Entrepreneurs and startups can make money by entering the manufacturing industry – if they choose the right market and product. In 2025, the Most Profitable Manufacturing Businesses opportunities will arise from the robust growth and demand of several industrial product categories. This article examines four promising manufacturing projects: Aluminium Beverage Cans (Alcohol), Agro-Waste pulp for paper/molded fibre, Saline Solution (0.9% sodium chloride), and Eggshell Powder.
These products are highly relevant to entrepreneurs because they tap into market trends, from sustainability and recycling needs to healthcare. We will dive into the market outlook of each product, its growth drivers, production processes, and startup potential, as well as data-driven insights to help you make informed decisions.
These sectors offer a high level of demand and easy entry for new manufacturers. You can read on to learn more about each opportunity and how Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS) can help you evaluate and launch these most profitable manufacturing businesses. Let’s begin with the booming aluminium beverage can market.
1. Aluminum Cans for Beverages
Aluminum beverage cans have become a staple in the drinks industry. They are used in everything from energy drinks and sodas to craft beer. Aluminium cans are a great opportunity for entrepreneurs who want to get into manufacturing. They’re in high demand and recyclable, with a steady market growth.
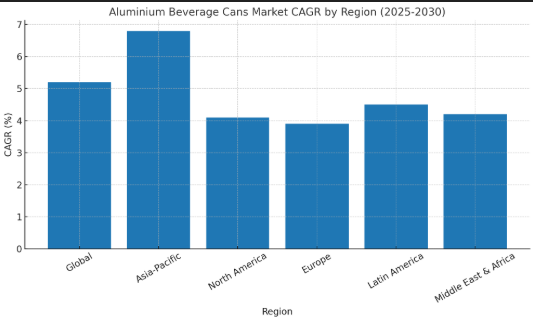
Chart of the global aluminum beverage cans market size from 2025 to 2030 (in USD billions). Demand for sustainable packaging is expected to drive the market growth.
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
Aluminum cans are a global market with a healthy growth rate. This is equivalent to a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR), of around 4%, over the next decade. This steady growth is driven by several factors:
- Eco-Friendly packaging trend: Aluminum is highly recyclable. Cans rank among the most recycled materials in the world. Aluminium cans are in high demand as consumers and governments move away from single-use packaging. Brands use aluminium cans to demonstrate their environmental commitment because aluminium can be recycled indefinitely without losing quality.
- Drinking More Beverages: The beverage market continues to grow in emerging markets. Cans are becoming more popular for soft drinks, beer, seltzer, iced drinks, health drinks and flavored coffees. They chill quickly and maintain flavor. Cans are also popular because of their portability and convenience. Single-serve (where people choose a smaller can over a larger bottle), adds to demand, especially for drinks in 200-450ml sizes.
- Aluminium cans are excellent for product preservation: Aluminium cans protect beverages against light and oxygen and preserve carbonation more effectively than plastic or glasses. They are ideal for carbonated beverages and keep drinks fresher for longer. This is a major selling point for both manufacturers and consumers.
- Recycling Economics: For manufacturers using recycled aluminum (also known as secondary aluminium), reduces costs and energy consumption compared to virgin metal. Recycling cans is a well-established system that ensures a constant supply of aluminium scrap, which supports the growth of can manufacturing economically and sustainably.
Market Forecast: This chart shows the trajectory of growth. This indicates a consistent expansion of demand. Asia-Pacific will see the most rapid growth thanks to rising incomes and urbanization. North America and Europe’s developed markets are mature, but they still experience incremental growth.
This is partly because consumers have switched from plastic to aluminum bottles. Can design innovation (lighter cans and better coatings) could also boost adoption, as it reduces material costs while improving functionality.
Related: Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up an Aluminium Recycling Plant
Aluminum Cans (Beverages – Key Market Statistics)
| Metric | You can also value |
| Global Market Size (by 2025) | $63.2 Billion |
| Market size projections (2035). | $94.5 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035). | Growth of 4.1% per annum |
| Key growth drivers | Cans are portable, have a high recycling rate and can be recycled. |
View our Handbooks on Steel, Iron, Ferrous, Non-Ferrous Metals with Casting and Forging, Aluminium, Ferroalloys Technology
Production Processes and Requirements
Aluminium can production is a complex industrial process. However, it can be automated and is widely understood. The cans are usually made from two pieces, the body and lid. This is an overview of the manufacturing process:
- Raw Material (Aluminium Sheets): The majority of can manufacturers begin with large coils. Most commonly, recycled aluminium is melted down and rolled out into thin sheets. It reduces raw material costs as well as energy consumption (recycling aluminum uses 95% less energy than making new aluminum).
- Body Forming: (Drawing & Wall Ironing): The sheet is punched into discs, which are then stretched to cup shapes. These are then thinned out and extended into cylindrical can bodies. Drawing and ironing is the name of this high-speed procedure. Modern lines can produce hundreds of cans in a minute.
- Trimming and cleaning: Automated equipment trims beverage cans to the correct height, cleans away residues and lubricants, and applies an inert, food-grade coating to prevent metal from affecting the drink’s taste.
- Cans have a 360-degree branding surface: High-quality machines print beverage cans and apply brand graphics. Manufacturers coat the inside with a food-grade epoxy or a newer BPA-free coating to protect the beverage from metal.
- Necking and Lid Sewing: The can top is narrowed to fit the diameter of the lid. The lid is attached by crimping after filling the can (usually by the beverage company). This creates an airtight seal.
Entrepreneurs would have to invest in special machinery, such as body makers, printers and curing ovens. Cans need to be uniform and able to withstand pressure from within (for carbonated beverages).
Although the initial investment is high, the process becomes highly automated and efficient when scaled up. New entrants often start out by providing cans for regional craft breweries or beverage bottlers that require a local supplier. They then scale up their production.
Startups: Opportunities and considerations
Aluminium can manufacturing is a great opportunity for startups to tap into an established market that has a stable demand. Consider these points:
- Cans will be in demand for a long time: New manufacturers may secure contracts with local beverage producers, such as breweries or soft drink makers. Cans are expensive to ship over long distances due to their size. Beverage companies prefer to work with local suppliers. This allows regional startups to compete against the big players, offering lower transport prices and more responsive service.
- Recycling and Sustainability Niche: If you position yourself as a green manufacturer, using a large percentage of recycled aluminum and energy-efficient processes, this can attract customers and possibly government incentives. This is a powerful marketing tool that could help beverage clients achieve their sustainability goals.
- Innovation Potential: There is room for innovation. For example, lightweight can designs that use less metal per can, new shapes and sizes for niche markets, or smart graphics such as thermochromic inks (that change color at cold temperatures, etc.). A small, nimble company could create a niche in the market by providing specialized cans.
- The entry barriers are high machine costs and a lack of technical expertise: The beverage industry must adhere to strict quality standards. Any defects could lead to product leaks or spoilage. It is therefore important to ensure technical expertise, either by hiring experienced engineers or partnering up with technology providers. A business plan will also include ensuring a constant supply of aluminium (and protecting against fluctuations in raw material prices).
Aluminium cans are a mature and growing industry. A new manufacturer with a good business plan, and a focus on sustainability and quality could find lucrative opportunities.
2. Pulp from Agricultural Wastes (Wheat Straws, Rice Straws & Cotton Stalks).
Innovative and environmentally friendly manufacturing, using agricultural residues such as wheat straw, cotton stalks, rice straw, and other straws to make pulp, is a great idea. This method provides raw material to make paper and fiber-based products, without having to rely on wood harvested from forests. Agro-waste production is a way for startups to solve two problems simultaneously: meet the increasing demand for packaging and paper, as well as reduce agricultural waste disposal. Examine the market and feasibility for this sector.
Chart of the global wheat straw (agro-waste) pulp market size from 2024 to 2030 (in USD billion). The demand for non-wood fibers is growing rapidly, mainly due to the move towards sustainable materials.
Market Outlook and Demand for Non-Wood Pulp
As environmental concerns and shortages of materials prompt the paper industry, they are looking for alternatives to wood. Here are some key market insights focusing on the plentiful farm byproducts of wheat straw, cotton stalks, and rice straw.
- The global market for wheat straw was estimated to be worth $0.8 billion in 2024. By 2033, it is estimated that this market will double to $1.7 billion. This represents a CAGR of 8+. This high growth is outpacing many of the traditional wood-pulp markets, which indicates that non-wood fibres are gaining in popularity. The graph above shows an upward trend that will continue to increase as we move closer to 2030 and beyond.
- Sustainability and Regulations The sustainability movement is a major driver. Consumers of pulp and paper (publishers and packaging companies as well as end users) are becoming more aware of the deforestation problem and its effects. Non-wood fibers like straw are a renewable and replenishable source of fiber. The government is also encouraging it: some regions have implemented restrictions on burning crop remnants (a major source of pollution) and instead support its use in industry applications.
- Agro-waste can be used to make various grades of paper and molded products. Packaging is a growing market. Paper packaging, especially biodegradable alternatives, is in high demand due to the growth of e-commerce. When wood pulp prices or supplies are low, non-wood pulp can fill this gap.
- The use of agricultural fibers as pulp has been pioneered in countries with large agricultural sectors and limited forests, such as India, China, Africa, and parts of the Middle East. In India, mills produce paper using bagasse (sugarcane residue) and wheat straw. China has historically used significant amounts of non-wood paper (from bamboo, rice straw, etc.).
Even though these regions remain key markets, interest is growing in greener packaging made from wheat straw in North America and Europe. - Non-wood fibers account for only a small portion of the global pulp supply (5-10%). This share is increasing slowly. Growth in the non-wood segment is outpacing that of wood pulp. There is plenty of room to innovate and enter the market, as it’s a niche that is becoming mainstream.
Key Market Stats – Agro-Waste Pulp
| Metric | You can also value |
| Global Non-Wood Pulp Market (2025 est.) | $0.85 Billion |
| Market Projections (Early 2030s). | $1.6 to 1.7 billion (by 2033) |
| CAGR (2024-2033). | ~8% (high growth) |
| The % of global pulp from non-Wood | 5% (and increasing gradually) |
| Main Uses | Packaging (molded fibre trays, containers), paper (printing and writing) |
| Key Drivers | High demand for sustainable packaging, eco-friendly materials, waste utilization and anti-burning regulations |
Production Process using Wheat/Rice Stalks & Cotton Stalks
It is possible to make pulp using agricultural wastes. The principle of the process is the same as wood pulping. However, there are some modifications for different raw materials. Startups interested in this process should be aware of the following steps:
- After harvest, farmers typically collect raw materials such as wheat straw, cotton stalks, and rice straw. Farmers often give or sell these materials at little or no cost to prevent burning. Collectors must gather straw immediately after harvest and store it properly because its availability depends on the season. Raw straw is low in bulk density so it’s important to have efficient logistics for transport and baling.
- Pre-processing: Workers clean the stalks and straws to remove dust or sand, chop them into smaller pieces, and pre-soak or moisten them to make cooking easier. In some cases, processors use alkali treatment to break down the waxes and silica in straw.
- Pulping (Chemical/Mechanical): The majority of agrofiber pulping is done using a chemical process (similar to the kraft pulping or soda pulping used for wood). Due to the straw’s soft structure, cooking times are generally shorter for straw than they are for wood chips. The process washes the mixture and separates the pulp fibers from the black liquor, which contains spent chemicals and dissolved organics. Some may also use mechanical pulping, which involves grinding the straws in water, for fiberboard and certain packaging materials. Chemical pulping, however, produces stronger fibers that are suitable for paper.
- Bleaching: If the final product is white, the straw pulp can be bleached with chlorine-free sequences, such as oxygen, peroxide, or ozone, to increase brightness. For many packaging applications (corrugation and cartons, molded pulp dishes, etc.), unbleached straw pulp is acceptable.Packaging manufacturers prefer unbleached pulp for corrugation and cartons because it delivers high yield and retains a natural appearance.
- The pulp that is produced can be used for different purposes: It could be sheeted, dried and made into pulp bales for sale to mills. If integrated, the pulp can be fed directly into a paper machine for the production of paper reels. Manufacturers use wet pulp to mold and dry biodegradable cups, plates, and egg cartons into their final shape.
- Byproduct management is a crucial part of the process: This includes handling spent chemicals and wastewater. The ideal large agropulp mill will have a chemical recycling system, which is common in wood pulp mills. This allows them to recycle and treat cooking chemicals as well as extract energy from waste biomass. Smaller operations use spent pulp liquor as bio-fertilizer, while larger facilities treat and dispose of it according to environmental regulations.
Some entrepreneurs choose to start a small-scale agro-pulp plant, which collects local agricultural waste directly and converts it into products like egg trays and food containers. It is possible to do this with modest capital and relatively simple machinery.
A full-fledged paper mill is more complex and capital-intensive, but government assistance or partnerships with technology providers could help mitigate the cost. The location is important: having access to power and water, as well as being close to the straw source, are key factors.
Entrepreneurship Opportunity and Benefits
Why should a startup look at agro-waste paper? The following are some of the most important advantages and things to remember:
- Eco-Friendly Proposition: Turning waste into a resource is what you’re doing. This circular economy can not only attract customers (who will be able to label their paper as eco-friendly), but also grant and subsidies in many areas. This is a business that makes you feel good and aligns with sustainability goals around the world (reducing pollution and deforestation).
- Millions of tons of straw from wheat and rice: are produced each year in agricultural countries. In parts of Asia, post-harvest burning of straw can cause severe air pollution issues. A pulp project could consume this straw, giving farmers an incentive to sell it rather than burn it.
The supply is abundant and cheap. A good supply chain will be key to success (perhaps by working with farmer cooperatives). - Growing End Markets: The end product can be varied – such as writing paper, tissue or containerboard, disposable dishes, etc. Compostable food packaging is an interesting option. Many food brands and restaurants are looking for biodegradable packaging as an alternative to foam plastic.
Straw-based fibre is perfect for this, and is often marketed to consumers as “natural” packaging. The demand for these products is increasing as the bans on single use plastics spread around the world. - Scalability and technology: Modern technologies improve the efficiency of pulping non-wood, addressing issues in the past (such as higher silica levels in straw which can damage equipment). In some places, small-scale digesters or even mobile pulping machines are being tested. Entrepreneurs could begin with a small facility and then expand it in modules.
Research into enzymes and the bio-pulping process could make the process more cost-effective and eco-friendly in the future. This would allow for the adoption of new technology as it becomes available. - Challenges: It is important to recognize challenges. Non-wood pulps can be different – for example, the straw fibers may be shorter than the wood fibers and affect paper strength. Paper made from straw alone is often weaker. It’s common to mix it with wood pulp or use it in products that don’t require a lot of strength. Entrepreneurs also have to deal with residue management, such as disposing of silica and dealing with higher ash contents.
It will be necessary to design the business in a way that can handle them (for example, by using ash as a soil conditioner). The business may be seasonal, but it must still be able to supply the product all year round.
Summary: Manufacturing pulp from agricultural wastes such as wheat straw, rice husk, and other similar materials is an opportunity for high growth at the intersection between industry and sustainability. Startups that are able to master the supply chain, processing, and distribution can make money while also making a positive impact on the environment. This is a win-win situation.
3. Saline Solution Manufacturing (0.9% Sodium Chloride IV Fluids)
The most important product in healthcare is normal saline, a 0.9% sodium-chloride solution in sterile water. Clinicians widely use this solution for intravenous (IV) therapy to hydrate patients and help maintain fluid balance. Medical teams also use it as a medication carrier and for other clinical purposes. Global health issues and the COVID-19 epidemic have highlighted the need for a stable supply of saline. Setting up a saline production plant is a lucrative venture for entrepreneurs in the pharmaceutical and medical supplies sectors, given the high demand.
Chart: Global Market for Normal Saline IV Solution (0.9 NaCl), 2025-2032. The demand for saline has been steadily increasing due to the growth of healthcare services around the world.
Market Demand and Growth in Healthcare
Market demand and growth in healthcare
The market for IV saline solutions is large and steadily growing. This growth trajectory is consistent with a CAGR of 6 to 7 percent. What are the factors that drive this constant growth?
- The Incidence Of Chronic And Acute Conditions: There has been an increase in the incidence of chronic conditions (such as kidney diseases that require IV fluids or chemotherapy treatments that require hydration), and acute conditions (dengue, seasonal flu complications etc.). This necessitates IV fluids. The medical necessity of saline keeps the demand constant and grows with population needs.
- Global expansion of healthcare infrastructure: Developing countries build more clinics and hospitals, while developed countries have aging populations that require more medical attention. Saline IV drips play a vital role in nearly every setting, from IV hydration to electrolyte balance and emergency treatments. Every hospital bed uses multiple units of sodium chloride per day to treat various conditions. The demand for saline increases as the number of beds and patients increases.
- Pandemic and Emergency Preparedness: Recent events have highlighted the importance of having a robust supply of medical consumables. Pandemics led to a surge in hospitalizations, where saline is crucial. They also exposed vulnerabilities within the supply chain (some regions experienced saline shortages due to global supply disruptions).
To reduce reliance on imported medical supplies, governments and health providers have a strong desire to stockpile essential medical supplies. It has created opportunities for new saline production units. - Global Distribution: Demand is global: North America and Europe are large markets, with the U.S. alone using a large portion of the IV fluids used in the world. However, the Asia-Pacific has the fastest-growing market in terms of volume. This is due to the large population in Asia-Pacific and the improved healthcare in countries such as China, India and Southeast Asia.
Even rural or remote areas within a country can benefit from local production, which can supply hospitals nearby without long transit times.
Key Market Statistics – IV Solution
| Metric | You can also value |
| Global Market Size (by 2025) | $3.9 Billion |
| Size of the market projected to 2032 | $6.3 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2032). | ~7.0% (steady growth) |
| Major Demand Drivers | Ageing population, more hospitals/clinics and higher surgery rates are all factors that will increase the need for emergency stockpiling. |
| Primary Use | Intravenous Fluid Therapy (dehydration and electrolyte balance), Medical Irrigation |
| Top Consumers in Each Region | North America, Europe (large use per capita); Asia-Pacific (fastest growth in volume) |
Saline Solution (Sterile NaCl 0.9% Solution) Manufacturing Process
Manufacturers produce saline solution using sterile pharmaceutical processes. Because clinicians inject or infuse it into the body, producers must meet strict quality and sterility standards. Here is what the process involves:
- Water Purification: By volume, water is the main ingredient. Water from the tap or source is not pure. Manufacturers use a water treatment system to produce deionized or distilled, pyrogen-free water, commonly called Water for Injection (WFI). It involves reverse osmosis (deionization), filtration and multiple distillation and ultrafiltration steps.
- Formulation: Manufacturers dissolve nine grams of pharmaceutical-grade sodium chloride in one liter of purified water to produce a 0.9% w/v (normal saline) solution for medical use. Salt must meet the pharmacopeia standard purity. The mixing tanks should ensure correct concentration and complete dissolution.
Too low or high salinity is dangerous to patients. Manufacturers often prepare solutions slightly hyper-concentrated and then dilute them to the precise final volume to ensure accuracy. - Filtration: Production filters the saline solution through sterilizing-grade 0.22-micron filters to remove bacteria and particulates, and teams perform this filtration in an aseptic environment immediately before filling the containers.
- Filling and packaging: Filtered, sterile salt water is poured into the containers for its final use. Packaging includes glass bottles, plastic bottles and IV bags. Filling takes place in a cleanroom, on an automated line. Each bottle or bag will be filled, then sealed. (Bags are heat-sealed and bottles receive sterile caps.
- Terminal sterilization may be required if the product is not fully aseptic: Manufacturers seal bottles and autoclave them to eliminate any microbial contamination. Many modern saline plants use aseptic filling to avoid exposing the product to high heat.
- Samples are tested to determine sterility: salt concentration, pH level, clarity, and endotoxins. Each batch must pass strict quality tests under pharmacopeial guidelines (USP, BP, etc.). Before release. The manufacturing process must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices, which are enforced by the health regulators.
- Labeling and batch release: Production teams label IV bottles or bags with lot numbers and expiration dates, package them in cartons for distribution, and ensure unopened saline retains a two-year shelf life.
A saline manufacturing facility will need specialized equipment, including large stainless steel mixing tank, a filtration unit, aseptic filling lines (often form, fill, seal machines for plastic bags, or vial filling machine for bottles), sterilization systems, and a laboratory for quality testing.
To operate, one must have a license from the drug regulatory authority (e.g. FDA approval in the US or equivalent in other nations) and adhere to all regulations.
Related: How to Start Manufacturing Business of Normal Saline
Why This Is A Good Business Opportunity
Saline may seem like a commodity with a low price per unit. Manufacturers produce saline in large quantities and sell it at high volumes, making it a lucrative business. Here are some reasons why entrepreneurs should think about it, and what they need to do:
- Saline is the lifeblood for hospitals: Saline is a fundamental part of medicine, unlike some products, which may become obsolete. Hospitals cannot reduce saline orders, even if they are not profitable. It is too important. The business is therefore recession-proof. A new manufacturer who can ensure supply will find an eager market, particularly if the region they enter currently imports salt or has very few local suppliers.
- Potential for local market entry: Since saline (which is mostly water) is heavy and bulky, it’s easier to produce locally. This reduces transport costs and provides a fresher supply. Many developing countries still depend on expensive IV fluids that have long lead times.
A startup that establishes a facility in such a place can gain market share and even receive government incentives or contracts (since self-sufficiency is a goal of many governments). - Volume and Scalability: A saline production line can produce thousands of bottles/bags an hour once it is running. Scaling up usually means adding additional filling lines or shifting the shifts. Startups may start with a small capacity for hospitals or veterinary uses, and then increase output or variety.
- Product diversification: Once you have a facility to produce saline, you can expand into other intravenous liquids, such as sterile injection water or irrigation solutions (different formulations depending on the medical need). You can expand your product range and revenue streams.
- Meeting pharmaceutical manufacturing standards is a major challenge: To set up GMP-compliant operations, entrepreneurs may need to hire an experienced pharma production manager or consultants. Initial regulatory approval can take a long time (plant inspections, product tests, validation of sterilization, etc.).
Once a quality system is in place, compliance with the regulations becomes second nature. A high-quality product is a marketing advantage. Hospitals and distributors are more likely to choose suppliers with a proven track record of quality, as patient safety is at stake. - Market Competition: Startups should research the saline producers in their target markets. A few large pharmaceutical companies dominate IV fluid production in many countries. Even so, there are periodic shortages, which can be an opportunity for new competitors or niches (such as specializing in small-volume saline bags for dialysis centres, etc.).
Due to government contracts or bulk purchases, pricing is fairly standardized. It can be difficult to compete on price. Instead, focus on reliability of supply, local presence and service.
Summary: Saline manufacturing is both a commercially and socially sound business. A well-run venture in saline manufacturing can generate stable returns, thanks to the continued growth of the healthcare industry. This requires diligence and compliance but offers the reward that you can enter a market with a guaranteed demand and a meaningful product.
4. Eggshell Powder is a calcium-rich powder from egg shells.
Food and nutraceutical companies turn discarded eggshells into valuable powder, aligning the process with zero-waste and sustainability trends. The main ingredient in eggshell powder is calcium carbonate (about 95% CaCO3), along with a small amount of protein from shell membrane. Manufacturers use this powder as a calcium supplement and as an ingredient in various products.
A business that sells eggshell powder is a low-cost venture for startups. It taps both into the health and wellness market as well as the sustainability movement by recycling waste. Explore the potential of this business.
Chart: Global Eggshell Powder market size (for nutraceutical uses and other related uses) between 2024 and 2034 (USD millions). Although a niche market, the growth rate is rapid as demand for calcium supplements increases.
Applications and Market Growth
The eggshell powder market is on the rise, as consumers are increasingly looking for eco-friendly and natural sources of nutrition. Here are some key facts about demand and application:
- Nutraceuticals and Supplements: Eggshell powder can be used as a calcium supplement. Producers finely grind and sterilize eggshells to make a calcium-rich powder that supports bone health. Many health-conscious consumers prefer this natural, food-based nutrient source over synthetic supplements. You can add eggshell powder to food (like smoothies or baked goods) or encapsulate it as a calcium booster.
Eggshell supplements can be beneficial for joint and skin health due to the presence of trace minerals and the inner membrane (which is rich in collagen and other beneficial ingredients). Nutraceutical products incorporating eggshell membrane powder to support joint health and eggshell calcium to promote bone health are on the rise. - Eggshell Powder for Food and Beverage Fortification: In addition to pills and capsules, eggshell powder is also used as a calcium supplement in foods such as orange juice, cereal, bread or pet food. When processed correctly, it is tasteless and increases the nutritional value of products. Pet nutrition is an important segment. Companies that produce pet food or pet supplements often use eggshell membrane or calcium in their formulations to promote joint and bone health for pets (especially older dogs and high-performance animals).
- Eggshell powder: It is particularly like its membrane component, is used in cosmetics. Consumers use finely ground eggshell powder as an exfoliant in DIY beauty treatments. Skincare brands add collagen- and mineral-rich eggshell membrane extracts to creams and anti-aging products. This is a niche application, but it increases the demand for high-quality eggshell powders.
- Eggshell powder can be used as a soil conditioner or organic fertilizer in agriculture: Farmers use eggshell powder to improve the mineral balance of compost and to add calcium to soils, which reduces soil acidity.
Ironically, hens are fed their eggshells (after processing), which provides calcium for them to make new eggshells. This creates a loop that is sustainable. Researchers use eggshell powder in emerging fields such as bioceramics for bone graft materials and in biodegradable polymers. - The eggshell powder industry is small in comparison to other industries: Its size is measured in tens and millions of dollars. It is still growing rapidly. By 2034, the global market for membranes and eggshell powder could reach $160+ million. This represents a CAGR of close to 10%. The chart shows that the growth is on the rise. While the base may be small, it’s the trend of natural health supplements that drives the growth. According to projections, we see “a major enlargement” in the market by mid-2030s. Consumers drive market growth by demanding organic and natural supplements, while sustainability initiatives push industries to reuse waste.
- Eggshell powder is a niche product with low competition: This allows for smaller and medium-sized companies to thrive. Most operations are small or artisanal, so there is room for new players to enter the market and gain market share.
Eggshell Powder: Market and Use Highlights
| Aspect | Details |
| Main Component | Calcium Carbonate (95% eggshell weight) |
| Global Market Size (Mid-2020s). | $70 Million (small but growing). |
| Projected market (2030s). | Cosmetics (eggshell) and fertilizer/soil amendment. |
| CAGR | ~9-10% (high growth rate) |
| Key Applications | Cosmetics (eggshell) and fertilizer/soil amendement. |
| Raw Material Source | Eggshells from the food industry (bakeries and restaurants, factories that process eggs, etc.) |
| Sustainability Benefit | Reduce landfill waste by upcycling food waste (eggshells). |
Production Process (From Eggshell Waste to Powder)
The simplicity of production is a major attraction for the eggshell powder industry. The production process is simple and does not require complex chemical processes or heavy industrial machinery. This means that startup capital requirements are lower. The steps in the process include:
- Collecting Eggshells: Your first step should be to source raw materials. The best sources of eggshells are large bakeries and restaurants, as well as poultry farms and hatcheries. These sources produce large amounts of eggshell waste every day. It is important to build a partnership with other companies that can collect the shells, often at minimal costs because it’s a waste. To make the shells easier to process, they should be as clean (with excess egg liquid removed).
- Cleaning and Sanitizing: Even after pre-rinsing, the shells may still contain some membrane residues and bacteria (such as Salmonella). It is important to wash and sterilize them thoroughly. You can do this by either washing the shells in hot water with a food-safe detergent or steaming/boiling them. Some processors use mild bleach solutions or acid washes to kill bacteria.
- Shells can be dried by using dryers, or in small settings, extended oven drying/sun-drying. For very small operations, sun drying may be an option, but for consistency and volume, a dehydrator or industrial-sized dryer is best. Shells must be completely dry to avoid clumping or microbial growth.
- Milling/Grinding: Processors grind dried eggshells into a fine powder using milling or crushing machines. Small businesses often start with a hammermill or grinder to achieve a uniform particle size that blends easily into food or capsules. Some processes separate the thin membrane from the shell and grind it to include it separately, or ensure that the product is very fine.
However, the inclusion of the membrane (which adds extra nutrients such as collagen) is often a point of selling. The powder can be sifted after grinding to remove larger grit, and then reground. - Packaging: The final eggshell powder is packaged into suitable containers. Manufacturers package eggshell powder in pouches or jars for retail dietary supplements and label them with nutrition information. For B2B sales, they use bulk bags or drums to supply food companies and feed producers. Packaging is mainly about keeping moisture away, using airtight packaging, and desiccant packs, if necessary.
- It is important to ensure that the powder is pathogen-free (by heat treating it) since it is often consumed by animals or humans. Testing batches for microbiological security is a good idea. Verifying the calcium content can also be a selling feature. This should be between 35-40% as elemental Calcium of the powder.
The equipment and processes are low-tech, which is one of the most attractive aspects of the business. It is easier to get started with this business because the equipment and process are low-tech. Even a small home-based business can grind, dry, and wash shells for a local market. You can invest in larger drying ovens and industrial grinders as your business grows. If you want to produce finished supplements, you may also need blending or capsule equipment.
For more information, check out these related videos from our YouTube Channel
Startup Notes and Advantages: Eggshell Powder Manufacturing
For new entrepreneurs, the business of manufacturing eggshell powder offers the following unique advantages:
The Cost of Production is Low
This business is very cost-efficient, and eggshells come at no cost since companies that produce them discard them as waste. Hence, the cost of acquiring eggshells is zero. You are solving a waste problem. Thus, there is a very high margin of profitability. As a bonus, some large egg processors produce massive amounts of shells every day, enabling them to haul away waste.
Pollution and Environmental Sustainability
In this day and age, every consumer craves sustainable goods. Brands promote supplements made from eggshells that would otherwise go to waste, and this sustainability message gives them a strong marketing advantage. It is a remarkable illustration of upcycling. It can become a strong part of the marketing story. This can enhance and attract eco-friendly consumers.
Different Market Segments
The versatility of the market allows you to sell eggshell powder in different segments. You may license to sell your health supplement as a packaged product brand or sell it as a B2B supply to nutraceutical brands that use it as a raw ingredient in their calcium tablets or protein shakes. Sell it to pet food manufacturers, to farmers, or to gardening stores as an additive for fertilizers.
It also enables you to begin from a strength. For example, a background in nutrition may steer you to focus on human supplements, while demand from poultry farms may lead you toward feed additive sales first.
Value Addition and Scalability
Initially selling simply powdered eggshell, one can add different forms of value over time. Some companies use eggshell powder to react with citric acid to create calcium citrate, making it a more absorbable supplement. This room for R&D allows expanding the product line. At the very least, the core powder is always in demand.
Regulatory Considerations
In most scenarios, eggshell powder may be classified as a food or a dietary supplement. Manufacturers must ensure food safety compliance by producing eggshell powder in FDA-registered, GMP-compliant facilities. If they make osteoporotic health claims, they must also follow strict marketing compliance rules. For the majority of food products, a calcium powder is classified as a basic food item. There will be little to no regulatory burden. Simply maintain standards on sanitation and label claims.
Market Education
For direct-to-retail consumers, one of the more challenging aspects may be the lack of awareness regarding the uses of eggshell calcium. But that is becoming easier as more and more people are writing wellness blogs that focus on natural sources of calcium. It is common to see people post recipes to make eggshell calcium on social media. This is a great marketing tool.
In conclusion, eggshell powder is an emerging eco-friendly product. This is a great business opportunity, where an entrepreneur can make a profit while also contributing to health and wellness, waste reduction, and natural health.
Getting Started: Business Prospects and Assistance
Manufacturing opportunities such as producing beverage cans and saline solutions or agro-fiber pulp and eggshell powder require a business plan and feasibility assessment. Here, professionals can be of assistance. One of the agencies, NPCS, helps new business owners capitalize on available opportunities. For numerous industries, NPCS prepares the Market Survey cum Detailed Techno-Economic Feasibility Report, incorporating the business overview and competition, the systematic manufacturing process, raw material procurement, optimal plant layout, machinery, and detailed financial forecasting, including capital and operating costs, revenue, and breakeven analysis.
With these reports, entrepreneurs can evaluate the prospects of establishing new industrial undertakings. NPCS assists entrepreneurs in determining the viability of their projects and in making informed strategic business decisions.
Using expert insights and data, you can reduce risks and optimize your manufacturing project for success. Whatever opportunity you decide to chase, market insights, technical readiness, and business strategy formulation will be critical. From 2025 onwards, these four sectors will be particularly promising: aluminum cans, agro-waste pulp, saline solution, and eggshell powder. Your startup could lead the way in these emerging industries with the right strategy.
Find the Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Do aluminum manufacturing businesses remain lucrative working under competition from big players?
A: With the right approach, even new entrants into the aluminum can production business stand to gain profits. Beverage companies drive strong and growing demand for cans. While national players dominate the market, regional manufacturers can gain an edge because beverage companies prefer local suppliers for faster lead times and lower shipping costs.
Success in these regions is possible by balancing operational efficiency to control costs while maintaining strict quality standards. Startups can gain a competitive edge by focusing on sustainability, serving niche customers, or specialty beverage makers.
Q2: What is the advantage of using wheat straw instead of wood for making pulp?
A: Paper manufacturers use agro-waste for pulp to protect the environment, since they repurpose straw and stalks that would otherwise be burned or left to rot instead of cutting down trees. This offers a pollution reduction and conserves greenhouse emissions. Economically, the agro-waste contributes to a lower production cost for farmers and straw collection. It also widens the fiber supply for the paper industry which enhances their ability to withstand shortages or price drops.
Economically, the agro-waste encourages a drop in production for farmers and straw collection. There are also benefits for the silk removal of straw pulp, which enhances the agro-pulp and brings it closer in quality to waraased wood.
Q3: What key factors should one consider when setting up a saline (IV fluid) manufacturing plant?
A: The key factors are:
- Approval and Regulatory Compliance – You need to meet GMP compliance and get licenses for production. Time and costs should be factored for approvals.
- Compliance – Requires clean distilled water and a cleanroom for sterile processing. Working sterilizers and automated filling lines are also important for maintaining product quality. IV fluids also require clean power and water for reliable production to ensure quality.
- Advanced Planning – Using advanced water purification, sterilization, and automated filling lines will require extensive initial investments but will allow for smooth financing. Clean quality control labs are also important for testing saline composition and sterilization for batches. Professional pharmacists and quality assurance managers are also critical to product outcomes and should be hired.
- Healthy market access with government programs and controlled pricing will also allow for increased production efficiency. You must also ensure scalability for rapidly expanding demand, as range and capacity might need to be quickly increased with additional IV solution products.







