Sugar is more than just a household essential. It’s a vital industry that supports millions of lives and feeds the economy. Sugar plants are the complex and powerful system that lies behind every grain of refined sugar. Sugar plants, or sugar factories, are where raw sugarcane and sugar beet are transformed into the white or brown sugar that we consume each day. These plants are the heart of the sugar industry. They combine agricultural products with heavy industrial machinery, skilled labor and specialized equipment.
Sugar plant industries in countries such as India, Brazil and Thailand have grown to be multi-billion dollar sectors over the years. This article will explore the entire sugar production process, from the arrival and processing of sugarcane through to its products. We’ll also explore the economic impact of sugar cane, its machinery, and environmental impact.
What is a Sugar Plant
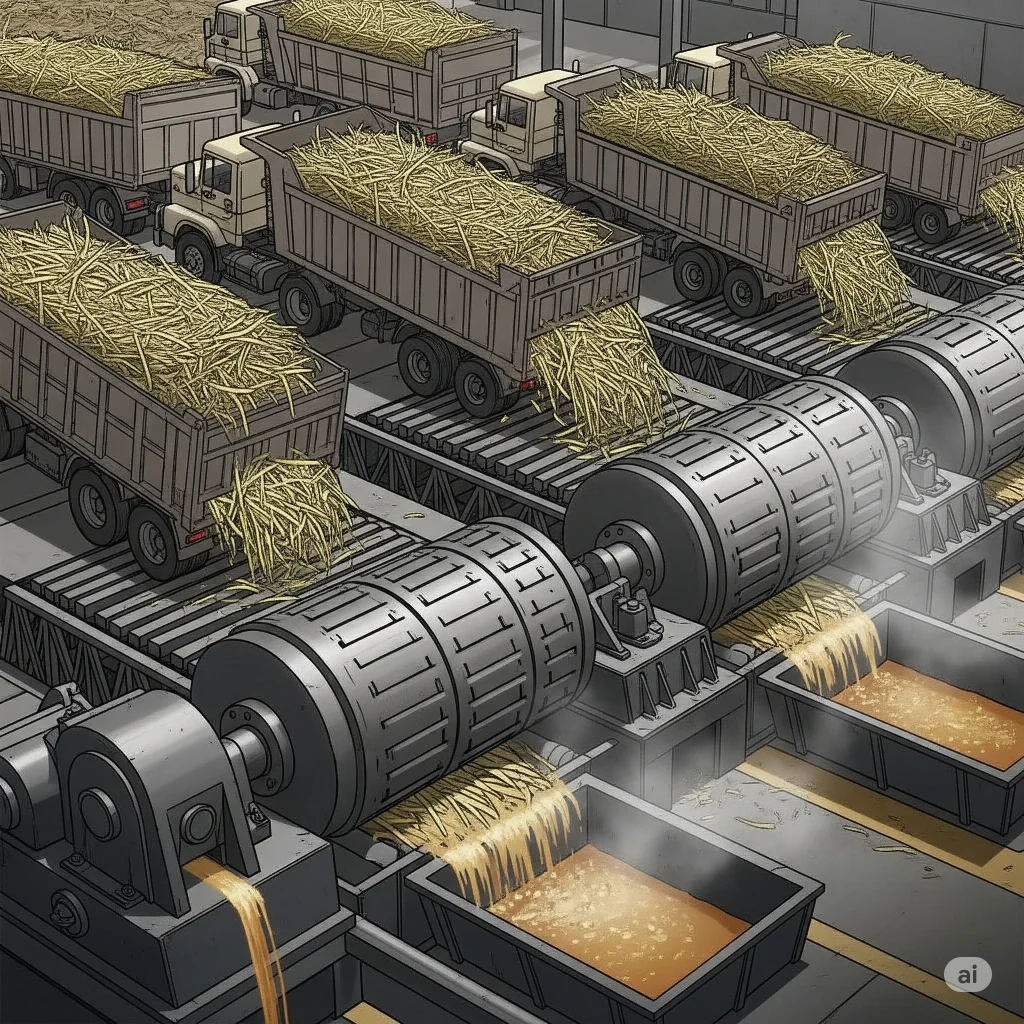
Sugar plants are factories that process sugar cane juice or sugar beet juice into sugar. Sugar plants are often located near sugarcane farms because the sugarcane must be processed as soon as possible after harvest. Sugar plants perform a variety of functions, including extraction, clarification and evaporation.
To complete the process, these plants use boilers, turbines and sophisticated chemistry. Modern sugar plants, while mostly automated, still require skilled workers to operate machines, monitor quality and manage production.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
The Step-by-Step Production Process for Sugar in a Plant
Step 1: Cane Reception & Weighing
Trucks bring sugarcane to the factory. Workers unload the cane onto feeders. Big scales (weighbridges) check how much cane each truck brought. This is important because people get paid based on how much cane they deliver. The cane must be crushed soon—if it waits longer than a day, the juice quality gets worse.
Step 2: Cane Preparation
Choppers cut the cane into small pieces. Then shredders tear it up even more. This helps get the juice out because small pieces give more juice than big ones.
Step 3: Juice Extraction
The shredded cane goes into heavy machines called mills. These squeeze the cane and force out the juice. One mill can crush thousands of tons of cane every day.
Step 4: Juice Clarification
The juice has dirt, bits of cane, and other stuff in it. Workers heat the juice and add lime. This helps the dirt and bits settle down in a tank. The clean juice goes forward for more processing.
Step 5: Evaporation
The clean juice needs to get thicker. It goes into big boilers called evaporators. Most of the water boils away. The juice turns thick, like syrup.
Step 6: Crystallization
The thick syrup goes into vacuum pans. Here, sugar starts to form crystals. Workers control the temperature carefully. They add “seed” sugar to help crystals form evenly.
Step 7: Centrifugation
Machines called centrifuges spin really fast. This separates the sugar crystals from the leftover liquid, called molasses. This step decides how much sugar and water are left in the crystals.
Step 8: Packing & Drying
The sugar crystals get dried. Machines pack the sugar into bags. The factory uses steam from burning leftover cane (bagasse) to run these machines.
Read More: List of Profitable Business Ideas in Production of Soy and Soya Based Food Products.
Sugar Plants: By-Products
A sugar plant doesn’t just produce sugar. Sugar cane is not the only by-product of a sugar plant.
- Bagasse: The fibrous remnant after juice extraction. Used to produce paper, biofuel and electricity, or as fuel
- Molasses: It is the leftover syrup from crystallization. Useful in the production of alcohol, as a cattle feed and an industrial input
- Press Mud : Solid waste from juice clarification. It is rich in nutrients and used as a fertilizer
Sugar plants are highly profitable and sustainable because of these by-products.
Sugar Plants: Their Importance in the Economy
- Employment generator: These factories offer jobs to drivers, farmers, factory workers and engineers. They also provide work for chemists
- Rural development: The majority of sugar plants are located rural areas, which boost village economies by providing infrastructure and support services
- Export potential: Countries such as India export millions and tons of sugar, which contributes to the foreign exchange reserves
- Energy production: Many plants produce electricity using bagasse and reduce their dependence on fossil fuels
- Strength of the supply chain: Sugar plant is a link between agriculture, retail, logistics and manufacturing industries
- Government revenue: The plants that pay taxes to the state government through levies and excise duty
Modern Sugar Plant Technology
Sugar plants have adopted new technologies as competition increases and efficiency is becoming more important.
- Automation and SCADA Systems: These systems watch over the whole production. They make sure everything runs right and nothing goes wrong.
- Boiler Efficiency: High-pressure boilers make more power and use less fuel. Basically, you get more energy without wasting as much.
- Waste Management Systems: These systems handle all the waste—like dirty water and smoke, so it doesn’t harm the environment.
- Water Recycling Systems: Plants use these systems to clean and reuse water. This way, they don’t use too much fresh water.
- Online Monitoring: The plant gets live updates about things like temperature and quality. This helps them fix problems quickly and make everything work better.
Sugar mills are also increasingly using AI, IoT sensors and smart control rooms.

Environmental Challenges
Sugar plants are under scrutiny for their environmental impact, despite the benefits they provide. They generate large amounts of industrial waste and consume a lot of water. Here are some of the concerns:
- Water pollution: If people dump dirty water anywhere, it can really harm the plants and animals living in the area.
- Air pollution: When sugar factories burn bagasse or coal and don’t use filters, tiny harmful particles go into the air and people can breathe them in.
- Land use issues: Growing more sugarcane fields often means cutting down forests, so trees and wildlife lose their home.
- Soil Degradation: Sugarcane farming uses up the good stuff in the soil, making it less healthy over time.
In order to combat this, many plants have installed pollution control devices and recycled water in order to meet environmental standards. Some even adopt zero liquid discharge (ZLD) systems.
Read Our Project: Click Here
Sugar Plants face a number of challenges
Sugar plants face many challenges, despite their value.
- Fluctuations in Sugar Prices: Global markets, the weather and government policies can make a impact on the suger price.
- Delays in Payment: Sometimes mills delay payments to farmers
- Uncertainty in Climatic Conditions: Droughts and floods can affect the supply of sugarcane
- Policy Uncertainty Government Subsidies, Export Bans, or Ethanol Blending Rules Often Change
- High capital requirement: To set up or upgrade a plant, hefty investment is necessary.
Read More: Build a Profitable EV Station Franchise: A Strategic Guide for New-Age Entrepreneurs
Conclusion
Sugar plants are much more than industrial buildings. Sugar plants are a combination of agriculture, engineering, chemistry and economics. Sugar plants are vital to the global economy and food supply. They harvest sugarcane, refine sugar, and produce valuable by-products. Modern sugar mills embrace innovation in order to become more efficient and sustainable as the world shifts towards cleaner, greener practices.
Sugar plants are vital in countries such as India where sugar is a cultural and economic staple. Understanding how these plants work will give you a better appreciation of the spoon of sugar you put in your tea, whether you are a student or an investor.
Sugar Plant: FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How much time does it take for sugarcane to mature before it is processed?
Answer: Sugarcane takes between 10-16 months depending on climate and location. Sugarcane must be processed in 24 to 48 hours after harvesting for the best results.
Q2: How long does a sugar cane plant live?
Answer: A sugar plant that is properly maintained can run for up to 40 years. Regular upgrades can extend its life.
Q3: Is it possible to operate sugar plants year-round in the United States?
Answer: No. The sugarcane harvest season, which lasts 4-6 months per year, is when most sugar plants are in operation. In the off-season, sugar plants may concentrate on maintenance or ethanol.
Q4: How does ethanol affect sugar production?
Answer: Many sugar factories have ethanol distilleries. The molasses is used to make ethanol which can be blended with petrol to reduce emissions.
Q5: How many tons of sugarcane is required to produce one ton?
Answer: Depending on the type of sugarcane and the extraction method, 1 ton can yield between 100-120 kg sugar.
Q6: Are sugar plants profitable?
Answer: Yes. Especially when plants use all by-products and adopt new technologies, as well as managing costs effectively. Profits are also boosted by ethanol, exports, and power.
Q7: Are sugar beets processed in the same manner?
Answer: Yes, in most cases. However, sugar beet is a soft plant and requires different techniques for shredding.







