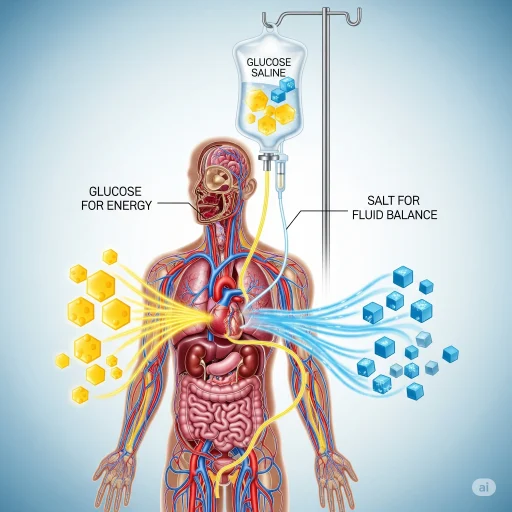
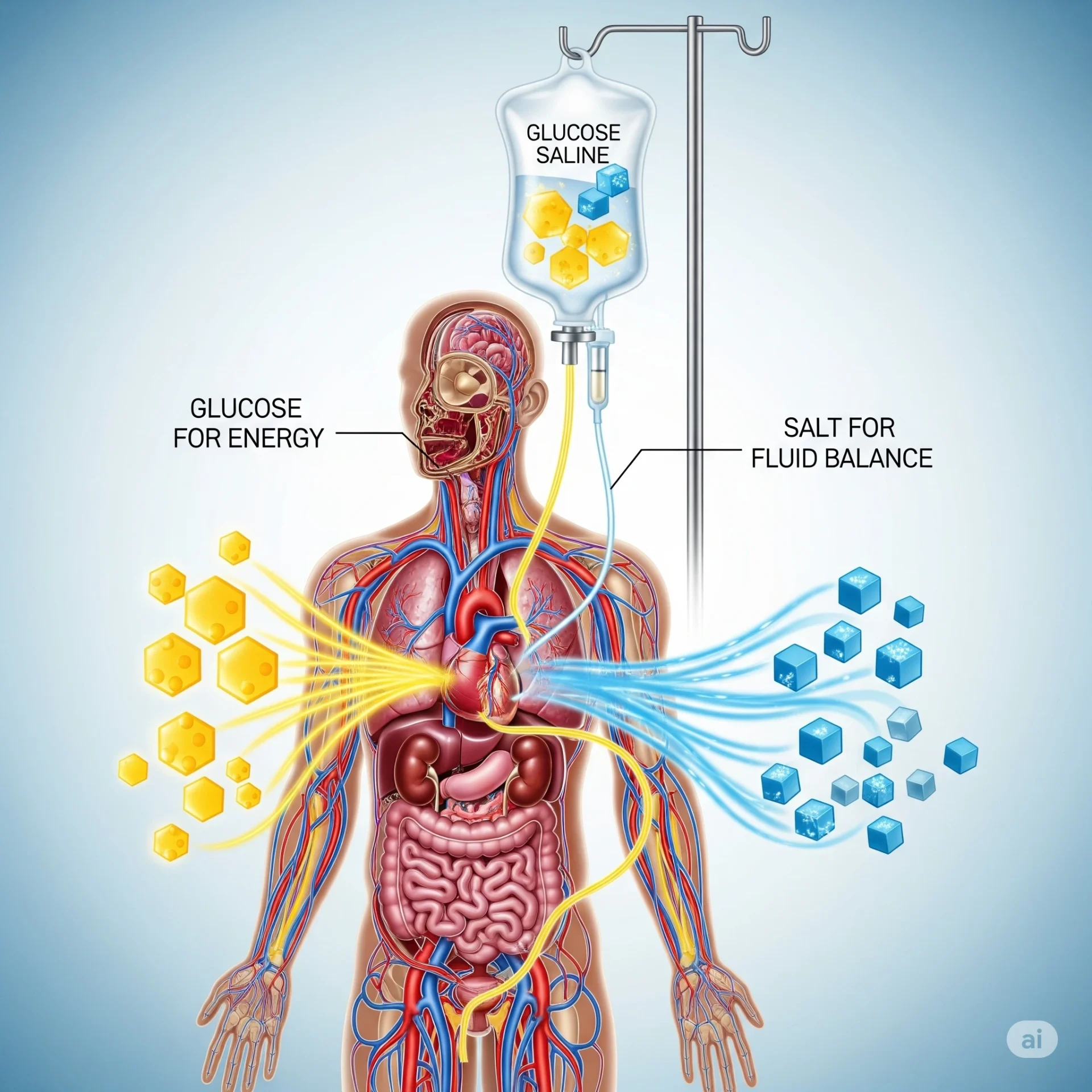
It is a clear, sterile liquid that contains glucose (a natural sugar) and saline (a mixture of water and sodium chloride). It is a clear, sterile fluid that contains sugar (a naturally occurring sugar) and sodium chloride. This mixture of water and sodium chloride provides the body with energy as well as hydration.
Sugar and salt are essential for energy and to keep our cells and muscles functioning properly. Many medical conditions prevent people from drinking water or eating food. It could be that they are too weak, unresponsive, or recovering after surgery. In these cases, glucose saline can be administered via intravenous drip to the bloodstream so that the body gets what it needs right away.
This article describes in detail what glucose-saline is and how it’s made. It also explains the types of it, why doctors use them, their benefits, precautions and more.
What Is Glucose Saline
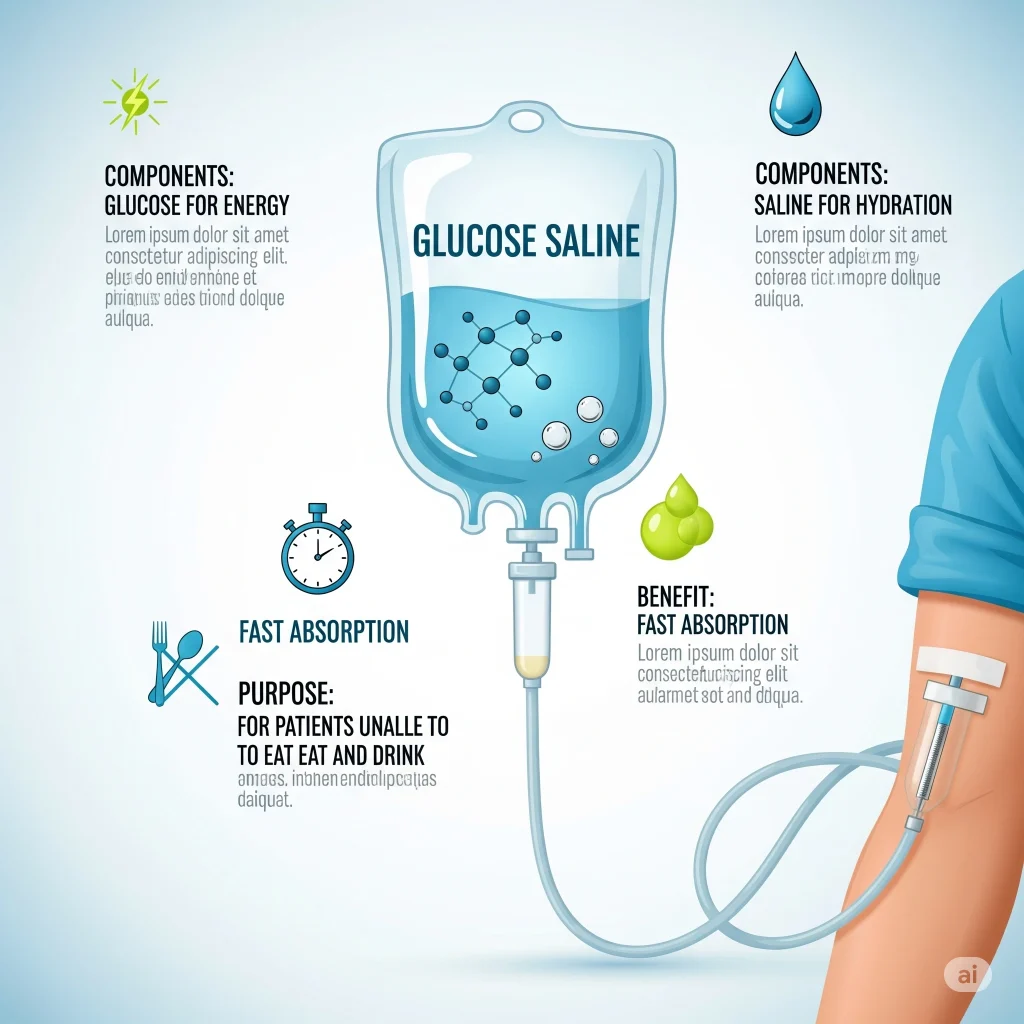
It is a intravenous solution which contains:
- Glucose: A simple sugar which provides energy to every cell of the body. The brain is heavily dependent on glucose for its function.
- Saline: A mixture of sterile salt and water. This is important for maintaining fluid balance, and supporting vital functions such as nerve signals and muscular contractions.
Combined, glucose and salt become a powerful tool in medicine. Saline and glucose work together to restore electrolyte and hydration balance. It is absorbed quickly by the body because it’s delivered directly into a blood vessel.
Composition Of Glucose Saline
The standard 1 liter bag may contain:
- Glucose is usually 5% or 10%. This means 50 grams or $100 grams of glucose in a liter.
- Sodium chloride: 0,9% (9 grams per 1 liter), the same concentration of salt as in human blood.
- Sterile Water : Main liquid that transports these ingredients into bloodstream.
Balance is key. A high sugar intake can cause dangerous blood glucose levels, while a high salt intake could lead to water retention or kidney strain. When the right amount of solution is given, most patients are safe when the concentration is close to the natural level in their body.
Types Of Glucose Saline
The type of glucose solution a doctor prescribes depends on the patient’s health.
- 0.9% Saline with 5% glucose is the most common combination. Ideal for mild dehydration or low energy.
- 10% glucose with 0.9% saline– Gives patients more sugar if they need to have quick energy. For example, after surgery or when they are weak.
- Saline with 0.45% Glucose Has less sodium and is used when the sodium level needs to be reduced. For example, in certain kidney or heart conditions.
The right type can prevent complications. A patient with high levels of sodium, for example, would not receive the full concentration of 0.9%.
How Glucose Saline Works In The body
When a patient is given glucose saline via an IV:
- Glucose is transported to the cells by the bloodstream. In the cells, glucose is converted into energy molecules known as ATP (adenosine Triphosphate). This energy is used to power muscles, the brain, and other body functions.
- Saline replenishes fluids and sodium lost in the body, helping to maintain blood volume. Sodium maintains electrical signals within the nervous system which allows the heart and muscles work correctly.
The body uses glucose saline almost instantly because it bypasses both the stomach and the intestines. This is crucial in an emergency.
Read More: A Feasibility Guide to Launching a Profitable Medical Device Manufacturing Startup in India
Medical Uses For Glucose-Saline
In several situations, glucose-saline can be used.
1Treatment of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when a person’s body loses fluids through vomiting, diarrhea or sweating. Dehydration can cause weakness, dizziness and confusion. It is not enough to drink water because salts are also lost in the body. Glucose salts quickly replenish both electrolytes and fluids.
Correction of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia).
Hypoglycemia is dangerous for diabetics or those who haven’t eaten in a while. The glucose saline quickly raises blood sugar levels, which prevents dizziness, confusion or unconsciousness.
Post-Surgery Rehabilitation
Patients may not be able drink or eat immediately after surgery. The glucose saline will keep them hydrated, and provide energy until they are able to eat solid foods.
Treatment of Shock
Shock may be caused by severe injuries, infection, or blood loss. Shock can cause the blood pressure to drop and the organs not to receive enough oxygen. Glucose saline helps stabilize blood pressure by restoring fluid volume.
Burn and Injury Rehabilitation
Burns that are severe can cause a large amount of fluid to be lost through the skin. The glucose saline is used to replace these fluids, and it also provides energy for healing.
Read More: Top Innovations in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Technologies
Benefits and Uses of Glucose-Saline
- Fast Energy Supply– The glucose is available to the body immediately.
- Quick Hydration– IV administration is faster than drinking water, because it bypasses the digestive system.
- Electrolytes in Balance– The sodium chloride balances the electrolytes of the body, which is essential for nerves and muscle.
- Multiple medical uses– It can also be used for emergencies, recovery and treatment of certain illnesses.
- Safe when monitored– When given in the correct dosage by trained staff it is safe for most patients.
How Glucose Saline Is Given
It is important to give glucose saline in a controlled manner.
- A healthcare professional will clean the skin before inserting a cannula or sterile needle into a vein.
- The IV bag can be hung from a stand, and the needle is connected using sterile tubing.
- A flow regulator is used to adjust the drip rate so that the fluid enters the system at the correct speed.
- During infusion, vital signs are monitored (pulse rate, blood pressure and breathing).
Infusions can last from 30 minutes up to several hours , depending on patient needs.
Read Our Book: Click Here
Safety Measures And Precautions
Although glucose saline can be helpful, doctors must take certain precautions.
- First Blood Test To check sodium and sugar levels before you start.
- Dosage Control– Too much may cause fluid overload, or dangerously high levels of sugar.
- Avoid Certain Patients– Patients with kidney disease, heart failure or uncontrolled diabetes require special attention.
- Sterility All equipment must comply with the sterility standard to prevent infection.
- Control of Flow– The infusion rate should be kept at a safe level to prevent swelling or pressure.
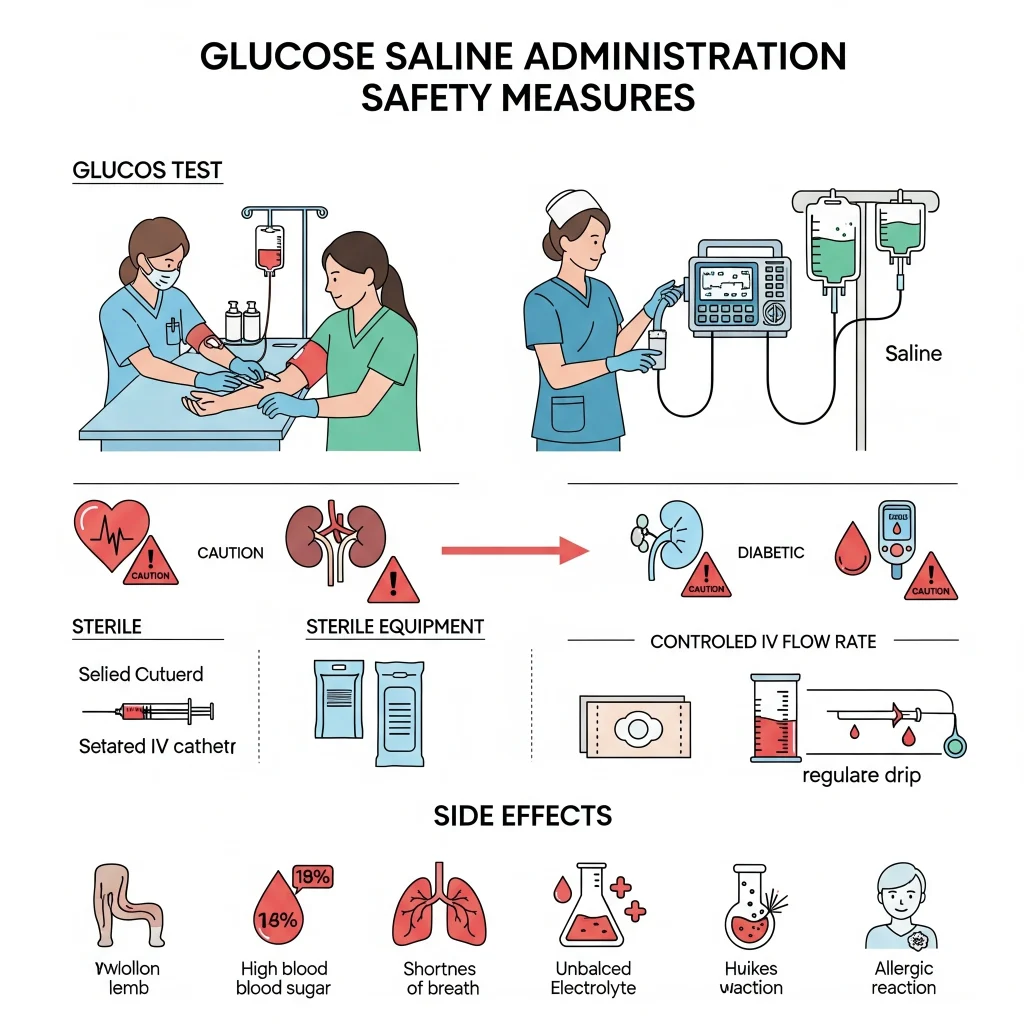
Possible Side Effects
Although side effects are rare, they can occur if the treatment is not administered correctly.
- Fluid leakage causes swelling to occur at the injection site.
- High Blood Sugar in diabetic patients.
- Fluid overload can cause shortness in breath for people with kidney or heart problems.
- Electrolyte Unbalance If given in the incorrect ratio.
- Allergic reactions (rare), such as rash and itching.
Read Our Project Report: Click Here
Storage Tips
To ensure safety, it is important to store and handle glucose saline properly.
- Keep your items in a dry, cool place that is away from the sun.
- The solution may be damaged if frozen.
- Before using, check the expiry dates.
- If the liquid has a cloudy appearance or contains particles, do not use it.
- Always use sealed, sterile IV bags.
Difference Between Glucose Saline
| Features | Glucose Saline | Normal Saline |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glucose + Sodium Chloride | Only Sodium Chloride |
| Purpose | Hydrates and provides energy | Hydrates and provides electrolytes |
| Best For | Dehydration due to low sugar or energy | Simple dehydration or salt imbalance |
| Calories | Sugar is a source of calories | No calories |
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Conclusion
It is an essential medical solution which can save lives. Combining hydration with electrolyte balance and energy, it helps patients recover after dehydration and low blood sugar. It also helps them recover from surgery, shock, or burns. It is important to use it under supervision because it affects the blood sugar levels and fluid levels. When administered correctly, glucose-saline can not only speed up the recovery process but also prevent serious complications.
Frequently Answered Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can glucose saline hydrate be given to diabetics?
Yes, with caution. Doctors closely monitor sugar levels to prevent dangerous spikes.
Q2. Is drinking glucose saline equivalent to drinking energy drinks?
Energy drinks are digested and can contain caffeine and additives. Glucose saline, on the other hand, is pure medical grade hydration with sugar that goes directly into your bloodstream.
Q3. Q3. Can children be given glucose saline if they are overweight?
The dosage will depend on the child’s weight and their medical needs in order to avoid excessive hydration or sugar levels.
Q4. Does it replace meals or snacks?
It gives you quick energy and hydration, but does not provide the necessary vitamins, proteins, or fats for a complete diet.