Consider your day to date. Have you opened a cardboard or plastic box, used a paper towel, read a book? You’ve probably used paper products multiple times. Paper is all around us, but we rarely consider where it came from. Behind every sheet, every tissue and every shipping container is the pulp and paper industry, a global enterprise that transforms natural raw materials into everyday essential products.
This industry is an intriguing blend of heavy engineering, nature, and chemistry. This is a tale that starts in a forest, and ends in a tangible product. This guide will take you on a journey through the worlds of pulp and papers.
What is Pulp, the heart of paper?

Pulp is necessary to make paper. The raw material for making paper is pulp. It is a thick, moist substance that looks like oatmeal. Pulp is a mixture of small plant fibers called fibers and water. Cellulose, the structural component in plant cell walls that gives paper its strength, is a strong and durable material.
This pulp comes from different trees that produce different types of paper.
- Softwood trees: Fir, pine, and spruce are softwoods with long cellulose fibres. Paper bags and cardboard boxes’ inner layers are made stronger by this.
- Hardwood trees: Birch, oak, and maple have shorter fibers. This produces a paper that is smoother and more opaque, which is great for writing and printing.
Although wood is the main source of pulp, it can be made using other materials as well:
- Recycled paper: Used papers are a major source for pulp and help to save trees.
- Other plants: In certain parts of the world pulp is made out of bamboo, sugarcane waste, straw or cotton.
Read More About Wood Pulp Manufacturing Business
The papermaking journey: From tree to sheet
This multi-step, complex process is what makes a sheet of perfect paper.
Harvesting and preparation
The forest is the first step. Workers cut down trees from managed forests and plant new ones to replace them. They load the logs into a big machine that spins and strips off the bark. They don’t use the bark for paper, but they burn it for energy. The logs are fed into a Chipper which is a giant machine that has spinning blades to chop the logs up into coin-sized wood chip.
Making the Pulp
The wood chips are then turned into pulp. This can be done in two ways:
- Mechanical Pulping Wood chips are ground with giant grinders. This is like making a wood smoothie. The method is effective and uses 95% of the trees, but it damages the cellulose fibers, which can result in paper that becomes weaker over time.
- The Kraft Process: It is the most popular method. They load wood chips into a pressurized vessel called a digester, then heat them up with a chemical mix. This process breaks down the wood and turns it into pulp.
This process dissolves lignin, a natural “glue”, that holds wood fibers together. It does not damage the strong cellulose fibers. You get strong, high-quality pulp—the stuff behind almost every sheet of paper you handle these days.
Read Our Project Report Here
Washing and Bleaching
The digester spits out brown pulp. Workers clean the pulp to get rid of chemicals, then bleach it so it turns white. In the past, they used chlorine gas for bleaching, which really hurt the environment. Modern mills now use safer processes, like the elemental chlorine free (ECF), or the totally chlorine free (TCF), processes.
The Giant Paper Machine
Paper machines are among the largest industrial machinery pieces in the world. They can be hundreds of feet long.
- In the Wet End, workers mix pulp with water—about 99.5% water to just 0.5% fiber. They spray this mixture onto a massive, fast-moving mesh screen. The fibers stick together as the water drains away.
- In the Press section, they lift a delicate mat of mostly water off the screen. Then, they run it through huge rollers that squeeze out most of the remaining water.
- In the Drying Section, the sheet travels through a long line of heated rollers. These rollers dry the paper completely.
- For finishing, workers can run the paper through a calendaring process to give it a glossy look. They wind the finished paper onto giant parent rolls, sometimes weighing several tons, before cutting it into smaller sheets or rolls for shipping.
Handbook on Pulp and Paper Processing: Read here
Paper is not just for writing: There are many uses of paper
Pulp and paper is a diverse industry that produces a wide range of products for various uses.
- Writing and Printing Paper: This paper is smooth and white, used in books, notebooks and printers.
- Boxboard: A stiffer and thicker paper that is used to make cereal boxes, book covers, and shoe boxes.
- Corrugated Board This what we call cardboard. The cardboard is made up of three layers: two flat outer layers, and an inner wavy layer (or “fluted”). It is extremely strong and lightweight thanks to this design.
- Toilet Paper, facial tissue, and paper towels are all included in. The paper is designed to be absorbent and soft. It also breaks down quickly in water.
- Specialty papers: This includes all other types of papers, including glossy photo paper and oil-resistant parchment for baking.
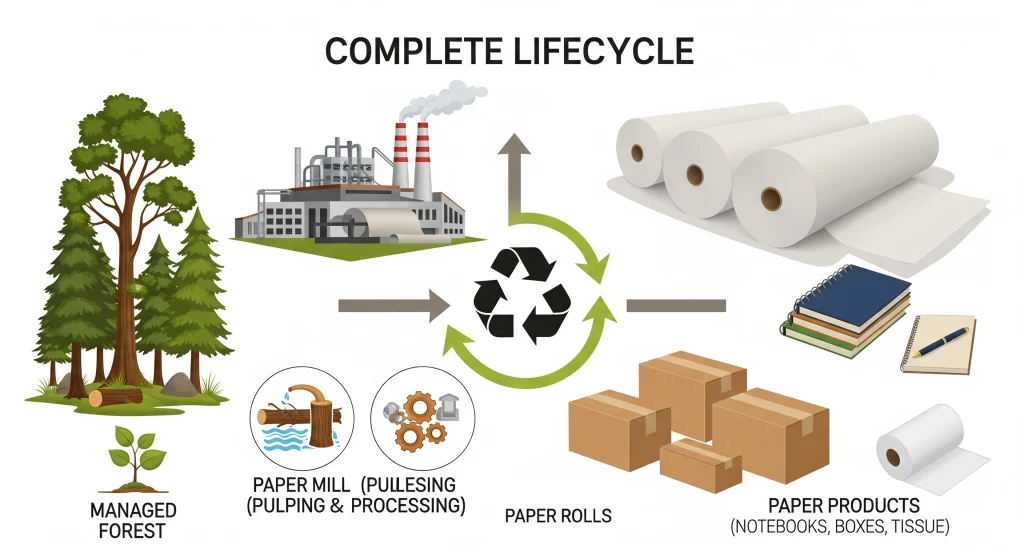
Paper and the Planet – A Focus on Sustainability
Paper industry leaves a large environmental footprint. It uses a lot of wood, energy, and water. But over the last few decades the industry has made huge strides towards becoming more sustainable.
Read More: Start an A4 Copier Paper Business in India with High Demand & Low Risk
- Sustainable forestry: The paper industry is a major owner of forestland, and has a stake in their health. People plant a few more trees every time they cut one down—at least, that’s the plan. Check for labels like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or PEFC when you buy paper. Those show the wood came from responsibly managed forests.
- Recycling: People recycle paper more than any other material on the planet. Paper recycling reduces the amount of trees needed, reduces energy consumption, and decreases landfill waste.
- Water and Energy Conservation: Modern Paper Mills are extremely efficient. In a closed-loop system, many paper mills clean and reuse the process water. Cogeneration is another way they generate electricity. Sometimes, this is done by burning wood waste such as bark.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Paper: Its Enduring Importance
Paper might be considered obsolete in a digital world. The pulp and paper industry has never been more important. The demand for newspapers may have decreased, but the growth of ecommerce has led to a huge need for packaging and cardboard boxes. Everyone uses tissue products for hygiene. You’ll also spot specialty papers in tons of industrial and consumer stuff.
The journey of a tree from the forest to your desk is an example of human ingenuity. Modern pulp and paper is a high tech industry that constantly innovates to create better products and reduce its environmental impact.
The Pulp and Paper Industry: FAQs
Q1 What is the difference between paper and pulp?
A1: You start with pulp, which is just wet, mashed-up wood fibers. Then, big machines process and dry those fibers. After all that, you get a flat, dry sheet of paper.
Q2 – Is paper making bad for forests?
A2: Yes, it can be if managed improperly. The modern paper industry relies heavily on sustainable forest management. This involves replanting trees that have been harvested. Recycled paper reduces the need for new trees.
Q3 How many times can a paper fiber be recycled?
A3: About five to seven times. The cellulose fibers become weaker and shorter each time they are recycled. In order to keep the recycling cycle going, we always add new (virgin fibers) from trees.
Q4 What does the term “acid free” paper mean?
A4: Acid-free paper uses alkaline pulp, so it has a neutral or slightly basic pH. It doesn’t yellow or fall apart as time goes by. People use it to keep important documents, photos, and books in good shape for years.
Q5 What is the most durable type of paper available?
A5: In general, the paper produced from softwood trees, such as pine, using the Kraft chemical process is the most durable because it contains long undamaged fibers.
Q6 : Does the paper industry suffer because of computers?
A6: No! The demand for some types of papers (such as newsprint) is increasing, while the use of others has declined. Online shopping boom has led to a massive demand for cardboard boxes and packaging. Demand for tissues and other hygiene items continues to increase worldwide.






