Chemical polymer form the invisible foundation of modern manufacturing. Polymers are used in everything from the bumpers of cars to the cling films that cover fresh produce. They enable industries to innovate and reduce costs while improving product performance. The idea of establishing a chemical polymer plant is now more relevant than ever, with a growing global demand for advanced materials. India has also emerged as a major manufacturing hub.
This guide was designed for entrepreneurs, industrial startups, and anyone who wants a clear overview of the polymer industry. It is aimed at those who are interested in a technical, informed, and strategic view. You will find information on the market outlook, growth of the sector, manufacturing processes, technology requirements, and future trends, without focusing on costs or project investments.
Chemical Polymer Industry: Understanding Its Basics
Polymers are large molecules that consist of monomers (repeating structural units) bonded together. Natural or synthetic polymers are used in industrial manufacturing due to their performance and versatility. Polymers can be classified based on their physical characteristics and final use. They are divided into thermoplastics (plastics that melt), thermosetting plastics (plastics that set), elastomers and specialty polymers.
It is common to use thermoplastics such as polyethylene (PE), PP, and PVC because they can be remelted without losing their integrity. Thermosetting resins such as epoxy and phenolic resins offer good heat and chemical resistance, but can’t be remolded after they are set.
The type of polymer you choose to manufacture will depend on the industries that you are targeting, the raw materials available, and whether or not your company can meet quality and regulatory standards in your market.
Related: Chemical Exports in 2025: Opportunities for Indian Startups
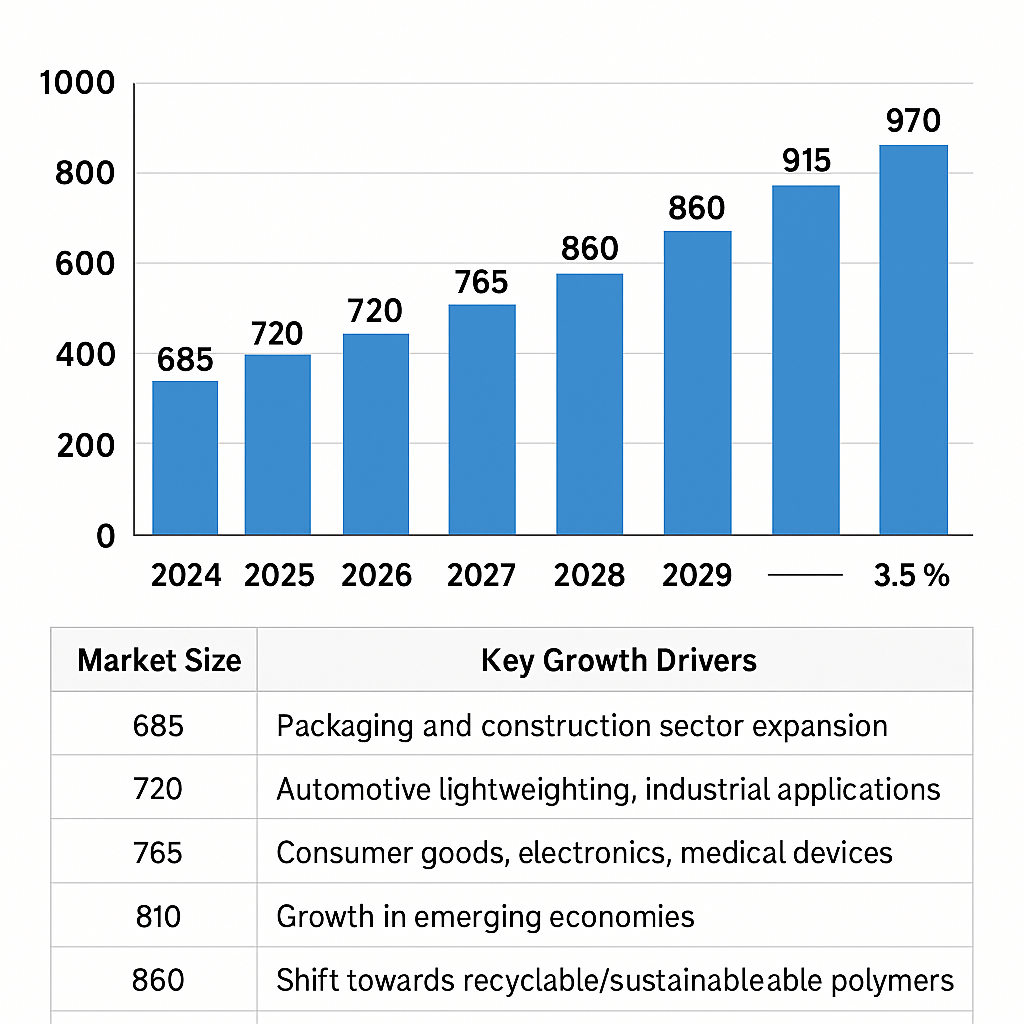
Market Outlook: Growth, Demand, and Opportunities
Polymer manufacturers are seeking lighter, stronger, and cost-efficient materials in all sectors, from packaging to aerospace. Urbanization, lifestyle changes of consumers, infrastructure developments, and the shift to sustainable materials are driving growth.
Global Polymer Market Forecast (2024-2030)
| Year | Market Size (USD Billions) | CAGR (Approx. | Key growth drivers |
| 2024 | 685 | — | Construction sector growth in packaging |
| 2025 | 720 | Automotive lightweighting, industrial applications | |
| 2026 | 765 | Consumer goods, electronics, medical devices | |
| 2027 | 810 | Growth in emerging economies | |
| 2028 | 860 | Shift towards recyclable/sustainable polymers | |
| 2029 | 915 | Infrastructure development, export markets | |
| 2030 | 970 | ~5.5% | R&D on bio-based polymers to increase |
India’s sector is growing faster than average. The domestic demand is expected to increase by about 8% per year through 2030. This growth will be driven by the packaging, automotive and agriculture industries. India’s polymer consumption per capita is below the average global level, which indicates that there is a significant potential for growth, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. India’s growing petrochemical industry and low production costs give it an advantage in international trade.
Why Starting Now Makes Strategic Sense
Multiple market signals indicate that it is a good time to establish a polymer manufacturing facility. The domestic market is expanding not only in urban areas but also into rural markets with agricultural films, low-cost packaging, and water storage solutions. India’s manufacturing capability makes it a desirable supplier to regions such as Africa, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
A growing demand for recyclable and sustainable materials is another important factor. Early movers in the market can establish a solid reputation by using bio-based polymers. Integrating polymer manufacturing into downstream industries, such as packaging, mold making, or textile production, can help entrepreneurs capture value and diversify their revenue streams.
Check our Handbooks on Chemical Technology (Organic, Inorganic, Industrial), Fine Chemicals
Source Raw Materials
Polymer raw materials are mostly petrochemical derivatives. However, bio-based alternatives have gained in popularity. Polyethylene, for example, is made from ethylene, while polypropylene comes from propylene. PVC relies on vinyl chloride monomer, and polystyrene uses styrene as its monomer. PET is made from terephthalic (PTA) acid and monoethyleneglycol (MEG).
It is important to find reliable and cost-effective suppliers for these inputs. Many producers choose long-term contracts with domestic petrochemical firms to ensure consistent quality and price stability. Some import monomers in order to fill supply gaps, or to gain access to specialty feedstocks that are not available locally. Businesses that are interested in sustainability can explore bio-based monomers. However, these can be more expensive and require special processing.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The exact process of manufacturing polymers varies, but the basic stages are similar. Take polyethylene for example:
The first step is to purify the ethylene feedstock. The polymerization takes place either under high pressure for low-density (or linear low-density) polyethylene, or at low pressure (for higher-density and linear low-density (HDPE), with the aid of Ziegler-Natta catalysts or metallocenes. The polymer produced is separated from the monomers that have not reacted. These are then recovered and recycled into the system.
The polymer melt is extruded and then cut into pellets. These are then cooled, dried and packaged. The process is characterized by strict quality control, including tests for density, melt flow index, tensile strength, and other parameters.
Technology, Infrastructure, and Equipment
Modern polymer plants require advanced equipment in order to produce consistently high-quality products and ensure efficiency. The core machinery includes, for example, polymerization reactors and extrusion systems, as well as storage tanks for monomers, catalysts and heat exchange systems. Infrastructure support, such as utilities, control systems and quality testing labs, is equally important.
In order to comply with environmental regulations, plants need to be equipped not only with the appropriate treatment systems and monitoring equipment but also with the necessary treatment facilities. The use of IoT monitoring and maintenance tools to improve operational efficiency is increasing.
Related: Chemical Products in High Global Demand with Local Production Potential
Quality, Safety, and Environmental Compliance
In a regulated sector, it is important to adhere to environmental and product standards. ISO 9001 certification for quality management is standard, but polymer-specific IS Standards may be applicable depending on the market. India’s environmental regulations are governed by the Central Pollution Control Board. In India, this often involves installing effluent-treatment plants (ETPs), for wastewater management, and emission control systems to reduce air pollutants.
Safety drills, training on handling hazardous chemicals and emergency response protocols are all important for worker safety. Safety culture not only helps reduce risks, but it also improves your reputation with regulators and customers.
Market Development and Customer Service
Building a sustainable customer base for a polymer plant involves strategic marketing and relationship-building. The large volume buyers, such as packaging companies and suppliers of construction materials, value consistency in quality, prompt delivery and technical support. Export opportunities can be opened by participating in international trade fairs or industry exhibitions such as Plastindia. Your plant can be positioned as a responsible producer to attract clients under pressure to achieve sustainability goals.
Future Trends in Polymer Manufacturing
Polymer production will undergo significant changes in the next decade. Environmental concerns and regulatory change will drive the market growth of bio-based and degradable polymers. New applications will be enabled by advanced catalysts that allow for more precise control of polymer properties. Automation, IoT, and AI integration will improve the efficiency and adaptability of production lines. The circular economy will have a major impact on the industry, as post-consumer materials are recycled into new feedstocks, thus reducing the dependency on virgin petrochemicals.
For more information, check out this video
NPCS is your partner in polymer plant setup
Niir Project Consultancy Services prepares detailed techno-economic feasibility reports for polymer projects. These reports provide a blueprint for entrepreneurs, covering the manufacturing process, raw materials, plant layout and financials. NPCS helps companies assess the feasibility of establishing new industries. This ensures that informed decisions are backed up by data and expert technical knowledge.
Find Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
The conclusion of the article is:
Chemical polymer manufacturing is one of the most adaptable and resilient segments in modern manufacturing. Polymer production plants offer entrepreneurs the opportunity to achieve long-term success in industry. They are characterized by rising demand, technological innovations, and a strong export and domestic potential. New entrants to the polymer industry can achieve success by aligning their production capabilities with the market’s needs, investing in compliance and quality, and keeping a close eye on emerging trends.






