Sugar isn’t merely sugar, but it’s a significant economic driver for the rural economy of India. In fact, the sector of sugar in India is a key part in the fields of agriculture, employment as well as manufacturing. Sugarcane is grown by millions of farmers and a large number of people process it in mills throughout the nation. In reality, following the textile industry sugar is second in importance as the largest Agro-based sector in India.
India is the biggest consumption market in the world and is also the second largest producers of sugar around the globe. The sector is a major contributor to the consumption of domestic consumers and trade internationally. But, the industry is also confronted with numerous issues, such as pricing issues, environmental issues and the impact of climate change on sugarcane production.
In this article, we’ll look at the development through the Indian sugar industry from cultivation to production and its advantages as well as the major players involved, present challenges, and the future opportunities. Let’s start by understanding how the industry operates.
How The Sugar Industry Works In India
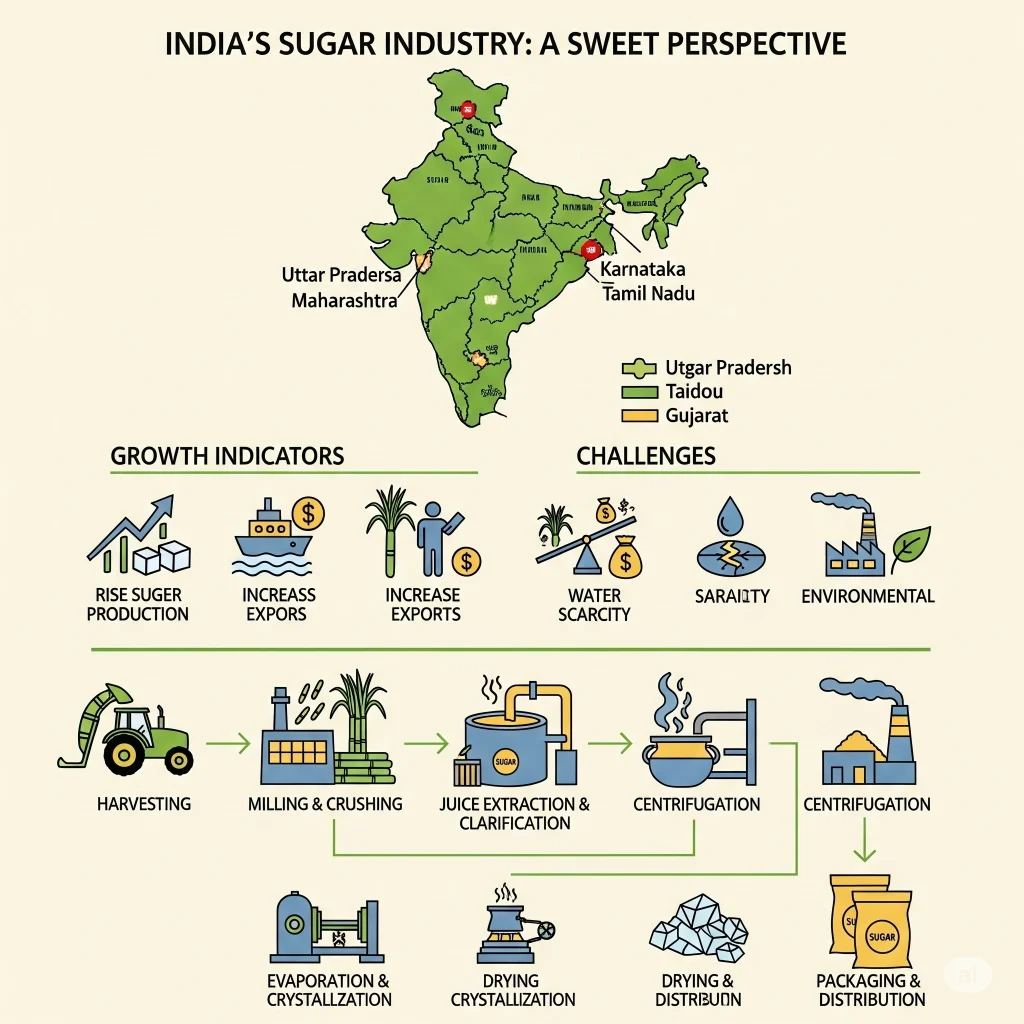
The sugar industry mostly depends upon sugarcane which is which is a subtropical and tropical crop that is grown in states such as Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Bihar.
This is how the industry of sugar operates:
- Sugarcane cultivation: Farmers cultivate sugarcane and care for it for 10 to 16 months. The crop requires warmer weather, plenty of fertile soil, and water.
- harvesting and Transportation: After harvesting, the cane needs to be quickly transported to nearby mills since delays can reduce the sugar recovery.
- Crushing and extraction: The sugar mills smash sugarcane in order to get juice. The juice is then filtered and then boiled to eliminate impurities.
- Drying and Crystallization: Concentrated juice is formed into sugar crystals. The crystals are then separated, dried and then packed.
- By-Product Utilization: Production produces by-products such as Molasses (used to make alcohol) and bagasse (used to generate power) and press dirt (used to fertilize).
Read More: How to start a Manufacturing Business of Sugarcane Juice Preservation and Bottling Plant
Major States Leading The Sugar Industry
The country’s sugar production is concentrated in a handful of important states:
- Uttar Pradesh (UP): The largest sugarcane producer in India. UP is home to greater than 100 sugar mills, and contributes to more than 35% of the nation’s production.
- Maharashtra: Famous for its sugar mills that are cooperative It is the second largest sugar mill in the world.
- Karnataka: A state of sugar growth equipped with modern mills and the latest ethanol production facilities.
- Tamil Nadu and Bihar: These states are significant contributors, particularly to the production from jaggery, and Khandsari (unrefined sugar).
Economic Importance Of The Sugar Industry
The sugar industry has a direct impact on India’s economy in many ways:
Supports Rural Livelihoods
Over 50 million farmers rely on the cultivation of sugarcane. Many more are employed within sugar mills, transportation and other related industries.
Contributes to Industrial Growth
Sugar mills also support other industries such as ethanol paper, electricity, and liquor with by-products.
Boosts Export Revenue
India exports its sugar products to nations such as Indonesia, Iran, UAE as well as Bangladesh and earns valuable foreign exchange.
Drives Ethanol Blending Program
The sugarcane-derived ethanol assists India reduce its import costs and reduces pollution caused by petrol.
Read More: Aluminium Can For Beverages : A High-Margin, Low-Waste Business Model for Emerging Markets
Key Challenges Faced By The Sugar Industry
Despite its size in terms of size, the sugar industry is faced with a myriad of issues:
Low Sugarcane Prices for Farmers
Sometimes, mills hold off the payment to farmers, leading to financial strain. The inconsistency between the Fair as well as Remunerative Prices (FRP) and market demand can cause this problem.
Overproduction and Surplus Stock
India has a higher production of sugar than is needed which results in lower prices and an excess of stock.
Water-Intensive Crop
Sugarcane is a major requirement for water. In states that are prone to drought this can lead to the shortage of water needed for other crops as well as household requirements.
Climate Impact
Extreme heat, delayed rains and floods caused by changes in the climate can impact crop yields as well as processing schedules.
Financial Stress on Mills
Many sugar mills, particularly those in the private sector, are facing loss due to the rising cost and delays in repayments from governments.
Read More: Is Goat Farming a Viable Startup Idea?
Recent Reforms and Government Support
To address these issues To address these issues, to address these challenges, the Indian government has brought in a variety of initiatives to address these challenges:
- Ethanol Blending Goals: Government has established a target for blending 20 percent Ethanol with petrol in 2025. This will create new opportunities in sugar production.
- Subsidy Schemes: Subsidy schemes for exports as well as soft loan are provided to mills in order to decrease sugar overproduction and increase liquidity.
- Minimum Selling Price (MSP): The government has established the minimum selling price for sugar to stop market crashes.
- Digital payment system for farmers: Innovative platforms are currently being launched to ensure farmers get promptly and directly paid.
Read Our Book: Click Here
Future Of The Sugar Industry In India
Despite its current difficulties India’s future sugar industry appears promising, thanks to several new trends:
Shift to Ethanol-Based Economy
Sugar mills are now biorefineries. Through focusing on ethanol they are able to reduce their dependence on sugar only.
Use of Modern Farming Techniques
Farmers are embracing drip irrigation and high yield varieties and smart farming techniques to grow more and use less water.
Green Power from Bagasse
Many mills utilize bagasse as a sugarcane by-product that generates electricity. Some even sell the energy directly to grids.
Value-Added Products
Mills are making jaggery as well as brown sugar and other sugars in order to satisfy the growing health-conscious demands.
Want To Know About Which Business Idea Would Be Better For You?
Go Through Our Startup Selector Tool
Comparison: Sugar vs Jaggery Industry
| Feature | Sugar Industry | Jaggery Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Mechanized | Most of the time, manual |
| End Product | White refined sugar | Brown jaggery, unrefined and unrefined |
| Shelf Life | Long | Short |
| Market Demand | Mass consumption | Health-conscious buyers |
| Water Usage | High | Moderate |
Read Our Sugar And Value Added Products And Projects Report
Conclusion: A Sweet Business with Bitter Challenges
It is believed that the Sugar industry of India is among the most enduring and important industries. It helps farmers, creates jobs for rural people, aids in exports, and also supplies important products like electricity and ethanol. However, it faces pricing environmental, as well as climate-related issues.
To be profitable and sustainable to sustain its business, it has to expand, modernize and concentrate on added value goods and renewable energy. If the policies are in place investment, strategies, and innovation sugar production can change from a supplier of sweeteners to becoming an multi-dimensional bio-economy engine.
India’s experience in the sugar industry shows how an old-fashioned industry is still evolving, serves the nation and also contribute to the global economy if handled with care.
FAQs About The Sugar Industry In India
Q1. Can sugarcane be a successful crop in India?
Yes. however, it is contingent on the yield, government pricing as well as the amount paid by mills. Farmers who have access to water and nearby mills typically make good money.
Q2. Which are byproducts from the industry of sugar?
Most important by-products are Molasses (used to make ethanol) bagasse (used to generate electricity) and press mud (used for organic agricultural practices).
Q3. Why do sugar mills hold off farmer payments?
Mills are facing problems with cash flow due to the high cost of sugar or government subsidies that are delayed, which can cause delays in payment.
Q4. What is the ethanol-blending programme?
India blends ethanol with petrol to decrease imports of oil and polluting. Sugar mills are the primary suppliers of ethanol, using Molasses and Cane Juice.
Q5. What state is home to the highest amount of sugar mills?
Uttar Pradesh has the most sugar mills as well as being the biggest sugar producer in India.
Q6. Does sugar production impact the environment?
Does it. Sugarcane is a major user of water. Also, untreated waste generated by mills may affect rivers. However, more modern eco-friendly methods are being developed.
Q7. How do we define MSP within the sugar sector?
MSP is Minimum Selling Price. It is the cheapest price that mills can offer sugar set by the government in order to limit losses.