite forward contracts that lock in exchange rates, enabling exporters to quote fixed prices without gambling on future market shifts.
7.4 Navigating Protectionist Policies
Sudden tariffs and quotas can shatter exporter confidence. To mitigate this, financing can be structured to align with local value-addition requirements in the importing country. For instance, offering lower guarantee fees for projects that involve local production can turn protectionist measures into incentives for exporters to establish a value-adding footprint abroad.
By addressing these challenges in a coordinated manner, the export ecosystem can ensure that trade flows smoothly and revenues remain steady. The councils and agencies that provide a clear toolkit of solutions will emerge as trusted anchors in every supply chain, successfully opening markets and closing funding gaps.
Find Best Business Ideas for Your State by Clicking Here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)?
EPCs are government-supported, non-profit organizations established to promote Indian exports. They act as a bridge between the government and exporters, offering services, policy advocacy, and strategic support for foreign trade.
2. How are EPCs registered in India?
They are registered under either the Companies Act or the Societies Registration Act, with official recognition from the Government of India.
3. What sectors do EPCs cover?
Each EPC specializes in a specific sector, such as engineering, textiles, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, chemicals, gems and jewellery, and more.
4. What is the role of FIEO?
The Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO) is the apex body representing over 20,000 exporters across all sectors and leads policy-level discussions on export promotion.
5. What is an RCMC, and why is it important?
The Registration-cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC) is issued by EPCs to certify an exporter’s eligibility for government incentives and schemes. It’s a prerequisite for availing many export-related benefits.







