Aluminium is one of the most popular industrial metals in our time. Aluminium is used in many everyday products, from cars and planes to power cables and packaging foils. It is unique in that it can be recycled infinitely. Aluminium, unlike steel or plastics which degrade after each recycling cycle, retains its strength and purity. Aluminium recycling is both an environmentally responsible business and a great opportunity because of this remarkable quality.
In the context of today’s sustainability-focused world, recycling aluminium has gained new relevance. Recycling aluminium is a more energy-efficient and less environmentally damaging alternative to primary aluminium production. Aluminium recycling has become a viable and profitable business due to the increasing alignment of industries, governments and consumers towards greener practices. It offers entrepreneurs and startups the chance to be part of a global shift towards circular economy models, while also building a profitable industry venture.
Market Outlook and Industry Growth
Globally, the market for recycling aluminium has seen steady growth thanks to multiple industries. Forecasts indicate that the industry will reach USD 140-150 billion in 2030. This represents a growth of 7-8% per year. This expansion is largely driven by the automotive sector, which is moving towards lightweight materials in order to improve battery performance and fuel efficiency for electric vehicles. The other two major growth drivers are packaging and construction, which is a result of the increasing demand for prefabricated structures, building frames and foils.
India’s prospects are particularly bright. India produces around 4 million tonnes per year of aluminium, and more than a quarter of that comes from recycled materials. The government’s focus is on urbanisation and affordable housing. Smart cities, electric mobility, and smart cities. Between 2025 and 2030, the Indian aluminium sector is predicted to grow by 8-9% per year. The resource efficiency framework of NITI Aayog and the extended producer responsibility rules (EPR) are helping to ensure that recycling is an integral part in industrial supply chains.
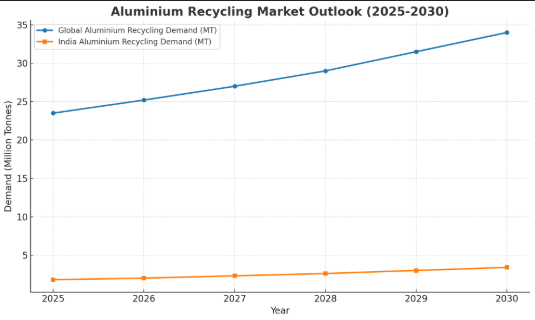
| Year | Global Recycling Demand (Million Tonnes). | Indian Recycling Demand (Million Tonnes). |
| 2025 | 23.5 | 1.8 |
| 2026 | 25.2 | 2.0 |
| 2027 | 27.0 | 2.3 |
| 2028 | 29.0 | 2.6 |
| 2029 | 31.5 | 3.0 |
| 2030 | 34.0 | 3.4 |
The table shows the expected growth of both the global and Indian markets over next five years. Global demand will be driven by electric vehicles and the use of renewable energy. India’s growth, however, will be determined by infrastructure and manufacturing expansion.
Related: How to Start a Manufacturing Business of Aluminium Recycling Plant
Why Aluminium Recycling Is a High-Potential Business
Aluminium recycling is attractive because it balances sustainability and profitability. It reduces emissions and energy consumption, and as a result, industries are encouraged to use secondary aluminium instead of primary. Recycling has a positive impact on the economy by reducing dependence on imports and mining.
Aluminium does not lose its quality when processed, unlike many other recyclables. Aluminium can be recycled forever, meaning that, once a collection system and processing system are in place, the cycle of supply and reuse is almost limitless. The infinite recyclability of this material ensures that entrepreneurs are not only entering a temporary trend but also positioning themselves as a permanent industry necessity.
This business is even more resilient because of the diversity of industries that use recycled aluminium. Almost every major industry has a demand for aluminium. From packaging to power and renewable energy, and automotive, recycled aluminium is preferred over virgin aluminium.
Aluminium Scrap: Sources
Scrap is the main source of raw material for aluminium recycling businesses. Scrap can come in many forms. The majority of the scrap comes from household and municipal waste, such as used foils and packaging trays, beverage cans and foils. Industry wastes such as offcuts from production, rejected parts and rolling mill residues are also a major source. Automobile scrap, such as wheels, body panels and engine parts, is a major contributor once vehicles have reached the end of their lifespan. Construction is another reliable contributor. Old roofing sheets, window frames and structural sections are all part of the scrap stream.
The recycling industry is based on a solid and consistent network of scrap collectors. Even the most sophisticated recycling plants can’t operate effectively without a steady supply of raw materials. To ensure a steady supply, partnerships with scrap dealers and municipal authorities, as well as industrial producers, are essential.
View our Handbooks on Steel, Iron, Ferrous, Non-Ferrous Metals with Casting and Forging, Aluminium, Ferroalloys Technology
Aluminium Recycling Process
The recycling of aluminium is an industrial process with multiple steps that starts with the collection and ends when new aluminium products are cast. The first step involves collection and separation. Scrap aluminium is collected from various sources and then sorted in order to separate pure aluminium, mixed alloys, plastics or other contaminants. To improve accuracy, advanced systems like eddy-current separators and automatic sensors are being used more often.
After sorting, aluminium is shredded into smaller, more uniform pieces. The surface area is increased by shredding, which makes cleaning more efficient. Cleaning and decoating are essential because paints or lacquers can damage the quality of recycled aluminum. The scrap type will determine whether chemical cleaning, mechanical abrasion, or thermal de-coating is used.
After cleaning, the aluminium is then melted. The metal is melted in furnaces such as reverberatory or rotary types, or even induction furnaces. The melting process consumes energy. However, advanced furnace designs that use regenerative burners and energy recovery systems reduce costs.
Related: How DPC Aluminium Wire Is Made: Step-by-Step Process Explained
Industrial Applications
One of the reasons that recycled aluminium has experienced such a strong growth is its versatility. It is used in the automotive industry to make wheels, engine blocks and battery housings. This helps reduce vehicle weight while improving efficiency. Aluminium is used in the packaging industry for cans of beverages, foils and containers. The recycling cycle, from collection to reuse, is very short, sometimes only a few weeks. In construction, recycled aluminium is used in doors, windows and roofing systems.
Aluminium is also used for conductors and cables in the electrical industry, as well as motor casings and solar panel frames. It is also vital to wind turbine and solar panel components. Consumer goods manufacturers also use recycled aluminium for appliances, utensils and electronic housings. The variety of uses ensures that the demand for aluminium remains steady even if a particular industry slows.
Aluminium recycling: Challenges and Opportunities
The business has many challenges, despite its high potential. The biggest challenge is to ensure that clean scrap is available. Recycling companies in regions with weak collection systems often face a lack of scrap or scrap that is highly contaminated, which increases costs. Paints, plastics and other metals contaminating scrap can be a serious operational problem because they affect product quality.
The energy demand is another challenge. Recycling consumes less energy than primary manufacturing, but melting furnaces require reliable and stable power. This can be expensive in regions where energy costs are high. Aluminium prices are volatile globally, and this can hurt profitability. Finally, to comply with safety and environmental regulations, startups will need to invest in systems for pollution control and workplace security.
Future Growth Drivers
The future of recycling aluminium is closely linked to global megatrends. Aluminium will play a major role in the battery housings of electric vehicles and structural components. Construction will be a major demand driver due to the push towards smart cities and eco-friendly buildings. In many countries, circular economy policies make recycling mandatory, especially for packaging, electronic devices, and automobiles.
The future of the industry is also shaped by technological innovations. The use of robotics, artificial intelligence, and energy efficient furnaces improves both the yield and cost structure. India, with its growing export demand, has the potential to become a major hub for secondary aluminium production.
For more information, check out this video
Role of Professional Consulting
It takes more than just enthusiasm to start an aluminium recycling company. It requires a thorough understanding of the market, technology, logistics and regulatory frameworks. Professional consultants such as Niir Project Consultancy Services can provide invaluable support. NPCS provides detailed techno-economic feasibility reports that provide details about manufacturing processes, raw materials, plant layouts and financials. Their experience helps entrepreneurs to evaluate projects and build businesses on solid foundations.
Find the Best Idea for Yourself With our Startup Selector Tool
The conclusion of the article is:
Aluminium recycling is a business that combines sustainability with profitability. Recycled aluminium has become the preferred metal across all sectors as industries, governments and consumers demand greener materials. This is a great opportunity for entrepreneurs to create an industrial venture which not only generates wealth but also contributes towards a resource-efficient future.
Startups can take advantage of expert consulting by understanding the market dynamics, creating a reliable scrap supply chain, mastering recycling processes, and understanding the market dynamics. Aluminium recycling, with its infinite recyclability and high demand, is more than just a business. It is the foundation of tomorrow’s circular economy.