A common industrial chemical is morpholine. It looks like a small, ring-shaped substance made of carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. Morpholine can improve the efficiency of many industries. It can cause irritation to the skin and lungs and has strict regulations for certain uses (for example, the EU bans it in some fruit wax products).
Now, this article will explain what morpholine, its behavior, how the industry uses it and why safety is important.
What Is Morpholine
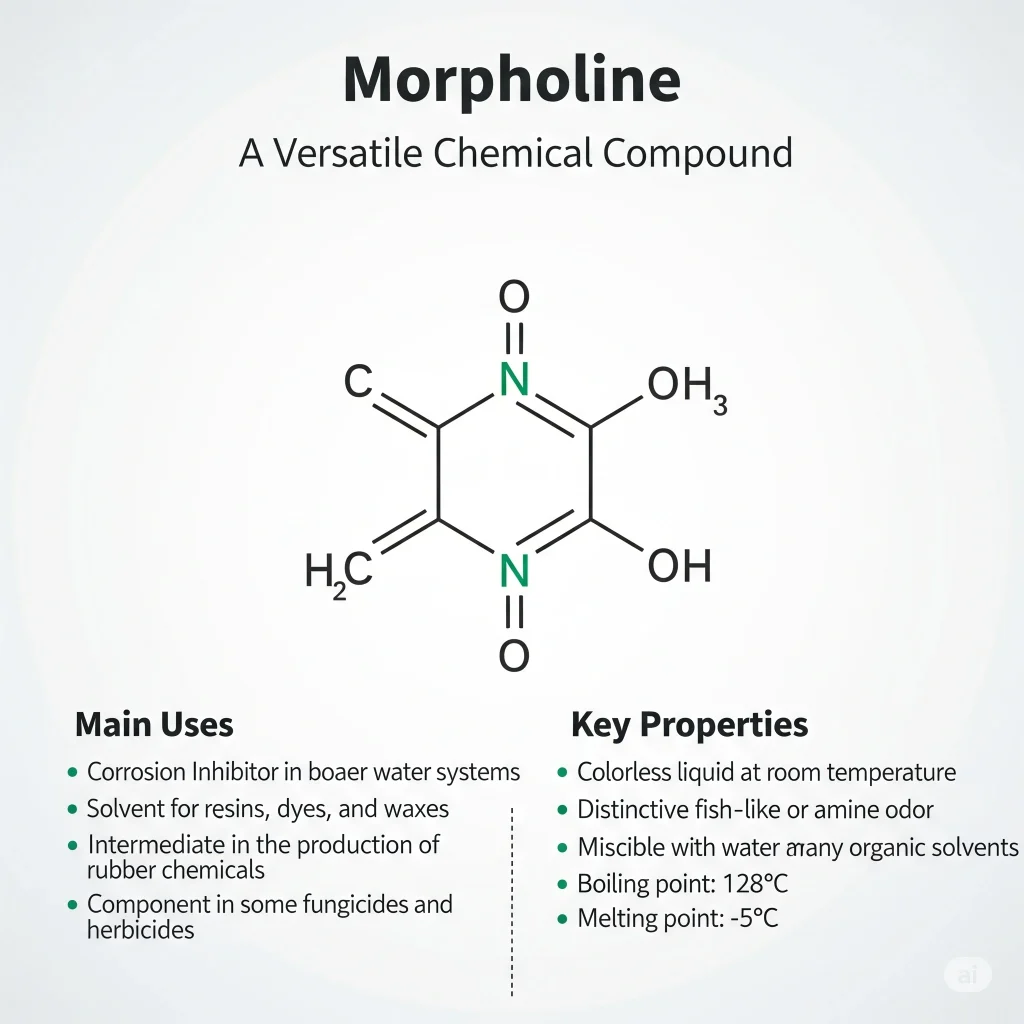
The organic compound morpholine has the formula C4H9NO. The ring is six members. It has one oxygen and one nitrogen in the ring. The nitrogen in morpholine makes it act like a weak acid (it can accept an electron). It is a colorless, odorless liquid at room temperature. Chemists also call it tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine.
Physical And Chemical Properties
- It is miscible.
- Its melting point is approximately -5 degC.
- Vapours that are heavier than air can accumulate near the floor and other low areas.
- On contact, it can cause metals to corrode and tissue to combust.
- Its conjugate has a pKa of 8.3, which means that morpholine acts like a mild acid in water.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
How Industry Makes Morphine
The morpholine ring is made by large chemical companies from simple chemicals containing nitrogen and two-carbon fragments. One common route starts from diethanolamine (itself made industrially from ethylene oxide + ammonia) and converts it into the morpholine ring using dehydration/cyclization steps under controlled conditions. Patent literature describes other routes using diethylene glycol and ammonia with catalysts. These are industrial processes that are carried out by chemical engineers in factories. They are not recipes.
Where To Find Morpholine, And Why
Morpholine is useful in many ways. Here are some of the most common:
- Steam and boiler systems (volatile ammonia / neutralizing ammonia): The morpholine keeps the pH of condensate lines and steam at a safe level so that metals don’t corrode. It vaporizes with steam, and then returns to the steam loop with condensate. Engineers use it because it can be distributed evenly throughout many systems.
- Solvent, chemical intermediate: Companies utilize morpholine both as a solvent to dissolve many organic compounds and as an ingredient in the production of other chemicals. Some pharmaceuticals and fine chemical products contain the morpholine ring.
- Rubber and chemical manufacturing: This compound is used to make rubber accelerators, as well as other additives for industrial chemistry.
- Waxes, coatings, and emulsifiers: In the past, morpholine derivatives were used to form wax emulsions that could be used for industrial paper and cardboard or for fruit coatings. Some regions restrict or prohibit certain food uses. (See the Regulation section).
Safety, Exposure Limits And Risks (very important)
The skin, the eyes and the airways can be irritated by morpholine. Liquid concentrated can cause skin and eye irritation. Inhaling high-level vapour can cause headaches, coughing and other side effects. Employers treat morpholine as both an inhalation and a skin hazard because it can enter the skin.
The following are the key occupational limits (for workplaces). The typical 8-hour limit is 20 ppm as a time weighted average (about 70 mg/m3); short-term limits are usually set at 30 ppm. Safety data sheets and emergency guidelines provide information on first aid, protective clothes, and ventilation. Consult the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) of the products you are using and adhere to workplace rules.
Environmental Behaviour And Biodegradation
Morpholine is easily dissolved in water. In many conditions, bacteria can break down morpholine. Some regulatory tests in controlled laboratories show that morpholine biodegrades well, but other tests indicate a slower rate of removal depending on the conditions. Under nitro sating circumstances, the biggest concern is that morpholine may form N-nitroso morpholine. NMOR, which is a known carcinogenic nitrosamine, can be formed. Due to this risk, regulators monitor morpholine levels in some food products and processing streams.
Read Our Book: Click Here
Special Cases And Regulations
The way regulators control morpholine depends on the country, the type of use and the regulation.
The EU, UK and do not allow the use of morpholine on fruit waxes for human consumption. They require testing and detection methods in order to ensure compliance. Other countries, such as the US and Canada, have historically allowed certain forms. However, rules change and industries adapt to market and law. Authorities are very cautious about any use of morpholine in food or water because it can produce nitrosamines. If a product will enter Europe, manufacturers avoid morpholine-containing waxes to meet EU rules.
Handling, Storage And Disposal (Practical Rules)
- Store properly: Store morpholine tightly sealed in a well-ventilated, cool area. Keep away from heat, strong acids and oxidizers.
- Safety Needed: When handling it, wear protective clothing, chemical-resistant gloves and splash goggles. If vapours are likely to form, work in a fume-hood or with local exhaust ventilation.
- Follow the SDS for spills: evacuate, ventilate, absorb using inert materials, and collect the waste to be disposed of properly. Do not flush concentrated materials down drains. The disposal of hazardous waste should be done according to local regulations. Many jurisdictions require that the hazardous waste is incinerated at approved facilities, or treated by licensed chemical waste handlers.
Read Our Project Report: Click Here
Alternatives And Safer Choices
Engineers can use other volatile amines (such as DEAE or cyclohexylamine) for certain uses, such as steam systems neutralizing amines. This will depend on the system requirements and regulatory restrictions. Fruit coatings are now coated with food-grade waxes approved for use without morpholine. Industries also seek out non-amine corrosion inhibitors and new technologies to reduce chemical usage.
Read More: Chemical Exports in 2025: Opportunities for Indian Startups
Conclusion
The chemical morpholine is widely used and useful. It is used in boilers as a solvent and to feed chemical production, soluble in water, and has both positive and negative traits. It can protect metals and can cause irritation to people. Under certain conditions it can also lead to the formation of nitrosamine (a health risk). Due to its dual nature, morpholine is used by industry with strict controls and some uses are restricted (such as certain food coatings within the EU). Follow the Safety Data Sheet and use appropriate ventilation and protective equipment. Also, obey local regulations for storage and disposal.
Morpholine: FAQs
Q. What is the chemical equation of morpholine?
C4H9NO. It is a six member ring that contains one oxygen atom and one nitrogen.
Q. Is it dangerous to breathe or touch morpholine?
Yes. It can burn the skin, eyes, and lungs. Air exposure is limited in workplaces (typically at 20 ppm TWA). Wear PPE and follow the SDS.
Q. Can morpholine finish fruit waxes in many countries?
Many countries (including the EU) have banned morpholine finishes for fruit waxes. In the past, some countries allowed certain morpholine-derived products. However, rules have changed. Check the target-market regulations prior to use.
Q. Does morpholine lead to cancer?
Morpholine is not classified as a clear carcinogen in humans by major agencies, like nitrosamines. Under certain conditions, morpholine may form N-nitrosomorpholine. NMOR has been classified as a potential human carcinogen. It is for this reason that regulators restrict the use of morpholine as a food additive.
Q. How should I store the morpholine?
Store it in a dry, cool, ventilated area away from acids and other oxidizers in a tightly-sealed container. Follow the SDS and use secondary containment.
Q. Is morpholine a biodegradable substance?
Microbes are able to break down morpholine, and lab tests have shown good biodegradation. The actual breakdown of morpholine in the environment is dependent on the conditions and the microbiological community.