Bamboo, often celebrated as “green gold” or the “ethical super plant,” is rapidly gaining prominence as a cornerstone of sustainable development and a compelling opportunity for modern industrial ventures. Its versatility and remarkable properties are driving a global shift toward eco-conscious materials, positioning it as a prime candidate for entrepreneurs aiming to build businesses with a positive environmental impact.
This handbook explores the enormous potential of bamboo products, from natural strengths to diverse uses, market trends, production techniques, and vital aspects of quality and regulation.
The growing international emphasis on sustainability means bamboo is not just a commodity; it acts as a driver for industries to achieve ecological targets and meet consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. For companies entering the marketplace, this positioning allows them to offer solutions to critical ecological challenges, increasing market attractiveness and competitiveness.
Bamboo’s Core Strengths: A Foundation for Sustainable Business
Bamboo’s unique features offer a strong platform for sustainable production. Its short growth cycle and minimal environmental impact during cultivation make it stand out from most conventional resources.
Rapid Renewability and Environmental Impact
Bamboo is fast-growing, taking only three to five years to mature, with certain species growing as much as a meter in a day. This rapid regeneration allows for frequent harvesting without depleting resources. Bamboo plantations can be harvested more often than regular hardwood forests, providing a reliable and continuous supply for manufacturing.
Bamboo acts as a significant carbon sink, absorbing substantial amounts of CO2. Studies indicate it can capture over five tons of CO2 per hectare annually, with some estimates reaching twelve metric tons. This carbon remains locked in bamboo fibers even after processing, contributing to long-term carbon storage and mitigating climate change.
Bamboo farming is eco-friendly, using minimal water and no pesticides or herbicides. Its extensive root system prevents soil erosion, improves water retention, enhances soil quality, and even removes heavy metals from the soil. Bamboo forests emit roughly 35% more oxygen than equivalent tree forests, further emphasizing their environmental contribution.
Related articles:- Bamboo and Bamboo-Based Products Business: Tips and Strategies for Aspiring Entrepreneurs
Versatility and Durability
Bamboo is renowned for its lightness, flexibility, and strength, offering a competitive alternative to wood, plastic, and steel. Its fibers naturally resist moisture, wind, heat, and insects without chemical coatings. This durability ensures long-lasting products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and fostering consumer loyalty.
Bamboo is also naturally hypoallergenic, anti-static, and highly breathable, making it ideal for sensitive uses such as textiles and personal care products. These characteristics make bamboo a perfect raw material for a wide range of industrial and consumer products, blending sustainability with high performance.
Related articles:- Bamboo Manufacturing Industry in Northeast India
Diverse Uses of Bamboo Products
Bamboo’s versatility allows it to be transformed into thousands of commercial products, with new applications constantly emerging. Its ability to replace conventional materials across industries presents substantial opportunities for entrepreneurs.
Construction and Engineered Materials
Bamboo is revolutionizing the construction sector through its strength, flexibility, and sustainability. Its flexibility makes it ideal for seismic regions. Engineered bamboo products, including laminated bamboo lumber and cross-laminated panels, provide stability for structural elements, flooring, and walls. Bamboo is also used in scaffolding and tested as reinforcement in concrete, offering a viable alternative to steel.
Textiles and Apparel
Bamboo fibers are soft, breathable, hypoallergenic, and moisture-wicking, making them suitable for clothing, sportswear, bedding, towels, and sanitary items. Bamboo textile production is highly efficient, yielding 50 times more fiber per acre than cotton. This highlights both environmental and economic advantages, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional fabrics.
Pulp and Paper
Bamboo has a long history in paper production and serves as an important raw material amid wood shortages and environmental concerns. Bamboo paper has a high tear index, good brightness stability, and uniform optical properties. It requires less power and fewer chemicals to pulp compared to wood. Common bamboo paper products include toilet paper, coffee filters, paper cups, paper towels, cardboard, and bond paper.
Detail project report on bamboo based products
Consumer Goods and Lifestyle
Bamboo’s durability, beauty, and health benefits make it popular in furniture, kitchenware, and personal care products such as toothbrushes and toys. Bamboo products are free from harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates, and their biodegradability provides a greener alternative to plastics.
Emerging Sectors
Innovation is diversifying bamboo into high-value applications. Bamboo is transformed into charcoal for cooking, heating, and water filtration, and as feedstock for bioenergy production, including bioethanol and biogas. Researchers are developing bamboo-based substrates for electronics such as flexible displays and solar cells. Bamboo fibers are also being explored for battery applications and advanced automotive parts. Bamboo shoots are used in food and beverages, including rum, vodka, gin, and beer.
Engineered bamboo, in laminated and cross-laminated forms, enables bamboo to transition from a craft material into a mainstream industrial input. This opens opportunities in B2B markets but requires investment in R&D and advanced manufacturing.
Major Applications and Advantages of Bamboo Products
Construction and Engineered Materials: Flooring, wall panels, structural beams, scaffolding, and concrete reinforcement.
Advantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, flexibility, rapid renewability, aesthetic appeal.
Textiles and Apparel: Clothing, activewear, bedding, towels, sanitary products.
Advantages: Softness, breathability, hypoallergenic, moisture-wicking, and high fiber yield per acre.
Pulp and Paper: Toilet paper, coffee filters, paper cups, cardboard.
Advantages: High tear index, stable brightness, eco-friendly pulping, and prevents deforestation.
Consumer Goods and Lifestyle: Furniture, kitchenware, toothbrushes, toys, diapers.
Advantages: Durable, aesthetic, free from harmful chemicals, and biodegradable.
Emerging Industries: Bamboo charcoal, biofuels, electronic substrates, batteries, spirits.
Advantages: Carbon sequestration, renewable energy source, natural flexibility, sustainable material for advanced technologies.
Market Dynamics: Demand, Growth, and Future Outlook
The global bamboo market is witnessing strong growth, driven by environmental concerns, technological development, and supportive government policies. This environment is highly favorable for industrial investment.
Global Market Size and Outlook
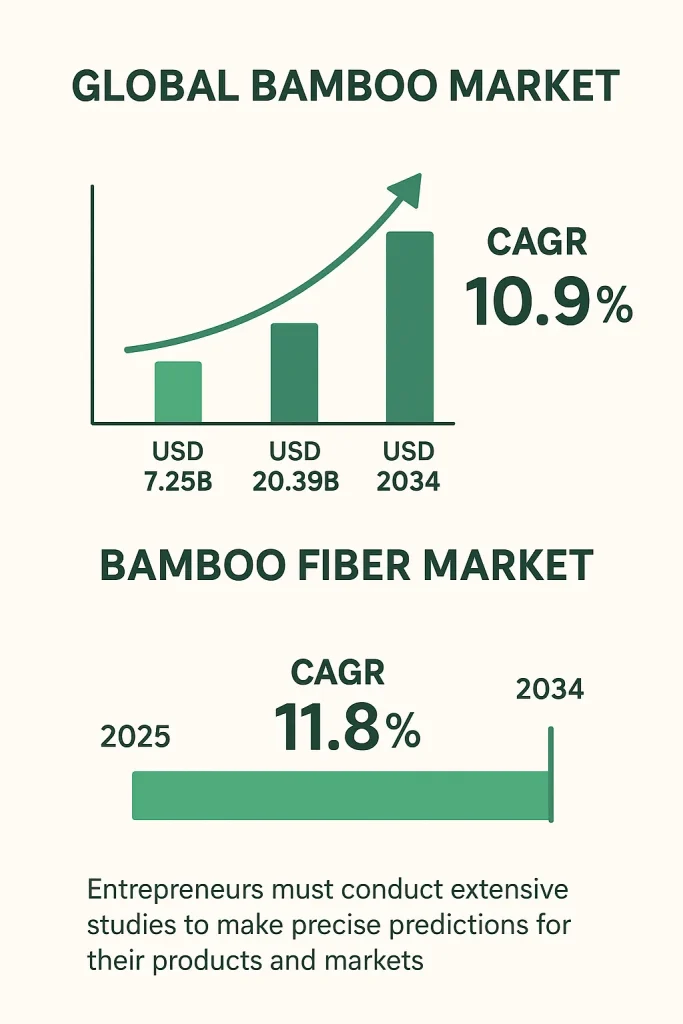
Projections suggest the global bamboo market will grow from USD 7.25 billion in 2024 to USD 20.39 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 10.9%. Other estimates project growth from USD 67.13 billion in 2024 to USD 88.44 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 4.7%. The bamboo fiber market is expected to grow even faster, with a CAGR of 11.8% from 2025 through 2034. Entrepreneurs must conduct extensive studies to make precise predictions for their products and markets.
Principal Growth Drivers
- Increased global demand for eco-friendly products
- Improvements in processing and manufacturing technology
- Government funding, subsidies, and regulatory support
- Multi-industry versatility
- Rising disposable income and urbanization in developing nations
Regional Hotspots
- Asia-Pacific: Highest share and fastest growth, led by China, India, and Indonesia.
- North America: Growing demand for sustainable building materials and eco-friendly products.
- Europe: Steady demand for bamboo flooring and associated products.
- Emerging Markets: South America, the Middle East, and Africa present untapped potential with government-led programs.
Find our Handbook
Challenges and Opportunities for New Ventures
While the bamboo industry holds great promise, entrepreneurs face challenges in sustaining growth.
Common Challenges:
- Lack of standardization in processing and quality control
- Supply chain intricacies in rural regions
- Competition from plastics and conventional materials
- Limited awareness and adoption of bamboo products
- Compliance with environmental regulations and associated costs
Recognizing these challenges alongside market opportunities is essential for effective business planning.
NPCS: Facilitating Bamboo Entrepreneurs
NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NPCS) provides comprehensive project reports, technical guidance, and market analysis for entrepreneurs interested in bamboo ventures. NPCS resources cover raw material procurement, manufacturing procedures, plant layout, machinery needs, and financial planning. By leveraging NPCS expertise, startups can assess feasibility, minimize risks, and make informed decisions to establish competitive and sustainable businesses in the bamboo industry.
Conclusion
Bamboo represents a unique intersection of sustainability, innovation, and commercial potential. Its rapid renewability, environmental advantages, and versatility across construction, textiles, paper, consumer goods, and emerging technologies make it an ideal raw material for modern industrial enterprises.
For entrepreneurs, bamboo is more than a material—it is an opportunity to create eco-friendly products while tapping into a rapidly expanding global market. By understanding market trends, embracing technological advancements, navigating challenges, and utilizing expert guidance from NPCS, businesses can unlock the “green gold” potential of bamboo and build a thriving, future-ready enterprise.
Find best business ideas for yourself using our startup selector tools
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes bamboo a sustainable material?
Bamboo grows quickly, requires minimal water, and does not need pesticides. It also absorbs significant amounts of CO2 and improves soil health.
How long does it take for bamboo to mature?
Bamboo typically matures in three to five years, depending on the species, making it highly renewable compared to hardwood trees.
Can bamboo replace traditional materials like wood and plastic?
Yes, bamboo’s strength, flexibility, and durability make it a viable alternative for construction, furniture, textiles, paper, and consumer goods.
What are the emerging applications of bamboo?
Emerging applications include bioenergy production, bamboo charcoal, electronic substrates, battery components, and food & beverage products like bamboo shoots and alcoholic beverages.
How can NPCS help in starting a bamboo business?
NPCS provides detailed project reports, market analysis, plant layout designs, machinery lists, and financial planning to help entrepreneurs assess feasibility and launch successful bamboo ventures.